* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cancerdevel4ned2014 20 KB
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
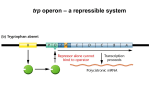
Nedwidek (SBS11QGR) Cancer & Development Stuyvesant HS January 2014 Aim 1: What is the connection between genetics, cancer and development? CANCER Examples of Oncogenes: Oncogene Origin/Source of Defect Src Rous sarcoma virus Ras Rat Sarcoma virus Myc Avian myelocytomatosis virus Fos FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus Abl Abelson murine leukemia virus Erb B Avian erythroblastosis virus Msh Colon Carcinoma/mismatch repair defect Sis Simian Sarcoma virus Bcr Breakpoint Cluster Regions (mutated in 30-40% of human cancers) Examples of Tumor Suppressor genes and where they reside Gene Chromosome Rb (Retinoblastoma) 13q Wt (Wilms tumor) 11p p53 17 BRCA1 17 (refer to Loss Of Heterozygosity, Knudson two-hit) (mutated in 50% of human cancers) Aim 2: What is the connection between defects in the germline and defects in somatic cells? DEVELOPMENT Model Organisms representing humans in their studies of development: Eukaryotes (Animals): Mus musculus: House mouse; same body plan/similar genetics: closest to us. Drosophila melanogaster: fruit fly; very short lifespan; excellent genetics, thorough understanding of life cycles. Caenorhabditis elegans: nematode worm; detailed understanding of cell lineages. Eukaryotes (Fungus): Saccharomyces cerevisiae: bakers yeast; great genetics Eukaryotes (Plant): Arabidopsis thaliana: flowering weed. Developmental defects stem from germline damage: Key research figures: MIT: Ruth Lehmann, Princeton: Eric Wieschaus (Nobel) and Gertrud Schupbach, Max Planck: Christiane Nusslein-Volhard. Gap, pair-rule, segment polarity and homeotic genes have been studied and analyzed by mutagenesis, expression, and even dissection. Homeotic or Hox genes, studied extensively in flies, affect patterning and placement of body parts by controlling fates of certain cell types. Examples are Antennapedia (Antp) and Ultrabithorax (Ubx), which when messed up, transpose whole body parts, causing severe damage. Mutations in these genes are most lethal early in development. Types of developmentally active genes in flies: think of the regulatory hierarchy here as you might think of the nested Russian Матрёшка dolls: Gap (primary control—first level): Anterior-Posterior positioning, regulates segmentation Pair rule (internal control 1): controls correct number of segments; striped expression by each gap segment alternates in the body plan. Messups lose segments. Segment polarity (internal control 2): Anterior-posterior regulation within each pair rule domain – messups cause loss of body parts. Homeotic (secondary control—final level): Genes control segment fates along anterior-posterior axis. Replace body parts if they are messed up. Antp: Antennae on head phenotype. Ubx: Double thorax, no proper abdomen phentotype. Extra wing sets phenotype in lieu of halteres (normally there are two wings, and a set of halteres provide balance in flight. This is the end of the revised version. The next file you get is an outline of the final exam, TBD in advance of the final of course. NED