28th Annual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium—Abstract #310
... yield 1066 ng, range 510 – 3276 ng) to run the standard Oncotype DX assay without preamplifying RNA. Gene expression profiles in all 8 specimens for the 21 gene Oncotype DX assay on unamplified RNA had strong signals and met all criteria for successful RTPCR. As has been observed in all other breast ...
... yield 1066 ng, range 510 – 3276 ng) to run the standard Oncotype DX assay without preamplifying RNA. Gene expression profiles in all 8 specimens for the 21 gene Oncotype DX assay on unamplified RNA had strong signals and met all criteria for successful RTPCR. As has been observed in all other breast ...
Nature Rev.Genet
... miRNAs are genomically encoded siRNAs are produced exogenously or from bidirectionally transcribed RNAs Drosha processes pri-miRNA to pre-miRNA in the nucleus miRNA is selectively incorporated into the RISC for target recognition Guide strand of siRNA is incorporated into the RISC for target recogni ...
... miRNAs are genomically encoded siRNAs are produced exogenously or from bidirectionally transcribed RNAs Drosha processes pri-miRNA to pre-miRNA in the nucleus miRNA is selectively incorporated into the RISC for target recognition Guide strand of siRNA is incorporated into the RISC for target recogni ...
RNA, Protein Synthesis, Transcription, and Translation
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
DNA Replication - Texas Tech University
... Do not bind directly onto DNA Usually too weak to act on their own ...
... Do not bind directly onto DNA Usually too weak to act on their own ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... • First cleavage site encountered is suboptimal and skipped in unstimulated cells • Antigen stimulation increases CstF levels to promote cleavage at first site ...
... • First cleavage site encountered is suboptimal and skipped in unstimulated cells • Antigen stimulation increases CstF levels to promote cleavage at first site ...
I - 國立彰化師範大學圖書館
... sequence involved in the regulation of X gene, she made a series deletions containing various lengths of the 5’ regulatory region and transfected into mammalian cells. The reporter gene activity in the absence (-) and presence (+) of metal ion were assay and the results were showed in above figure. ...
... sequence involved in the regulation of X gene, she made a series deletions containing various lengths of the 5’ regulatory region and transfected into mammalian cells. The reporter gene activity in the absence (-) and presence (+) of metal ion were assay and the results were showed in above figure. ...
PG1005 Lecture 17 Gene Transcription
... cytosine and uracil) -Intramolecular complimentary sequences found in RNA Can form intramolecular bonds permitting folding and generation of precise 3D structures ...
... cytosine and uracil) -Intramolecular complimentary sequences found in RNA Can form intramolecular bonds permitting folding and generation of precise 3D structures ...
CRISPR-Cas Genome Manipulation
... (German Cancer Research Center); http://www.rgenome.net/cas-offinder/ (Center for Genome Engineering, Institute for Basic Science, Korea) 3. What’s the function of the gene(s) being targeted? 4. What’s the objective in using CRISPR? a. Gene drive b. Gene knockout/indel c. Genome-wide screening d. Ac ...
... (German Cancer Research Center); http://www.rgenome.net/cas-offinder/ (Center for Genome Engineering, Institute for Basic Science, Korea) 3. What’s the function of the gene(s) being targeted? 4. What’s the objective in using CRISPR? a. Gene drive b. Gene knockout/indel c. Genome-wide screening d. Ac ...
Lecture 5
... •Can use radiolabeled ATP or GTP •Can use Western blotting to detect phosphorylated substrate. ...
... •Can use radiolabeled ATP or GTP •Can use Western blotting to detect phosphorylated substrate. ...
Genetic Controls in Eukaryotes
... o Controlled by regulatory proteins specific to each cell type o Consequence = a single gene can code for more than one polypeptide = alternative RNA splicing o Humans can have fewer genes than proteins that are made. - mRNA degradation o How long mRNA stays in cytoplasm will determine how much prot ...
... o Controlled by regulatory proteins specific to each cell type o Consequence = a single gene can code for more than one polypeptide = alternative RNA splicing o Humans can have fewer genes than proteins that are made. - mRNA degradation o How long mRNA stays in cytoplasm will determine how much prot ...
How do we get proteins? - Sebastian Charter Junior High
... DNA is used to make a single strand of RNA that is ...
... DNA is used to make a single strand of RNA that is ...
Abstract
... in a wide range of developmental pathways in plants through ARGONAUTE1 (AGO1) post-transcriptional regulation of target mRNAs. Genetic analysis of ago1 mutants with informative defects has provided valuable insights into AGO1's biological functions and its corresponding miRNAs. Tomato encodes two AG ...
... in a wide range of developmental pathways in plants through ARGONAUTE1 (AGO1) post-transcriptional regulation of target mRNAs. Genetic analysis of ago1 mutants with informative defects has provided valuable insights into AGO1's biological functions and its corresponding miRNAs. Tomato encodes two AG ...
What happens to the repressor when lactose is present?
... Operons generally are not found in 1. ___________ eukaryotes 2. Most eukaryotic genes are controlled Individually ___________ and have __________ Regulatory sequences that are much more Complex ______ than those of the lac operon. ...
... Operons generally are not found in 1. ___________ eukaryotes 2. Most eukaryotic genes are controlled Individually ___________ and have __________ Regulatory sequences that are much more Complex ______ than those of the lac operon. ...
SA Pathology IBC response to Consultation Questions 1. Which
... components against the same genes would have the same effect for a much shorter timeframe, and hence would be much safer (to the researcher). The half-life of RNA interference components may also wish to be considered – current siRNA half-lives are relatively short but conceivably, with modification ...
... components against the same genes would have the same effect for a much shorter timeframe, and hence would be much safer (to the researcher). The half-life of RNA interference components may also wish to be considered – current siRNA half-lives are relatively short but conceivably, with modification ...
Transcription and Translation
... Usually double stranded Stores the code (like the master blueprint) ...
... Usually double stranded Stores the code (like the master blueprint) ...
RNA and Transcription Worksheet File
... The DNA molecule, with its sequences of nitrogen bases, contains the code for building ___2___. The expression of genes requires what two processes? ...
... The DNA molecule, with its sequences of nitrogen bases, contains the code for building ___2___. The expression of genes requires what two processes? ...
Epigenetics ppt
... The study of the mechanisms by which genes bring about their phenotypic effects ...
... The study of the mechanisms by which genes bring about their phenotypic effects ...
Chapter 11 and 12 Genetics is the scientific study of heredity
... Genetics is the scientific study of heredity. Heredity is the passing of traits (characteristics) from generation to generation. Gregor Mendel is considered to be the father of genetics. He studied inheritance using pea plants. Pea plants are usually self pollinating (meaning they reproduce within t ...
... Genetics is the scientific study of heredity. Heredity is the passing of traits (characteristics) from generation to generation. Gregor Mendel is considered to be the father of genetics. He studied inheritance using pea plants. Pea plants are usually self pollinating (meaning they reproduce within t ...
Gen660_Lecture9B_GeneExpressionEvo_2014
... These cases can be distinguished by measuring the: Mutational variance (Vm) = how much expression of a given gene varies in response to mutation but in the ABSENCE of selection? Genetic variance (Vg) = how much expression of a given gene varies in natural populations (i.e. influenced by mutation + s ...
... These cases can be distinguished by measuring the: Mutational variance (Vm) = how much expression of a given gene varies in response to mutation but in the ABSENCE of selection? Genetic variance (Vg) = how much expression of a given gene varies in natural populations (i.e. influenced by mutation + s ...
Slide 1
... How 24,000 genes in the human genome encode more than 100,000 proteins. How information flows through Transcription and Translation. 4 points of information control in the cell. Explain RNA splicing with respect to Exons and Introns. Explain the difference between a Haploid and a Diploid Cell. ...
... How 24,000 genes in the human genome encode more than 100,000 proteins. How information flows through Transcription and Translation. 4 points of information control in the cell. Explain RNA splicing with respect to Exons and Introns. Explain the difference between a Haploid and a Diploid Cell. ...
From Gene to Protein
... •Transfer of Information from DNA to RNA • Transcription: mRNA production, or the synthesis of other types of RNA • Short segment of DNA (gene) is transcribed into mRNA for movement out of the nucleus to the ribosome • DNA is used as a template to make a complementary piece of “messenger RNA”. This ...
... •Transfer of Information from DNA to RNA • Transcription: mRNA production, or the synthesis of other types of RNA • Short segment of DNA (gene) is transcribed into mRNA for movement out of the nucleus to the ribosome • DNA is used as a template to make a complementary piece of “messenger RNA”. This ...
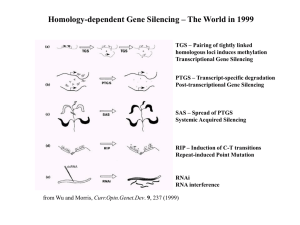
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.