* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nuc Chem PP - Liberty Union High School District
Marie Curie wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion–fission hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Gamma spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive waste wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission wikipedia , lookup
Fallout shelter wikipedia , lookup
Ionizing radiation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Background radiation wikipedia , lookup
Technetium-99m wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive decay wikipedia , lookup
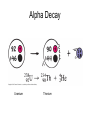
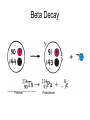
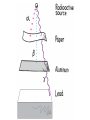
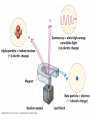
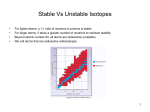
Intro to Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry Mrs. Meemari http://www.chem.orst.edu/graduate/pics/Reactor.jpg How does a nuclear reactor work? http://www.lanl.gov/science/1663/images/reactor.jpg How does a small mass contained in this bomb cause…… • Nuclear Bomb of 1945 known as “fat man” http://www.travisairmuseum.org/assets/images/fatman.jpg …this huge nuclear explosion? http://library.thinkquest.org/06aug/01200/Graphics/705px-Nuclear_fireball.jpg Is there radon in your basement? http://a.abcnews.com/images/Blotter/abc_1radon_ad_070625_ssh.jpg Notation Nucleons • Protons and Neutrons • The nucleons are bound together by the strong force aka binding force . Isotopes • Atoms of a given element with: same #protons but different # neutrons H H http://education.jlab.org/glossary/isotope.html H Isotopes of Carbon Radioactive Isotopes • Isotopes of certain unstable elements that spontaneously emit particles and energy from the nucleus. • Henri Beckerel 1896 accidentally observed radioactivity of uranium salts that were fogging photographic film. • His associates were Marie and Pierre Curie. Marie Curie: born 1867, in Poland as Maria Sklodowska • Lived in France • 1898 discovered the elements polonium and radium. http://www.radiochemistry.org/nuclearmedicine/pioneers/images/mariecurie.jpg Marie Curie a Pioneer of Radioactivity • Winner of 1903 Nobel Prize for Physics with Henri Becquerel and her husband, Pierre Curie. • Winner of the sole 1911 Nobel Prize for Chemistry. 3 Main Types of Radioactive Decay • Alpha a • Beta b • Gamma g Alpha Decay Emission of alpha particles a : • • • • • helium nuclei two protons and two neutrons charge +2 (but its never written) can travel a few inches through air can be stopped by a sheet of paper, clothing. Alpha Decay Uranium Thorium Alpha Decay http://education.jlab.org/glossary/alphadecay.gif Beta Decay • Beta particles b: electrons ejected from the nucleus when neutrons decay ( n -> p+ +b- ) • Beta particles have the same charge and mass as "normal" electrons. Beta Decay • Beta particles b: electrons ejected from the nucleus when neutrons decay n -> p+ +b• Beta particles have the same charge and mass as "normal" electrons. • Can be stopped by aluminum foil or a block of wood. Beta Decay Beta Decay Thorium Protactinium Gamma Decay • Gamma radiation g : electromagnetic energy that is released. • Gamma rays are electromagnetic waves. • They have no mass. • Gamma radiation has no charge. – Most Penetrating, can be stopped by 1m thick concrete or a several cm thick sheet of lead. Examples of Radioactive Decay Alpha Decay Po Pb + He Beta Decay p n + n p + e C N + e Gamma Decay Ni Ni + g (excited nucleus) e Part II •Nuclear Stability •Half-Life Nuclear Stability • Depends on the neutron to proton ratio. Band of Stability Number of Neutrons, (N) Number of Protons (Z) What happens to an unstable nucleus? • They will undergo decay • The type of decay depends on the reason for the instability What type of decay will happen if the nucleus contains too many neutrons? • Beta Decay Example: 14 6 C 14 N 7 + 0 e -1 In N-14 the ratio of neutrons to protons is 1:1 • Nuclei with atomic number > 83 are radioactive Radioactive Half-Life (t1/2 ): • The time for half of the radioactive nuclei in a given sample to undergo decay. Common Radioactive Isotopes Isotope Half-Life Radiation Emitted Carbon-14 5,730 years b, g Radon-222 3.8 days a Uranium-235 7.0 x 108 years a, g Uranium-238 4.46 x 109 years a Radioactive Half-Life • After one half life there is 1/2 of original sample left. • After two half-lives, there will be 1/2 of the 1/2 = 1/4 the original sample. Graph of Amount of Remaining Nuclei vs Time A=Aoe-lt A Example You have 100 g of radioactive C-14. The half-life of C-14 is 5730 years. • How many grams are left after one halflife? Answer:50 g • How many grams are left after two halflives? Problem A sample of 3x107 Radon atoms are trapped in a basement that is sealed. The half-life of Radon is 3.83 days. How many radon atoms are left after 31 days? answer:1.2x105 atoms