* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell-discovery-notes-1
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
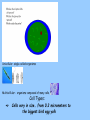
Warm –up 1. Where does life come from???? Explain. 2. 2. What are living things made of? Can life be made from nonliving things? Where does life come from???? Life comes from life. Back in the old days, scientists believed life came from nonliving things- spontaneous generation Aristotle- believed dirty clothes + dark corner= mice Others- horse hairs +stagnant water = snakes Dead meat= maggots- most popular support for spontaneous gen. Frances Redi did not believe in spontaneous generation and chose to disprove the idea of spontaneous generation through a controlled experiment. Cell History & Structure Standard: Students will analyze the nature of the relationship between structures and functions in living cells. EQ: What is the Cell theory? RECAll the Characteritics of Life… All living things are made up of cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things much like an atom is the basic unit of matter Cell- basic unit of structure and function in an organism. Cell Discovery 1st lenses used- 1500s (simple microscope) Compound microscope invented- 1590- led to discovery of cells 1663- Robert HookeCut thin slices of plant tissues Observed thin slices of cork from tree under compound microscope he made himself - noticed small rectangular chambers and named them “cells” 1600s- Anton van Leewenhoek- 1st person to use simple microscope to study nature. - he found tiny organisms in pond water “animalcules” - made detailed drawings - looked at teeth scrapings and noticed tiny organisms- now we know as bacteria These discoveries led to new discoveries about cells…. 1833- Robert Brown discovered the nucleus 1834- Schleiden concluded plants are made of cells 1839- Schwann- all living things made of cells 1855- Virchow- noticed cell reproduction “All cells come from cells” All Discoveries led to the Cell Theory- All living things are composed of cells - Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things - All cells are produced from other cells http://rap.stevius.com/ Cell Theory Rap Hierarchy/Levels of Organization in Living Things Atom Elements Tissues CELLS Organs Systems Ecosystem Macromolecules Organelles Complex organisms Community Biome Population Biosphere Basic Cell Structure 1. cell membrane- thin, flexible barrier around cell 2. cytoplasm- gel-like fluid between cell membrane and nucleus 3. nucleus- contains genetic material and controls cell activity Unicellular- single-celled organisms Multicelllular- organisms composed of many cells. Cell Types: Cells vary in size… from 0.2 micrometers to the biggest bird egg yolk There are 2 types of cells… OBSERVATION- On your own paper, list similarities and differences you can describe from the drawings below- PROKARYOTIC – NO nucleus No membrane-bound organelles Evolved first smaller and simpler than eukaryotes. Ex: All bacteria are prokaryotes Escherichia coli, which live in your intestines Staphylococcus aureus, which can cause skin infections. EUKARYOTIC – true nucleus - Evolved from prokaryotes – specialized membrane-bound organelles, that perform important cellular functions - Ex. Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL