* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Reproduction - Wythe County Schools Moodle Site
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
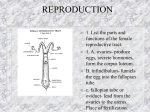
REPRODUCTION 1. List the parts and functions of the female reproductive tract: 1. A. ovaries- produce eggs, secrete hormones, form the corpus luteum. B. infindibulum- funnels the egg into the fallopian tube c. fallopian tube or oviduct- lead from the ovaries to the uterus. Place of fertilization. D. uterus- where the embryo implants and develops e. cervix- thick muscular folds that seal off the uterus when pregnancy occurs f. vagina- organ of copulation where natural insemination occurs. G. urethra- pathway for urine h. vulva- external opening clitoris- homologue to male penis, 2. List the parts and function of the male reproductive tract: 2. The parts are: a. scrotum- protection and temperature regulation b. testicles- the production of sperm cells and testosterone c. epididymis- long tube outside of testicles for storage of sperm until it matures d. vas deferns- tube leads from epididymis to urethra e. seminal vesicles- secretes fluid for transport f. prostate gland- secretes thick rich protein g. cowpers gland- secretes an alkaline to clean urethra h. urethra- tube extends from bladder out the penis I. Penis- organ of copulation. 3. List and explain the female hormones: The female hormones are: a. fsh- causes the ovaries to produce estrogen b. estrogen- causes the female to come into heat. C. lh- cause the formation of the corpus luteum d. progestrone- produce by the cl and is for the maintenance of pregnancy. 4. List the hormones produced by the testes: 4. Testosterone is the hormone produced by the testes and it is for the development and function of male reproductive organs, male characteristics, and sex drive. 5. What are the lengths of heat for beef, sheep, swine and horses? 5. The lengths of heat are: Horse- occurs every 21 days and lasts avg. 6 days Swine- occurs every 21 days and lasts 44 hrs Sheep- occurs every 16 days and lasts 30 hrs beef- occurs every 21 days and lasts 12 hrs. 6. What occurs during the heat period in terms of preparation and hormone activity? 6. The anterior pituitary gland (ap)produces FSH which cause a follicle in the ovaries to grow, as the grow they produce estrogen, and when the estrogen levels peak the animals comes into heat. This is also the time that the follicle ruptures and releases and egg. When this occurs LH is released and cause the follicle to turn into a corpus luteum which produces Progestrone for the maintenance of pregnancy. 7. What are some causes of sterility in males and females? 7. Some causes of sterility in males and females are: A. females- only one functional ovary, freemartin, one uterine horn, and blind cervix B, males- Genital infections( Brucelossis, vibriosis), poor feeding or management, inherited abnormalities( cryptorchidism, scrotal hernia) 8. What is a free martin? 7. A free martin is a heifer born twin to a bull. There is a 75 % chance that this heifer will be sterile due to testosterone leaking and cause her reproductive tract to not fully develop. 9. What is flushing? 9. Flushing is increasing the amount and quality of feed two weeks prior to breeding to increase fertility. 10. How do you AI and PregTest? The insemination process is quite straightforward. However, since relatively few sperm cells will be used, their placement is critical. The semen should be placed in the body of the uterus just in front of the cervix. You can recognize the proper site by the change in tissue consistency— from firm and hard in the cervix to soft and spongy in the uterus. To achieve the highest possible fertility rate, semen should be deposited at the very front end of the cervix. The internal (or front) end of the cervix is often called the anterior cervical . To deposit semen at this location requires the use of a special device called Cassou pipette, or “AI gun.” The recto-vaginal insemination process is used. The inseminator places his hand in the rectum and manipulates the reproductive tract so that the gun passes through the vagina, then it is manipulated through the cervical rings, and then held at the internal opening of the cervix for semen deposition. In adequately restrained cattle this will take 30 seconds to 2 minutes. At first, however, passing an insemi-nation syringe might not be easy because you might encounter natural obstructions on your way to the target. 11. Define: 11. A. Allele- are pairs of genes located at same place on chromosomes. B. phenotype- Physical appearance of the animal. C. genotype- genetic make-up of the animal D. Monohybrid- cross of one set of genes E. Dihybrid- Cross of two gene characteristics. F. dominant- gene that hides or masks other genes. G. recessive- refers to genes that get masked H. homozygous- an animal that carries two identical genes in its allele I. Heterozygous- two unlike genes J. chromosomes- gene carriers K. Gene- Single unit of inheritance L. Co-Dominance- or incomplete dominance- genes blend