* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics of prokaryotic cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
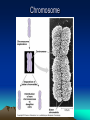
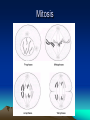
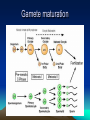
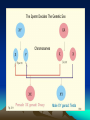
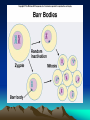
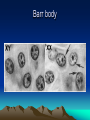
Cytogenetics in Humans Marie Černá Chromosome Chromosome On each chromosome • is apparent the centromere as a primary constriction • dividing the chromosome into two arms – a short arm p (for petit) a long arm q Chromosomes are classified by their length the position of the centromere into four types: • metacentric • submetacentric • acrocentric (satellites attached to short arms) • telocentric (do not occur in humans) Karyotype Haploid: 1n chromosome complement 23 chromosomes (gamete) Diploid: 2n chromosome complement 46 chromosomes (somatic cell) Human karyotype: • 46, XY - male • 46, XX - female Chromosome - homologous: autosomes heterologous: sex chromosomes Human karyotype Cell cycle interphase • G1 (Gap 1) • S phase (DNA synthesis) • G2 (Gap 2) M mitosis Mitosis Meiosis Gamete maturation Barr body Literature Biology, eighth edition, Campbell, Reece Unit three: Genetics Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Concept 15.1, 15.2, 15.3. Pages 286 – 296