* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Homework Chapters 8
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
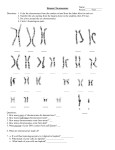
BSC 103 Chapters 8-9 Homework Class# _________ ____ 1) A bacterial cell splits into two new cells by A) duplication. B) forming a cell plate. C) binary fission. D) mitosis. ____ 2) When does DNA (chromosome) replication occur? A) prophase B) metaphase C) anaphase D) interphase E) telophase _____ 3) If diploid cells of the fruit fly Drosophila have 10 chromosomes, how many chromosomes would a haploid Drosophila gamete have? A) one B) two C) five D) ten E) twenty _____ 4) Most genes come in alternate forms called A) chromosomes B) alleles C) loci D) gametes E) homologues _____ 5) A cell is divided into two approximately equal halves, each with about the same amount of cytoplasm, during A) interphase. B) cytophase. C) cytokinesis. D) anaphase E) telophase _____ 6) Sister chromatids are A) replicated chromosomes held together by a common centromere. B) specialized gamete-forming cells. C) non-functional chromosomes. D) homologous pairs of chromosomes. E) different in their genetic content. _____ 7) Meiosis results in the production of A) diploid cells with unpaired chromosomes. B) diploid cells with paired chromosomes. C) haploid cells with unpaired chromosomes. D) haploid cells with paired chromosomes. _____ 8) Mitosis usually results in the formation of A) 2 diploid cells. B) 4 diploid cells. C) 2 haploid cells. D) 4 haploid cells. E) sperm or egg cells. Match the lettered choices with the examples below. Choices will be used only once. (9-14) A. Polygenic inheritance B. Incomplete dominance C. Co-Dominance D. Dominant allele disorder E. Recessive allele disorder F. Disorder due to non-disjunction of autosomes ____ 9) ABO blood groups in humans ____ 10) Sickle-cell anemia ____ 11) Down’s syndrome ____ 12) In snapdragons, red × white produce pink hybrids ____ 13) Huntington’s’ disease ____ 14) Human skin pigmentation and height _____ 15) When Mendel used true-breeding white flowers (recessive trait) and true-breeding purple flowers (dominant trait) as the parental generation, he observed that: A) all offspring had white flowers. B) all offspring had purple flowers. C) 3/4 of the flowers produced by offspring were purple and 1/4 were white D) all the flowers were lavender _____ 16) Gametes differ from somatic cells in A) having only one member of each pair of homologous chromosomes. B) being haploid. C) functioning in sexual reproduction. D) having half the amount of genetic material. E) All the above choices are correct. _____ 17) All of the following take place during meiosis EXCEPT A) two rounds of DNA replication. B) crossing over. C) reduction of chromosome number. D) separation of sister chromatid. E) pairing and separation of homologous chromosomes _____18) Which is NOT a source of variety in sexually reproducing species? A) crossing over B) correct DNA replication C) distribution of chromosomes in gametes D) fertilization E) independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis ____ 19) An individual with two identical alleles of a gene is said to be ________, while one with two different alleles for the same gene is said to be __________. A. Genotype; Phenotype B. Incomplete; dominant C. Heterozygous; Homozygous D. Homozygous; Heterozygous ____ 20) If an individual with sickle-cell anemia has 2 parents that do not have the disease, both parents must be __________ _________ for the trait. A) homozygous recessive B) homozygous dominant C) heterozygous ____ 21) A colorblind boy has a normal mother and a colorblind father. From which parent did he get the X-linked colorblind gene? A) father B) mother C) Either parent could have given him the gene. Match the lettered choices with the statements below. Choices will be used only once. (22-25) A. Metaphase B. Prophase C. Telophase D. Anaphase E. Cytokinesis ____ 22) Chromosomes line up along the equator of a cell. ____ 23) Replicated chromosomes coil and condense; Nuclear envelope reforms. ____ 24) Sister chromatids are pulled apart and move to opposite ends of the cell. ____ 25) Duplicated chromosomes condense; Spindle microtubules form; Chromosomes attach to spindle ____ 26) Which of the following occurs in mitosis but NOT in meiosis? A) production of genetically identical cells B) pairing up of homologous chromosomes during prophase C) crossing over D) independent assortment of chromosomes E) separation of sister chromatid ____ 27) A(n) ________ is the physical location of a gene on a chromosome. A) trait B) genome C) allele D) loci ____ 28) A recessive gene is one: A) blends into a dominant allele B) whose effect is masked by a dominant allele. C) that appears only in a heterozygous individual. D) disappears when exposed to a dominant allele. ____ 29) Assume yellow seed color in peas is dominant over recessive green seed color. If you cross two heterozygous yellow-seeded pea plants, then the expected ratio of yellow to green seeds among the offspring will be: A) 25% yellow: 75% green B) 50% yellow: 50% green C) 75% yellow: 25% green D) 100% yellow ____ 30) Traits controlled by sex-linked recessive genes are expressed more often in males because: A) the male has only one gene for the trait. B) males inherit these genes from their fathers. C) all male offspring of a female carrier always get the gene. D) males get more recessive genes than do females.