* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
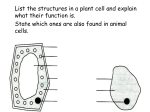
Animal Plant & algae B290 Function Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell wall __________ cells Mitochondria Ribosomes Specialisation – structure gives clues to function Cell membrane e.g. muscle and sperm need lots of energy so have lots of ___________ , Vacuole Root hair cells have Gland cells produce enzymes so need lots of ______________ . Chloroplasts Molecules enter and leave cells by Examples: In lung, ____ into blood, ____ out of blood Cells Animal Tissue Functions In intestines, _______ into blood Muscle – Process is faster when Glandular - _____________________ 1) _____________________ 2) Plant Tissue Functions Epidermal - __________________ Mesophyll - __________________ Xylem/Phloem - _______________ Epithelial - Tissues _____________________ Organs Organ systems Organs and functions? ___________ Photosynthesis _____________ Leaf adaptations ___________ Palisade layer __________ Stomata _________ Spongy mesophyll ___________ Plant transport: Root adaptations: B291 Released via Xylem Phloem + + Plant Nutrients: Nitrates Magnesium Yields optimised in greenhouses by… Limiting factors: Used in _____________ to release ______ Test for this: Add _________ goes 1) 2) ______/______ Must consider.. 3) Describe: Physical factors affecting distribution of organisms: Converted into insoluble _________ for storage Also converted to _____ & _____ for storage, made into _____________ or used to produce ___________ that strengthens cell walls 1) 2) Explain: Sampling techniques:2 ways to use quadrats? 3) 4) 5) 6) Reproducible vs Repeatable Proteins and their uses Proteins are made from __________ ___________ and used for: Structural tissues Hormones Antibodies Catalysts Advantages: B292 “_____ & _____” 2) 3) 1) Where it works best Enzymes -Known as _____________ catalysts because they _____________ reactions e.g. respiration in the mitochondria -Can change one molecule into another, break down large molecules into smaller ones or build small molecules into larger ones Uses in industry Shape makes the enzyme ________ to one substrate Shape can be changed by ________ and ____, the enzyme stops working, its is said to have been ______________ Break down needed so molecules can be __________ Digestion: Disadvantages: Digestive enzyme + Carbohydrases converts cheap _______ into _________ Aerobic Respiration Made by Works on Breaks it down to Special conditions Amylase Protease Lipase _______ + ______ ―> _______ + _______ This reaction releases energy, it takes place in __________ and enzymes are involved Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Used when muscles can’t get enough ______ The _______ is not completely broken down and ________ ______ is produced leading to fatigue. ______ energy is released than with aerobic respiration. After exercising there is an _________ _______ and this must be repaid to allow the lactic acid to break down Energy used for: Building larger molecules Muscle ___________ To maintain _______ ______________ Build sugars in plants More _________ is needed by muscles ________ + ________ need to be transported to the muscles faster and _________ ________ needs to be removed faster _______ + ___________ rate increase, depth of breathing also increases (to improve oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide removal) Muscles store glucose as ____________ - this can be converted back to glucose during exercise Gametes Formed by Concept of an inherited factor, now known as a _______, was suggested by ___________ after his studies in _____ plants. Process: M_________ f___________ Embryo Cells divide by Allele Dominant Recessive Heterozygous Cystic Fibrosis Caused by _________ allele (so ___ copies of allele are needed). Concerns about use? ________ __________ . Meiosis Systems affected ___________ & ___________________ How can parents without CF have a child with the illness? Parent genotypes: Gametes: How many daughter cells are produced? Possible Outcomes: How many chromosomes does each cell have? Chances of illness ____%, carrier ___%, unaffected ____% Are the daughter cells genetically identical? Does it lead to variation? _____________ provide evidence for how organisms have changed over time. Don’t form when: DNA are _______________ and many cell types. _______ Form by: Chromosome Homozygous Mitosis B293 Phenotype can ______________ into Why is it needed? Gene Has ________ cells, these cells are also found in Meaning Genotype M_________ Where does it happen? Key term Species become extinct due to P_______________ Caused by __________ allele (so ___ copy of allele needed). New species develop because