Previously in Bio308
... How would a neuropeptide get made (in general terms)? What are the basic parts of DNA, RNA, and proteins? What is the difference between hnRNA, mRNA and tRNA? ...
... How would a neuropeptide get made (in general terms)? What are the basic parts of DNA, RNA, and proteins? What is the difference between hnRNA, mRNA and tRNA? ...
Chapter 11.2 Notes RNA and Protein RNA Contains the sugar and
... ____________________ – the process of ________________________ the info in a sequence of nitrogenous ______________ in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in _______________ ...
... ____________________ – the process of ________________________ the info in a sequence of nitrogenous ______________ in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in _______________ ...
miRNA - apctp
... is identical to the one of al-1 mutants. • This phenomenon was termed quelling. ...
... is identical to the one of al-1 mutants. • This phenomenon was termed quelling. ...
DNA Function: Information Transmission
... ● genome sequencing has shown that protein-coding DNA only accounts for 1.5% of the human genome (& other eukaryotes) ● a small fraction of the non-protein coding DNA consists of genes for rRNAs and tRNAs ● until recently, researchers assumed that most of the remaining DNA was untranscribed…”junk” D ...
... ● genome sequencing has shown that protein-coding DNA only accounts for 1.5% of the human genome (& other eukaryotes) ● a small fraction of the non-protein coding DNA consists of genes for rRNAs and tRNAs ● until recently, researchers assumed that most of the remaining DNA was untranscribed…”junk” D ...
Investigating the Role of RNA Polymerase II in RNAi
... heterochromatin around centromeric repeats depends on the coordination of two pathways: RNAi and histone modification. Current models suggest that initiation of heterochromatin formation begins with transcription of centromeric RNA by RNA polymerase II. These RNA transcripts are converted to dsRNA b ...
... heterochromatin around centromeric repeats depends on the coordination of two pathways: RNAi and histone modification. Current models suggest that initiation of heterochromatin formation begins with transcription of centromeric RNA by RNA polymerase II. These RNA transcripts are converted to dsRNA b ...
Plant Biotechnology
... Flavr SavrTM tomato introduced in 1994 Ripe tomatoes normally produce the enzyme, polyglacturonase (PG) which digests pectin Scientists isolated gene, produced a complementary gene which produces a complementary mRNA that binds to the normal mRNA inactivating the normal mRNA for this enzyme (figure ...
... Flavr SavrTM tomato introduced in 1994 Ripe tomatoes normally produce the enzyme, polyglacturonase (PG) which digests pectin Scientists isolated gene, produced a complementary gene which produces a complementary mRNA that binds to the normal mRNA inactivating the normal mRNA for this enzyme (figure ...
Double-Stranded RNA: The Enigmatic Helix
... Viruses have long been known to produce dsRNA, and when dsRNA binding proteins (dsRBPs) in our bodies bind viral dsRNA they send an SOS that initiates an immune response to fight the infection. For many years it was thought that animals, including humans, did not make their own dsRNA. However, over ...
... Viruses have long been known to produce dsRNA, and when dsRNA binding proteins (dsRBPs) in our bodies bind viral dsRNA they send an SOS that initiates an immune response to fight the infection. For many years it was thought that animals, including humans, did not make their own dsRNA. However, over ...
Exam 4 Key Fa08
... 8. What do homeotic genes control? (1 pt) [pattern formation] 9. What effect does microRNAs (miRNAs) have on messenger RNA (mRNA)? (1 pt) [Degrades it or stops it from being translated] 10. Transcribe the following single strand of DNA into a strand of RNA: ATCCGCTAAGTCAG (1 pt) [UAGGCGAUUCAGUC] 11. ...
... 8. What do homeotic genes control? (1 pt) [pattern formation] 9. What effect does microRNAs (miRNAs) have on messenger RNA (mRNA)? (1 pt) [Degrades it or stops it from being translated] 10. Transcribe the following single strand of DNA into a strand of RNA: ATCCGCTAAGTCAG (1 pt) [UAGGCGAUUCAGUC] 11. ...
Jeopardy
... 100 special genes that code proteins that promote normal cell growth and division 100 Bonus: cells that inhibit cell growth 100 Bonus: what are cancer causing genes? 200 genes that when altered are responsible for more than 50% of all human cancers 200 Bonus: Acetylation allows what to occur? 300 ca ...
... 100 special genes that code proteins that promote normal cell growth and division 100 Bonus: cells that inhibit cell growth 100 Bonus: what are cancer causing genes? 200 genes that when altered are responsible for more than 50% of all human cancers 200 Bonus: Acetylation allows what to occur? 300 ca ...
Expressing Genetic Information
... 1. Study the scanning electron micrograph of human chromosomes during mitosis. Locate the chromatids and centromere. Now, study the fine detail of the chromatin. How would you describe it? 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in ...
... 1. Study the scanning electron micrograph of human chromosomes during mitosis. Locate the chromatids and centromere. Now, study the fine detail of the chromatin. How would you describe it? 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in ...
Three Types of RNA and Their Functions
... Like rRNA, tRNA is located in the cellular cytoplasm and is involved in protein synthesis. Transfer RNA brings or transfers amino acids to the ribosome that corresponds to each three-nucleotide codon of rRNA. The amino acids then can be joined together and processed to make polypeptides and proteins ...
... Like rRNA, tRNA is located in the cellular cytoplasm and is involved in protein synthesis. Transfer RNA brings or transfers amino acids to the ribosome that corresponds to each three-nucleotide codon of rRNA. The amino acids then can be joined together and processed to make polypeptides and proteins ...
Chapter 18 - Regulation of Gene Expression - Bio-Guru
... • 5’ caps and 3’ tails can be removed or changed and this will prevent translation ...
... • 5’ caps and 3’ tails can be removed or changed and this will prevent translation ...
Reverse Genetics -
... RNAi findings in C. elegans • For >1000 genes where lf phenotype is known from classical genetics, RNAi gives partial lf, or hypomorphic phenotypes, and in many cases, the Null phenotype. ∴ Can give lf, but not necessarily the null phenotype. • RNAi phenotype is gene specific, unless gene under te ...
... RNAi findings in C. elegans • For >1000 genes where lf phenotype is known from classical genetics, RNAi gives partial lf, or hypomorphic phenotypes, and in many cases, the Null phenotype. ∴ Can give lf, but not necessarily the null phenotype. • RNAi phenotype is gene specific, unless gene under te ...
Synthetic lethal analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans posterior
... Synthetic lethal analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans posterior embryonic patterning genes identifies conserved genetic interactions L Ryan Baugh, Joanne C Wen, Andrew A Hill, Donna K Slonim, Eugene L Brown & Craig P Hunter* ...
... Synthetic lethal analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans posterior embryonic patterning genes identifies conserved genetic interactions L Ryan Baugh, Joanne C Wen, Andrew A Hill, Donna K Slonim, Eugene L Brown & Craig P Hunter* ...
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics
... Basic Genetic Mechanisms are Universal The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in ...
... Basic Genetic Mechanisms are Universal The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in ...
Document
... a. nitrogen-containing base b. amino acid c. sugar d. enzyme 2. ___In RNA, thymine is replaced by: a. adenine b. guanine c. cytosine d. uracil 3. ___The type of RNA that carries the instructions for making a protein is called: a. mRNA b. pRNA c. rRNA d. tRNA 4. ___In eukaryotic cells, RNA is copied ...
... a. nitrogen-containing base b. amino acid c. sugar d. enzyme 2. ___In RNA, thymine is replaced by: a. adenine b. guanine c. cytosine d. uracil 3. ___The type of RNA that carries the instructions for making a protein is called: a. mRNA b. pRNA c. rRNA d. tRNA 4. ___In eukaryotic cells, RNA is copied ...
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
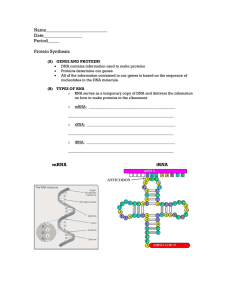
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
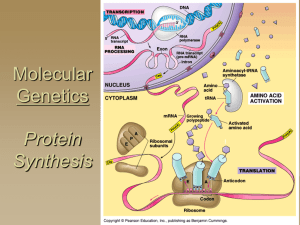
Powerpoint
... contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an organism ...
... contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an organism ...
Let-7 is - University of Colorado-MCDB
... C. Likely a small RNA that inhibits translation of its target mRNA D. A small RNA that inhibits transcription of its target gene ...
... C. Likely a small RNA that inhibits translation of its target mRNA D. A small RNA that inhibits transcription of its target gene ...
Part 4 Transcription
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
Supplementary
... colony diameter in different RNAi-treated groups. (A) Position of siRNAs along the VdAAC gene. siRNAs were designed and synthesized by Oligobio, Beijing, China; (B) Colony diameters of control and siRNA groups observed 2 weeks after transformation on PDA agar plates. The bars with different letters ...
... colony diameter in different RNAi-treated groups. (A) Position of siRNAs along the VdAAC gene. siRNAs were designed and synthesized by Oligobio, Beijing, China; (B) Colony diameters of control and siRNA groups observed 2 weeks after transformation on PDA agar plates. The bars with different letters ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.