* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
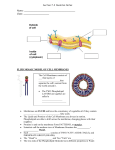
Slide 1 Chapter 7: Membranes: Their Structure, Function, and Chemistry Slide 2 Membrane Functions Slide 3 The Fluid-Mosaic Model • First proposed in 1972 by Singer and Nicolson • Lipids: The “fluid” portion • Proteins: The “mosaic” portion Slide 4 Membrane Lipids • Three major classes of lipids found in membranes 1. Phospholipids 2. Glycolipids 3. Sterols Slide 5 Phospholipids • The most abundant membrane lipid • Glycerol based vs. Sphingosine based • Type and portion varies with membrane source Slide 6 Glycerol vs. Sphingosine Slide 7 Phospholipids (cont.) • The most abundant membrane lipid • Glycerol based vs. Sphingosine based • Type and portion varies with membrane source Slide 8 Phospholipid Composition of Membranes Slide 9 Membrane Lipids (cont.) • Three major classes of lipids found in membranes 1. Phospholipids 2. Glycolipids 3. Sterols Slide 10 Glycolipids • Carbohydrate attached to a lipid • Some are glycerol based, but most are sphingosine based • Glycosphingolipids • Cerebrosides • Gangliosides Slide 11 Glycolipids (cont.) Slide 12 Membrane Lipids (cont.) • Three major classes of lipids found in membranes 1. Phospholipids 2. Glycolipids 3. Sterols Slide 13 Sterols Several types of sterols found in membranes: • Cholesterol • Phytosterol • Ergosterol • Sterols absent from some membranes • Hopanoids Slide 14 Sterols (cont) Slide 15 Fatty Acids • Component of all membrane lipids (except cholesterol • Essential to membranes because of hydrocarbon chains • Presence of double bonds alters structure Slide 16 Fatty Acids (cont.) Slide 17 Membrane Asymmetry Slide 18 Membrane Fluidity • Lateral movements of proteins and lipids is common • Lipids move rapidly • Proteins move slower • Necessary for proper membrane function • Tm = transition temperature Slide 19 Factors Membrane Fluidity • Length of fatty acid chains • Amount of fatty acid saturation • Number of sterols Slide 20 Fatty Acids and Membrane Fluidity Slide 21 Fatty Acids and Membrane Fluidity cont Slide 22 Factors Membrane Fluidity (cont) • Length of fatty acid chains • Amount of fatty acid saturation • Number of sterols Slide 23 Sterols and Membrane Fluidity Slide 24 Regulation of Membrane Fluidity Why important? • Membranes would “gel” at lower temperatures • Increased fluidity at higher temperatures makes it difficult to maintain ion concentration Homeoviscous adaptation Slide 25 Lipid Rafts Slide 26 The Fluid-Mosaic Model (again) • First proposed in 1972 by Singer and Nicolson • Lipids: The “fluid” portion • Proteins: The “mosaic” portion Slide 27 Membrane Proteins Classes of membrane proteins: 1. Integral 2. Peripheral 3. Lipid anchored Slide 28 1. Integral Membrane Proteins • Have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions • Two types: 1. Monotropic 2. Transmembrane - Single pass - Multi pass - Multi-subunit Slide 29 1. Integral Membrane Proteins (cont.) Slide 30 Membrane Proteins Classes of membrane proteins: 1. Integral 2. Peripheral 3. Lipid anchored Slide 31 2. Peripheral Membrane Proteins Slide 32 Membrane Proteins Classes of membrane proteins: 1. Integral 2. Peripheral 3. Lipid anchored Slide 33 3. Lipid Anchored Membrane Proteins • Covalently bound to lipids in the membrane bilayer • Interior • Bound to fatty acid • Bound to isoprenyl • Exterior • Bound to glycosylphosphatidlinositol (GPI) Slide 34 3. Lipid Anchored Membrane Proteins Slide 35 Glycosylation • Process of adding a carbohydrate side chain to a protein • N – linked vs O – linked • Carbohydrate chains branched and vary in length and composition • Carbohydrate chains generally on exterior of cell Slide 36 N – Linked vs. O – Linked Slide 37 Glycosylation • Process of adding a carbohydrate side chain to a protein • N – linked vs O – linked • Carbohydrate chains branched and vary in length and composition • Carbohydrate chains generally on exterior of cell Slide 38 Glycosylation Slide 39 Glycosylation • Process of adding a carbohydrate side chain to a protein • N – linked vs O – linked • Carbohydrate chains branched and vary in length and composition • Carbohydrate chains generally on exterior of cell