* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rxn Types
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic reforming wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Spinodal decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Surface properties of transition metal oxides wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
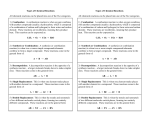
Types of Chemical Reactions Predicting Chemical Reactions Types of Reactions Many chemical reactions have defining characteristics which allow them to be classified as to type. Types of Chemical Reactions • The five types of chemical reactions in this unit are: Synthesis (S) Decomposition (D) Single Displacement (SD) Double Displacement (DD) Combustion (C) Synthesis Reactions • Two or more substances combine to form one substance. The general form is A + X AX Example: Magnesium + oxygen magnesium oxide 2Mg + O2 2MgO Synthesis Reactions • Synthesis reactions may also be called composition or combination reactions. Combination of elements K + Cl2 KCl ONLY One product will be formed Decomposition Reactions One substance reacts to form two or more substances. The breaking apart of a compound into smaller elements or smaller compounds. The general form is AX A + X Decomposition Reactions There are 5 general Types of Decomposition Reactions: Decomposition of a binary compound When the right energy is applied to a binary compound it will break apart into its respective elements. 2NaCl 2Na + Cl2 Water can be decomposed by electrolysis. 2H2O 2H2 + O2 Decomposition Reactions Types of Decomposition Reactions: Decomposition of carbonates When heated, carbonates break down to form the metal oxide and carbon dioxide. CaCO3 CaO + CO2 H2CO3 H2O + CO2 Decomposition Reactions Types of decomposition reactions: Decomposition of metallic hydroxide Some metal hydroxides decompose into metal oxides and water when heated. Ca(OH)2 CaO + H2O Note that this is the reverse of a similar synthesis reaction. Decomposition Reactions Types of decomposition reactions: Decomposition of metallic Chlorates Metal chlorates decompose into the metal chlorides and oxygen when heated. 2KClO3 2KCl + 3O2 Zn(ClO3)2 ZnCl2 + 3O2 – Some of these reactions are used in explosives. Decomposition Reactions Types of decomposition reactions: Decomposition of Oxy-Acids and Bases Oxy-acids decompose into water and the non-metal oxide. H2SO3 H2O + SO2 Ammonium hydroxide is actually ammonia gas dissolved in water. NH4OH NH3 + H2O Single Displacement Reactions A metal will replace a metal ion in a compound. The general form is A + BX AX + B A nonmetal will replace a nonmetal ion in a compound The general form is Y + BX BY + X Cations replace Cations Anions replace Anions Single Displacement Reactions Examples: Ni + AgNO3 • Nickel replaces the metallic ion Ag+. • The silver becomes free silver and the nickel becomes the nickel(II) ion. Ni + AgNO3 Ag + Ni(NO3)2 Balance the equation: Ni + 2AgNO3 2Ag + Ni(NO3)2 Double Displacement Reactions Ions of two compounds exchange places with each other. The general form is AX + BY AY + BX Cations replace Cations Anions replace Anions Double Displacement NaOH + CuSO4 The Na+ and Cu2+ switch places. Na+ combines with SO42- to form Na2SO4. Cu2+ combines with OH- to form Cu(OH)2 NaOH + CuSO4 Na2SO4 + Cu(OH)2 Balanced 2NaOH + CuSO4 Na2SO4 + Cu(OH)2 Combustion Reaction When hydrocarbon compounds are burned in oxygen, the products are water and carbon dioxide. Methane, CH4, is natural gas. CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O balanced CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O Combustion Reactions Combustion reactions involve light and heat energy released. Natural gas, propane, gasoline, etc. are burned to produce heat energy. Most of these hydrocarbon reactions produce water and carbon dioxide. Combustion Reactions Show the combustion of Propane (C3H8) C3H8 + O2 H2O + CO2 C3H8 + 5O2 4H2O + 3CO2 Practice Classify each of the following as to type: 1) H2 + Cl2 2HCl Synthesis 2) Ca + 2H2O Ca(OH)2 + H2 Single displacement Practice 3) 2CO + O2 2CO2 Synthesis and combustion 4) 2KClO3 2KCl + 3O2 Decomposition Practice 5) FeS + 2HCl FeCl2 + H2S Double displacement 6) Zn + HCl ? Single displacement Products? Zn + 2HCl ZnCl2 + H2 Single Displacement Reactions Not all single displacement reactions that can be written actually happen. The metal or non-metal must be more active than the ion it is replacing. It will depend upon the element’s Activity as determined by the Activity Series (Sec. 3) Single Displacement/ Replacement Reactions An active nonmetal can replace a less active nonmetal. The halogen (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2) reactions are good examples. F2 is the most active and I2 is the least. Cl2 +2 NaI 2 NaCl + I2