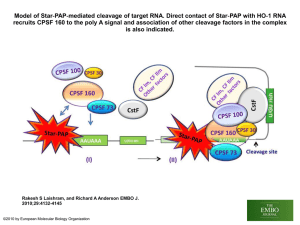
Noushin Farnoud Presentation
... functional group of genes (nearly all of the tested genes encoding ribosomal components exhibited similar quantitative phenotypes). • Analysis of the phenotypes from independent dsRNAs targeting the same gene (show similar phenotypes). ...
... functional group of genes (nearly all of the tested genes encoding ribosomal components exhibited similar quantitative phenotypes). • Analysis of the phenotypes from independent dsRNAs targeting the same gene (show similar phenotypes). ...
Functional genomic analysis of cell division in C. elegans
... RNAi therapeutics, and was curious about your thoughts on that? Could ones' genome be sequenced, bad things identified, and then specific RNAs given to silence problematic genes? This is almost like gene therapy which could someday become more of a reality. ...
... RNAi therapeutics, and was curious about your thoughts on that? Could ones' genome be sequenced, bad things identified, and then specific RNAs given to silence problematic genes? This is almost like gene therapy which could someday become more of a reality. ...
Protein Synthesis SG
... 1. DNA is also known as the _________________________________. 2. A protein is made up of ____________________________. 3. A protein’s function is determined by its ___________ and ______________________________________. 4. Draw and label the 3 major parts of a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide. ...
... 1. DNA is also known as the _________________________________. 2. A protein is made up of ____________________________. 3. A protein’s function is determined by its ___________ and ______________________________________. 4. Draw and label the 3 major parts of a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide. ...
Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
... Secretory Protein— A protein that will be _________ from the cell. The mRNA for this protein contains a signal recognition sequence that is recognized by a signal recognition particle (SRP). The SRP brings the growing polypeptide to the receptor protein in the ___________________. ...
... Secretory Protein— A protein that will be _________ from the cell. The mRNA for this protein contains a signal recognition sequence that is recognized by a signal recognition particle (SRP). The SRP brings the growing polypeptide to the receptor protein in the ___________________. ...
Review L14 Gene to Protein L15 Gene Reg
... Review Questions - Lecture 15: Gene Regulation, Part 1 ...
... Review Questions - Lecture 15: Gene Regulation, Part 1 ...
Previously in Bio308
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
iclicker - University of Colorado-MCDB
... A. inhibit expression of all C. elegans genes B. Inhibit gene expression in other organisms C. Inhibit gene expression in the next generation in C. elegans D. Completely eliminate the expression of a C. elegans gene E. None of above ...
... A. inhibit expression of all C. elegans genes B. Inhibit gene expression in other organisms C. Inhibit gene expression in the next generation in C. elegans D. Completely eliminate the expression of a C. elegans gene E. None of above ...
Regulating Protein Synthesis
... ! siRNAs and miRNAs (smallinterfering RNAs and micro RNAs) can regulate translation ! siRNAs and miRNAs are cut from double-stranded RNA; one strand joins a protein complex ! The protein-siRNA complex breaks down mRNAs that contain complementary sequences ! The protein-miRNA complex breaks down mRNA ...
... ! siRNAs and miRNAs (smallinterfering RNAs and micro RNAs) can regulate translation ! siRNAs and miRNAs are cut from double-stranded RNA; one strand joins a protein complex ! The protein-siRNA complex breaks down mRNAs that contain complementary sequences ! The protein-miRNA complex breaks down mRNA ...
Write True if the statement is true
... Write True if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers am ...
... Write True if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers am ...
Unit 7 Study Guide ANSWERS 2014
... What events occur directly after RNA polymerase recognizes the transcription start site of a gene? Creates an mRNA molecule from a DNA template by bonding RNA nucleotides (A, U, G, C) ...
... What events occur directly after RNA polymerase recognizes the transcription start site of a gene? Creates an mRNA molecule from a DNA template by bonding RNA nucleotides (A, U, G, C) ...
RNA
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – formed during transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – formed during transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
Dissection of a DNA-damage-induced transcriptional network using
... each probed at two time points: without treatment and 4 h after exposure to NCS.14 (All samples were probed in independent triplicates) ...
... each probed at two time points: without treatment and 4 h after exposure to NCS.14 (All samples were probed in independent triplicates) ...
ppt presentation
... The precise role of 25-nt RNA in PTGS remains to be determined. However, because they are long enough to convey sequence specificity yet small enough to move through plasmodesmata, it is possible that they are ...
... The precise role of 25-nt RNA in PTGS remains to be determined. However, because they are long enough to convey sequence specificity yet small enough to move through plasmodesmata, it is possible that they are ...
RNA interference (RNAi)
... • Short regulatory RNA molecules are transcribed from a cell’s DNA • There are two types of this RNA – microRNA (miRNA) – small interfering RNA (siRNA) • A single-strand of miRNA or siRNA can bind to a protein in the cytoplasm to form a complex, called an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) ...
... • Short regulatory RNA molecules are transcribed from a cell’s DNA • There are two types of this RNA – microRNA (miRNA) – small interfering RNA (siRNA) • A single-strand of miRNA or siRNA can bind to a protein in the cytoplasm to form a complex, called an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) ...
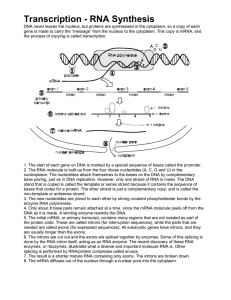
Transcription
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
Dictyostelium discoideum, an interesting model organism for
... interference (RNAi) pathway. This pathway can affect the important process of synthesizing proteins from the information in genes (in eukaryotes, genes are located on chromosomes in the nucleus). The RNAi pathway interacts with an intermediate in this process (messenger RNA) and hinders the producti ...
... interference (RNAi) pathway. This pathway can affect the important process of synthesizing proteins from the information in genes (in eukaryotes, genes are located on chromosomes in the nucleus). The RNAi pathway interacts with an intermediate in this process (messenger RNA) and hinders the producti ...
Chapter 19: Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
... 2.) What problem with the eukaryotic genome did the discovery of chromatin solve? 3.) What are histones? What are nucleosomes? 4.) What is the gene promoter? In order for RNA Polymerase to gain access to the promoter, what state must chromatin be in? 5.) What are the 3 ways (from lecture) that chrom ...
... 2.) What problem with the eukaryotic genome did the discovery of chromatin solve? 3.) What are histones? What are nucleosomes? 4.) What is the gene promoter? In order for RNA Polymerase to gain access to the promoter, what state must chromatin be in? 5.) What are the 3 ways (from lecture) that chrom ...
Integrace „hormonálních“ signálů
... conserved N-terminal half of these Hsfs. We have speculated about possible exon-intron borders in this region in the ancient precursor gene of plant Hsfs, similar to the exon-intron structure of the present mammalian ...
... conserved N-terminal half of these Hsfs. We have speculated about possible exon-intron borders in this region in the ancient precursor gene of plant Hsfs, similar to the exon-intron structure of the present mammalian ...
Parallel Chemical Genetic and Genome
... Ulrike Eggert, Amy Kiger, Constance Richter, Zachary Perlman, Norbert Perrimon, Tomothy Mitchison, Christine Field ...
... Ulrike Eggert, Amy Kiger, Constance Richter, Zachary Perlman, Norbert Perrimon, Tomothy Mitchison, Christine Field ...
Alnylam Licenses Intellectual Property from Cold Spring Harbor
... has built in the fundamental patents, technology, and know-how that underlie the discovery, development and commercialization of RNAi therapeutics Under the terms of the agreement, Alnylam receives a non-exclusive license from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory to therapeutic uses of patent applications ...
... has built in the fundamental patents, technology, and know-how that underlie the discovery, development and commercialization of RNAi therapeutics Under the terms of the agreement, Alnylam receives a non-exclusive license from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory to therapeutic uses of patent applications ...
Epigenetics - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... generates the siRNAs and miRNAs -RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC): contains various proteins including a member of the Argonaute family (Slicer) and the siRNA/miRNA which is denatured to a guide RNA. Some RISC complexes can be directed to the nucleus to recruit chromatin modifying complexes….sil ...
... generates the siRNAs and miRNAs -RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC): contains various proteins including a member of the Argonaute family (Slicer) and the siRNA/miRNA which is denatured to a guide RNA. Some RISC complexes can be directed to the nucleus to recruit chromatin modifying complexes….sil ...
Chapter 14 – RNA molecules and RNA processing
... Eukaryotic mRNA • mRNA requires posttranscriptional modifications before exiting nucleus to cytoplasm (site of ...
... Eukaryotic mRNA • mRNA requires posttranscriptional modifications before exiting nucleus to cytoplasm (site of ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.