* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 6 Genetics - centralmountainbiology
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
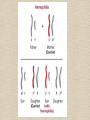
Unit 6 Genetics Module B: Continuity and Unity of Life Objectives: 1. Genes and inheritance 2. Mutations and chromosome abnormalities 3. Genetic engineering Lesson 1: Genes and Inheritance • Gene – region of DNA that codes for a specific protein. • Allele – different versions of a gene • Polygenic – trait that is determined by more than one gene. Dominant and Recessive Alleles • Phenotype: physical appearance of a trait. (physical appearance) • Genotype: the alleles of a trait. (genetic makeup) • Dominant allele – when present it is expressed. • Recessive allele – masked if a dominant allele is present. • Dominant and Recessive Alleles • Pea plants inherit two alleles for traits. – Tall is dominant “T” – Short is recessive “t” Pea plant’s possible genotypes for height: Genotype Phenotype TT (homozygous dominant) tall Tt (heterozygous dominant) tall tt (homozygous recessive) short Homozygous: when there are two of the same alleles for a trait. Ex. TT, tt Heterozygous: when there are two different alleles for a trait. Ex. Tt Identify the following: Tt Answer: genotype, heterozygous Tall Answer: phenotype Homozygous recessive Answer: genotype • Punnett Squares - Shows the possible allele combinations and phenotypes of the offspring of a given set of parents. A = dominant yellow a = recessive green Probability: Yellow = Green = Ratio = • Pedigree chart – can be used to trace inheritance of a trait through multiple generations of related individuals. • Males = squares • Females = circles • Shaded shapes indicate that person has the trait. AA or aa • Half-shaded shapes indicate that person is a carrier, doesn’t express trait. Aa • Horizontal bar connecting two individuals represents a set of parents. • Vertical bar represents offspring. Incomplete Dominance, CoDominance, and Multiple Alleles - Incomplete dominance – heterozygous individual has a phenotype that differs from those with either homozygous genotype. - Blending of two alleles. Co-dominance – heterozygotes express both the dominant and recessive phenotypes, rather than a blend. -expresses both traits. Ex. Roan cattle • Multiple-allele – some genes have more than two possible alleles. • Ex. ABO blood type Alleles: IA, IB, i (i is O type) • Blood type is determined by the presence of a carbohydrate group attached to a protein on the surface of red blood cells. Sex-linked traits • Traits found on the genes on a sex chromosome. • Sex chromosomes are XX female or XY male. • X chromosome is larger and contains more genes than the Y. • Ex. Hemophilia – blood-clotting disorder is determined by a single gene on the X chromosome. • The allele is recessive, males get it more because they only have one X chromosome. • A man with hemophilia and a woman who has no history of the disease in her family plan to have a child. The parents’ genotypes are XhY and XHXH • Homework: pg. 138 – 140 • Questions 1-6 • Due Wednesday