* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapters 14 and 15 Anthony Todd http://by123si
Survey
Document related concepts
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
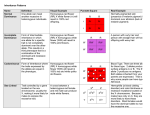
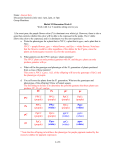
Chapters 14 and 15 Anthony Todd [email protected] http://by123si.yolasite.com/ Part 1: Warm-Up for Chapter 14 Please define the following terms… I GET ALL DEFINITIONS FROM THE GLOSSARY AT THE END OF THE BOOK!!! 1. Character: 2. Trait: 3. True-breeding: 4. Allele: 5. Law of segregation: 6. Punnett square: 7. Phenotype: 8. Genotype: 9. Testcross: 10. Law of independent assortment: 11. Incomplete dominance: 12. Codominance: 13. Pleiotropy: 14. Epistasis: Part II: Applications for Chapter 14 Just a few short-answer questions. You can work alone or with your neighbor… 1. Give the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of a NON-true-breeding widow’s peak individual with a continuous hairline individual. Ww x ww W w w Ww ww w Ww ww Phenotypic: 2 widow’s peak : 2 continuous hairline Genotypic: 0 homozygous dominant : 2 heterozygous : 2 homozygous recessive 2. A purple flower (dominant allele) is testcrossed, and half of the offspring are white and the other half are purple. What is the genotype of the purple flower? Pp; if PP, all offspring would be purple 3. Show two generations of crossing a true-breeding purple flower with a white flower. Parent: PP x pp F1: All Pp F2: 1 homozygous dominant : 2 heterozygous : 1 homozygous recessive 4. Do a dihyrbid cross of PpWw and PpWw. What are the phenotypic ratios? PW Pw pW PW PPWW PPWw PpWW Pw PPWw PPww PpWw pW PpWW PpWw ppWW pw PpWw Ppww ppWw pw PpWw Ppww ppWw ppww Both dominant: P_W_ = 9 1 dom./1 rec: P_ww = 3 1 rec./1 dom.: ppW_ = 3 Both recessive: ppww = 1 5. Describe the autosomal recessive disorders. (Must be homozygous recessive) Cystic fibrosis – caused by a recessive allele for a chloride channel protein; characterized by an excessive secretion of mucus and consequent vulnerability to infection; fatal if untreated; European descent Albinism – individuals can’t make melanin Tay-Sachs Disease – caused by a dysfunctional enzyme, leading to accumulation of certain lipids in the brain; seizures, blindness, and degeneration of motor and mental performance usually arise a few months after birth; Jewish descent. Sickle-cell anemia – results in the substitution of a single amino acid in a globin polypeptide that is part of the hemoglobin protein; characterized by deformed red blood cells (due to protein aggregation) that can lead to numerous symptoms (African-descent) Phenylketonuria – individuals can’t breakdown phenylalanine, so it must be limited in the diet (accumulation could lead to mental retardation) 6. Describe the autosomal dominant disorders. (Heterpzygotes express disorder) Achondroplasia – a form of dwarfism; heterozygotes have the dwarf phenotype Hypercholesterolemia – causes cholesterol level to be around 500, causing cardiovascular problems Huntington’s Disease – characterized by uncontrollable body movements and degeneration of the nervous system; symptoms usually appear in your 40’s Polydactyly – causes one to have extra fingers or toes Part III: Introduction to Chapter 15 Just a few terms to get you thinking about Chapter 15… 1. Chromosome theory of inheritance: 2. Wild type: 3. Sex-linked gene: 4. Linked gene: 5. Genetic recombination: Part IV: Closing We are short on time because of this short summer semester. BE SURE to go over these items at home, in your dorm, at the library – basically anywhere you study: Chapter 14 o Know who the father of genetics is (p. 262) o Understand the basic genetics terms (p. 263-264) o Understand Mendel’s Law of Segregation and its parts (p. 264-267) o Understand how to use a Punnett Square and perform a testcross (p. 266-267) o Understand Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment (p. 268-269) o Become acquainted with the multiplication and addition rules to solve genetics problems (p. 269-270) o Know the difference between complete dominance, incomplete dominance, and codominance (p. 271-272) o Understand pleiotropy, epistasis, and polygenic inheritance (p. 273-274) o Understand how a pedigree is used (p. 276) o Understand the autosomal recessive and dominant disorders (p. 277-279) o Understand the different types of fetal testing (p. 280) Chapter 15 o VERY IMPORTANT TO UNDERSTAND FIGURE 15.2 (p. 287) o Understand Morgan’s experiment with the fruit fly (p. 288; Figure 15.4, p. 289) o Know the chromosomal basis of sex and the inheritance of sex-linked genes (p. 289-290) o Understand the X inactivation of females (p.291-292) o Know what linked genes are (p. 292)