* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L24_Krebs
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
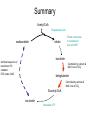
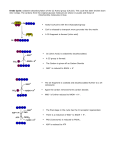
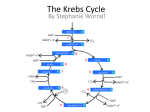
Lecture 24½ Krebs Cycle Overview Condensation • Formation of citrate – One of the methyl-Hs can easily come off acetyl CoA – Gives a very reactive species that reacts with oxaloacetate • Citrate – Contains 6 carbons – 3 carboxylic groups Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) – Very symmetrical, but the enzyme can still distinguish which carboxylic group comes from acetyl CoA & oxaloacetate prochiral • Citrate can leave the mitochondria or be oxidised – Depending on whether the cell is doing lipogenesis or needs energy Regulation • Krebs cycle activity is controlled early on – At isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICDH) – alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (aKGDH) • ICDH and OGDH are stimulated by rise in Ca2+ – Such as is found during exercise • ICDH & OGDH are also sensitive to NAD levels – Activity is dependent on availability of NAD Important Features of Krebs Cycle • During the cycle, 2 carbon atoms come in, 2 carbon atoms has gone – but on each cycle only 1 carbon atom from acetyl CoA gets released as carbon dioxide • The other carbon dioxide comes from oxaloacetate • Generates 3 NADH, 1 reduced FAD, i.e. FADH2 plus a GTP – Each NAD gives 2.5 ATP in oxidative phosphorylation • Oxaloacetate is not ‘net’ consumed in the cycle – acts as carrier • Fluoroacetate is a strong inhibitor of the cycle – Creates fluorocitrate which inhibits citrate utilisation – Very toxic and used as poison(1080) Carriers • Krebs cycle can only go faster if we provide enough carrier – need more oxaloacetate during exercise • In muscle pyruvate carboxylase supplies extra oxaloacetate – Anaplerotic reaction - “filling” reaction – So not only the liver has pyruvate carboxylase • Krebs cycle regenerates the carrier CoA – Enables fatty acids to be oxidised faster • Sequence of reactions from succinate to oxaloacetate have similar ‘strategy’ to oxidation of fatty acids – –CH2- going to –C=O – Oxidation with FAD hydration oxidation with NAD Summary Acetyl-CoA Regenerates CoA oxaloacetate citrate Citrate could leave to cytoplasm in liver and WAT isocitrate Identical sequence of reactions to FA oxidation: FAD, water, NAD Controlled by calcium & NAD, loss of CO2 ketoglutarate Controlled by calcium & NAD, loss of CO2 Succinyl-CoA succinate Generates GTP