Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... tRNA: transfer appropriate amino acid to the ribosome to build proteins. Short ~70-90 nucleotides. rRNA: structural component of ribosome, along with a protein it forms the ribosome which provides the construction site for polypeptide assembly snRNA: small nuclear RNA involved in modification of mRN ...
... tRNA: transfer appropriate amino acid to the ribosome to build proteins. Short ~70-90 nucleotides. rRNA: structural component of ribosome, along with a protein it forms the ribosome which provides the construction site for polypeptide assembly snRNA: small nuclear RNA involved in modification of mRN ...
Messenger RNA profiling: a prototype method to supplant
... Why use mRNA to identify body fluids? ...
... Why use mRNA to identify body fluids? ...
[pdf]
... Arturas Petronis, research scientist at the University of Toronto, Canada, comments that the study has proved its worth by “…quantifying how genetically identical individuals could differ in gene expression on a global level due to epigenetics.” (The Scientist, 7 July 2005). It is hoped that future ...
... Arturas Petronis, research scientist at the University of Toronto, Canada, comments that the study has proved its worth by “…quantifying how genetically identical individuals could differ in gene expression on a global level due to epigenetics.” (The Scientist, 7 July 2005). It is hoped that future ...
MTC19: transcription and gene expression 02/10/07
... A gene in transcription can be defined as a segment of DNA extending from the site of initiation to the site of termination Genes consist of exons (sequences to be subsequently translated into proteins) separated by introns, which can contain other control regions or even other genes to allow more c ...
... A gene in transcription can be defined as a segment of DNA extending from the site of initiation to the site of termination Genes consist of exons (sequences to be subsequently translated into proteins) separated by introns, which can contain other control regions or even other genes to allow more c ...
Lecture TandT
... The Flow of Genetic Information from DNA to RNA to Protein – DNA functions as the inherited directions for a cell or organism. ...
... The Flow of Genetic Information from DNA to RNA to Protein – DNA functions as the inherited directions for a cell or organism. ...
Protein Synthesis - science4warriors
... separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled. ...
... separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled. ...
Dysregulation of CD69 in Dcr / CD4+CD8+ (DP) thymocytes
... ● Pooled Ebola or scrambled siRNA ● 1 mg/kg siRNA in SNALP2 liposomal formulation given i.p. 1 hr after EBOV infection and then daily on days 1-6. ● Sacrifice on day 7 for viremia (n=5 per group) Reference: Geisbert et al., JID (2006) 193:1650-7. ...
... ● Pooled Ebola or scrambled siRNA ● 1 mg/kg siRNA in SNALP2 liposomal formulation given i.p. 1 hr after EBOV infection and then daily on days 1-6. ● Sacrifice on day 7 for viremia (n=5 per group) Reference: Geisbert et al., JID (2006) 193:1650-7. ...
Gene Expression
... • Production of enzymes to break down milk sugar • An activator and repressor have roles • Conditions tightly controlled – Lactose must be high, but no other sugar present – [Lactose] and [glucose] ...
... • Production of enzymes to break down milk sugar • An activator and repressor have roles • Conditions tightly controlled – Lactose must be high, but no other sugar present – [Lactose] and [glucose] ...
powerpoint
... SEQUENCES OF MONOMERS- NUCLEOTIDES AND AMINO ACIDS, RESPECTIVELY. • TRANSCRIPTION IS THE NUCLEOTIDE-TONUCLEOTIDE TRANSFER OF INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA, WHILE TRANSLATION IS THE INFORMATIONAL TRANSFER FROM NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE IN RNA TO AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A POLYPEPTIDE. ...
... SEQUENCES OF MONOMERS- NUCLEOTIDES AND AMINO ACIDS, RESPECTIVELY. • TRANSCRIPTION IS THE NUCLEOTIDE-TONUCLEOTIDE TRANSFER OF INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA, WHILE TRANSLATION IS THE INFORMATIONAL TRANSFER FROM NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE IN RNA TO AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A POLYPEPTIDE. ...
The analysis of exosomal micro-RNAs in peripheral blood
... Tuberculosis (TB) is a major global threat to human health, especially in low-income countries. The diagnosis of TB is challenging because of the limitations of specificity and sensitivity with the current diagnostics. Novel, selective biomarkers for TB would be of great practical value. Exosomes ar ...
... Tuberculosis (TB) is a major global threat to human health, especially in low-income countries. The diagnosis of TB is challenging because of the limitations of specificity and sensitivity with the current diagnostics. Novel, selective biomarkers for TB would be of great practical value. Exosomes ar ...
Regulación Post-transcripcional en eucariotas Biología Molecular
... degradation at the post-transcriptional level. mRNAs containing an AU-rich element (ARE) in their 3' untranslated region (UTR) undergo rapid ARE-mediated mRNA decay (AMD) in resting cells. Stabilization of ARE-containing mRNAs by various stimuli contributes to the induction of gene expression. (B) Q ...
... degradation at the post-transcriptional level. mRNAs containing an AU-rich element (ARE) in their 3' untranslated region (UTR) undergo rapid ARE-mediated mRNA decay (AMD) in resting cells. Stabilization of ARE-containing mRNAs by various stimuli contributes to the induction of gene expression. (B) Q ...
Test: Gene Regulation Free Response Questions It is known that
... 1. It is known that very little of the human genome actually codes for proteins. a. Briefly explain how microRNAs, also called miRNA, regulate gene expression. miRNA: a single stranded micro RNA forms a complex with proteins. The complex binds to mRNA with complementary base sequences and the mRNA i ...
... 1. It is known that very little of the human genome actually codes for proteins. a. Briefly explain how microRNAs, also called miRNA, regulate gene expression. miRNA: a single stranded micro RNA forms a complex with proteins. The complex binds to mRNA with complementary base sequences and the mRNA i ...
Section: Gene Regulation and Structure
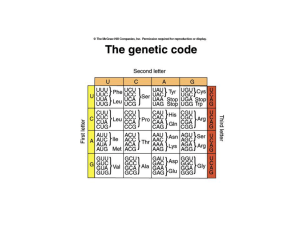
... tRNA that is complementary to one of the codons of the genetic code ...
... tRNA that is complementary to one of the codons of the genetic code ...
Print edition PDF
... free-floating cell,” says Schroth. Smart-Seq doesn’t work on crude tissue preparations, though, so RNA-Seq remains the preferred method for studying those samples. As transcriptome sequencing continues developing and sequencing costs continue falling, many biologists are now using RNA-Seq for routin ...
... free-floating cell,” says Schroth. Smart-Seq doesn’t work on crude tissue preparations, though, so RNA-Seq remains the preferred method for studying those samples. As transcriptome sequencing continues developing and sequencing costs continue falling, many biologists are now using RNA-Seq for routin ...
Transcription Regulation (Prof. Fridoon)
... Many genes also have enhancer (1000 nucleotide away) where specific activators only made by certain cells can bind. ...
... Many genes also have enhancer (1000 nucleotide away) where specific activators only made by certain cells can bind. ...
Word of the Day
... One-stranded Instead of Thymine, RNA has Uracil Three types of RNA: mRNA –carries copies of DNA from nucleus to the cytoplasm .(messenger RNA) tRNA – folded RNA that connects to mRNA to connect amino acids. (transport) ...
... One-stranded Instead of Thymine, RNA has Uracil Three types of RNA: mRNA –carries copies of DNA from nucleus to the cytoplasm .(messenger RNA) tRNA – folded RNA that connects to mRNA to connect amino acids. (transport) ...
Improving site-directed RNA editing by screening RNA editing
... Recoding genetic information through RNA editing is a process catalyzed by adenosine deaminases that act on RNA (ADAR). ADARs are an evolutionarily conserved family of enzymes that convert adenosines to inosines within mRNA transcripts. Because inosine is read as guanosine during translation, RNA ed ...
... Recoding genetic information through RNA editing is a process catalyzed by adenosine deaminases that act on RNA (ADAR). ADARs are an evolutionarily conserved family of enzymes that convert adenosines to inosines within mRNA transcripts. Because inosine is read as guanosine during translation, RNA ed ...
RNA base pairing Worksheet
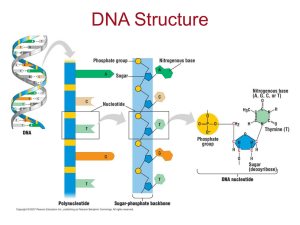
... When a cell creates RNA (transcription), the original DNA ladder is broken apart and new RNA nucleotides are added to one of the strands (template strand). This creates a single stranded RNA molecule. ...
... When a cell creates RNA (transcription), the original DNA ladder is broken apart and new RNA nucleotides are added to one of the strands (template strand). This creates a single stranded RNA molecule. ...
DNA -> RNA -> Proteins
... mRNA finds a ribosome • mRNA moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm of the cell where it finds a ribosome • The ribosome is made of RNA and it will serve as a work bench for making ...
... mRNA finds a ribosome • mRNA moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm of the cell where it finds a ribosome • The ribosome is made of RNA and it will serve as a work bench for making ...
Features of the genetic code
... • Splicesome is needed to identify and catalyze the sequence of events leading to removal of the intron and rejoining of the two successive exons. The splicesome consists of snRNP (snRNA 100300 nucleotides long + proteins). Each splicesome is composed of four snRNPs together and each snRNP is five s ...
... • Splicesome is needed to identify and catalyze the sequence of events leading to removal of the intron and rejoining of the two successive exons. The splicesome consists of snRNP (snRNA 100300 nucleotides long + proteins). Each splicesome is composed of four snRNPs together and each snRNP is five s ...
Gene disruption-Why?
... -Give a profile like Ergosterol mutant Phenotype similar to Erg2 (sterol isomerase) -Human Sigma receptor is closest to Erg2 -Sigma receptor regulate K+ conductance ...
... -Give a profile like Ergosterol mutant Phenotype similar to Erg2 (sterol isomerase) -Human Sigma receptor is closest to Erg2 -Sigma receptor regulate K+ conductance ...
Interfering RNA
... • showing of antisense targets across mRNA may be sufficient, but not all antisense targets are open to siRNA • intron targets may not be active for siRNA but may be for antisense – identify all elements claimed and their support in the description – identify species explicitly or implicitly disclos ...
... • showing of antisense targets across mRNA may be sufficient, but not all antisense targets are open to siRNA • intron targets may not be active for siRNA but may be for antisense – identify all elements claimed and their support in the description – identify species explicitly or implicitly disclos ...
Modification of Genes and Proteins - sharonap-cellrepro-p2
... Alteration of ends of transcript: › 5’ end capped with modified guanine Keeps RNA from degrading in the cytoplasm › Cleavage factors and stabilizing factors bind ...
... Alteration of ends of transcript: › 5’ end capped with modified guanine Keeps RNA from degrading in the cytoplasm › Cleavage factors and stabilizing factors bind ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.


![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008789110_1-03a81e28d94c74d682b307dd66c7080a-300x300.png)