* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
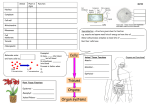
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
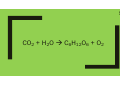
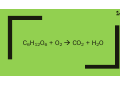
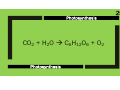
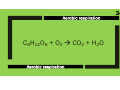
1 The spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. 2 These are where photosynthesis occurs. They contain green chlorophyll. 3 A cell with a cell wall and cell membrane but no nucleus; the DNA is loose in the cytoplasm. 4 A gamete with lots of mitochondria and enzymes. 5 CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 6 Whichever one of the conditions required for photosynthesis is in the shortest supply. 7 Damage an enzyme irreversibly by changing its shape. 8 Plants store this in seeds or as starch, make cell walls from it, convert it to protein and use it for respiration. 9 A square frame enclosing a known area. 10 Mean no of organisms per m2 x total area (m2) 11 Repeatable and Reproducible. Increasing sample size will increase this. 12 Used for biological catalysts, muscles, hormones and antibodies. 13 Breaking down large insoluble molecules into small soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the blood and used by the body. 14 C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O 15 Releasing energy from food for building up large molecules from smaller ones, contracting muscles to move, maintaining constant body temperature etc 16 Cell division producing 2 identical daughter cells. 17 Undifferentiated cells found in early human embryos and bone marrow. 18 A way to show the genotype of offspring from genetic crosses. Dominant and recessive alleles are identified using capital and lower case letters. 19 The remains of plants and animals made from the gradual replacement of hard parts with minerals (or from casts and impressions or, by preservation when no decay occurs). 20 This occurs when populations of the same species become so different they can no longer breed together. Often due to physical separation. Diffusion The spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Diffusion 21 Chloroplasts These are where photosynthesis occurs. They contain green chlorophyll. Chloroplasts 22 Bacterial cell A cell with a cell wall and cell membrane but no nucleus; the DNA is loose in the cytoplasm. Bacterial cell 23 Sperm A gamete with lots of mitochondria and enzymes. Sperm 24 Photosynthesis CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 Photosynthesis 25 Limiting factor Whichever one of the conditions required for photosynthesis is in the shortest supply. Limiting factor 26 Denature Damage an enzyme irreversibly by changing its shape. Denature 27 Glucose Plants store this in seeds or as starch, make cell walls from it, convert it to protein and use it for respiration. Glucose 28 Quadrat A square frame enclosing a known area. Quadrat 29 Population size Mean no of organisms per m2 x total area (m2) Population size 30 Reliability Repeatable and Reproducible. Increasing sample size will increase this. Reliability 31 Proteins Used for biological catalysts, muscles, hormones and antibodies. Proteins 32 Digestion Breaking down large insoluble molecules into small soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the blood and used by the body. Digestion 33 Aerobic respiration C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O Aerobic respiration 34 Respiration Releasing energy from food for building up large molecules from smaller ones, contracting muscles to move, maintaining constant body temperature etc Respiration 35 Mitosis Cell division producing 2 identical daughter cells. Mitosis 36 Stem cells Undifferentiated cells found in early human embryos and bone marrow. Stem cells 37 Genetic diagram A way to show the genotype of offspring from genetic crosses. Dominant and recessive alleles are identified using capital and lower case letters. Genetic diagram 38 Fossils The remains of plants and animals made from the gradual replacement of hard parts with minerals (or from casts and impressions or, by preservation when no decay occurs). Fossils 39 Speciation This occurs when populations of the same species become so different they can no longer breed together. Often due to physical separation. Speciation 40