* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download U3A-ClimChange06 10384KB Oct 27 2012
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
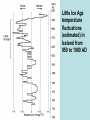
CLIMATE CHANGE THE GREAT DEBATE Session 6 HOLOCENE CLIMATE CHANGE • The Holocene is generally taken to begin at about 12,000 BP, following the end of the Younger Dryas cold period we discussed last week • The Holocene epoch has been a period of climatic stability compared with the Last Glacial that preceded it • Nevertheless, even minor changes have had major impacts on human activities, both in prehistoric and historic times The Younger Dryas was followed by rapid climate warming with relatively stable temperatures during the last 10,000 years HOLOCENE CHANGES • The warmer temperatures caused rapid melting of the continental ice sheets in the Northern Hemisphere and rapid retreat of mountain glaciers elsewhere • This led to a rapid rise in sea level until it reached its present level about 6,500 years ago. This had a big impact on coastal areas due to inundation and changing coastal currents causing localized climate changes • Globally precipitation was much higher than it had been during the Last Glacial SEA LEVEL CHANGES • They caused many continental areas to be separated as islands • Tasmania and New Guinea were separated from the Australian mainland • Britain and Ireland were separated from Europe • The land bridge between East Asia and Alaska was flooded • Populations of humans, plants and animals became isolated BLACK SEA CATASTROPHY • During the Last Glacial the Black Sea had been cut off from the Mediterranean and had become a freshwater lake – the Euxine Lake • About 7500 years ago the rising Mediterranean flooded back through the Bosporus into the lake causing a very rapid rise in water levels (80 meters) creating the Black Sea • Human populations around the lake were displaced and the event probably gave rise to the story of Noah’s flood HOLOCENE MAXIMUM • Minor climate changes are not necessarily in phase between the two hemispheres • In the Northern Hemisphere a warm period lasted from approx. 8000 to 4000 years ago. The Arctic was up to 3°C warmer than today with evidence from Greenland, Iceland and Canada • The Sahara had a much wetter climate with rock paintings of animals and people found in areas that are now desert and have been for the last 4000 years TASMANIAN HOLOCENE CLIMATE CHANGES • In eastern Tasmania the climate was mild and wet during the early Holocene with evergreen beech (myrtle) growing in the Derwent Valley • From 4500 to 3000 years ago the climate was dry and windy, fires were frequent and fossil dunes were being re-activated by the wind MIDDLE EAST • Early civilizations in the middle East were based on irrigation agriculture and their fortunes were strongly affected by periods of drought associated with climate cooling. Early cities in the Indus valley were abandoned about 4000 years ago • Millennia later the Mayan Empire in Central America also reliant on irrigation agriculture collapsed in about 900 AD ROMAN WARMING • The Mediterranean climate warmed between 250 BC and 450 AD and gave rise to the flowering of the Roman Empire. Grapes were drown in Britain and olive trees in the Rhine Valley. • The climate was wetter as well as warmer and agriculture thrived. North Africa became a breadbasket for the Romans THE DARK AGES • It was a time of sudden cooling that lasted from 530 to 900 AD. It caused food shortages which led to famine, war and disease • The Black Sea froze in 800, 801 and 829 AD and ice formed on the Nile River • There were large scale migrations of people. By 590 AD an estimated 25 million people in Europe had died of the plague MEDIEVAL WARMING • This occurred from 900 to 1300 AD. Summers were warmer and longer and crops were plentiful. The amount of agricultural land increased and extended to higher altitudes and latitudes. • In the Middle East the Muslim Empire reached its zenith and the Vikings prospered in Scandinavia and colonized Iceland and Greenland and even reached North America LITTLE ICE AGE • It lasted from 1300 to 1850 AD. It is a misnomer because it was not an ice age or even a glacial but simply another period of unusually cool climatic conditions. Glaciers advanced all over the world. • The Vikings were cut off from their colonies in Greenland and Iceland by sea ice and the Greenland population died out between 1420 and 1500 AD. Iceland’s population suffered famine Little Ice Age temperature fluctuations (estimated) in Iceland from 950 to 1980 AD LITTLE ICE AGE • After a brief warming during the first half of the 16th Century, the second phase from 1550 to 1850 AD was even colder than the first phase. • Temperatures in Europe were lower than at any other time since the Last Glacial. Much agricultural land at higher latitudes and higher altitudes was abandoned. • Glacial ice in the Alps reached its maximum extent in the first half of the 19th Century Holland in the Little Ice Age – a 17th Century Painting by Hendrik Averkamp Little Ice Age winter scene in Holland painted by Van der Keer. Source: Brian John in “The Winters of the World” Most recent temperature reconstruction is in dark blue, the oldest is in red RECENT WARMING • Since 1850 world climates have warmed significantly and most glaciers are retreating rapidly • The climate is now similar to what it was in the Roman and Medieval warm periods but probably not quite as warm as it was in the early Holocene • The warming is generally blamed on the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere but we must be aware that the recent warming is not unprecedented Global Warming from 1880 to 2003 Athabasca Glacier in retreat, Canadian Rockies Mueller Glacier in retreat, New Zealand Retreating Hooker Glacier and meltwater lake