Use of RNAi silencing to explore gene function during soybean
... Nodulation is the result of a symbiotic association between bacteria within the family Rhizobiaceae and a specific legume host. The interaction between the plant host and the bacterium leads to the formation of a novel, highly efficient, nitrogen-fixing organ, the nodule. The symbiotic partners reco ...
... Nodulation is the result of a symbiotic association between bacteria within the family Rhizobiaceae and a specific legume host. The interaction between the plant host and the bacterium leads to the formation of a novel, highly efficient, nitrogen-fixing organ, the nodule. The symbiotic partners reco ...
Lecture #7 Date ______
... of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule ...
... of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule ...
gene expression - Aurora City Schools
... • RNA’s “language” is translated into amino acids (which will become a protein) • RNA’s language is set of three nucleotides called a codon…3 nitrogen bases in a row • Codons match with specific amino acids to make polypeptide chain (which will be modified to make a protein) • 20 amino acids all tog ...
... • RNA’s “language” is translated into amino acids (which will become a protein) • RNA’s language is set of three nucleotides called a codon…3 nitrogen bases in a row • Codons match with specific amino acids to make polypeptide chain (which will be modified to make a protein) • 20 amino acids all tog ...
the soybean pgip family contains members with different inhibiting
... In order to characterize the genomic organization of the soybean pgip family, we have screened a BAC library prepared from genomic DNA of the cv. Williams82. A total of 7 BAC clones were isolated and characterized further to identify novel pgip genes. These analysis allowed the identification of two ...
... In order to characterize the genomic organization of the soybean pgip family, we have screened a BAC library prepared from genomic DNA of the cv. Williams82. A total of 7 BAC clones were isolated and characterized further to identify novel pgip genes. These analysis allowed the identification of two ...
Central Dogma WebQuest - Life Science
... 3. In a eukaryotic cell, transcription occurs in the nucleus, and translation occurs in the ______________. 4. Write the functions of the following forms of RNA: mRNA: ___________________________________________________________________________ tRNA: __________________________________________________ ...
... 3. In a eukaryotic cell, transcription occurs in the nucleus, and translation occurs in the ______________. 4. Write the functions of the following forms of RNA: mRNA: ___________________________________________________________________________ tRNA: __________________________________________________ ...
18. Gene Expression
... Three main phases: Initiation Elongation Termination Initiation: • Promoter = nucleotide sequence 5’ to the transcription start site o binding site of RNA polymerase initiation factor (sigma subunit, σ) o Promoter recognition by RNA polymerase is a prerequisite for transcription initiation o Many pr ...
... Three main phases: Initiation Elongation Termination Initiation: • Promoter = nucleotide sequence 5’ to the transcription start site o binding site of RNA polymerase initiation factor (sigma subunit, σ) o Promoter recognition by RNA polymerase is a prerequisite for transcription initiation o Many pr ...
With the relatively recent development and adoption of new gene
... adequately cover the use of these technologies so do not see a benefit to adding additional governance above what is currently required. In more detail: 1. Which option do you support and why? We support option 1 as we believe that this adequately covers the new technologies which in many ways pose ...
... adequately cover the use of these technologies so do not see a benefit to adding additional governance above what is currently required. In more detail: 1. Which option do you support and why? We support option 1 as we believe that this adequately covers the new technologies which in many ways pose ...
Science 103: Outline 17
... (a) Transcription (b) Translation 2. Transcription (a) Overall Process Gene (DNA) (b) Functions (i) (ii) (c) Location (d) Process A single-stranded RNA copy of the DNA is made by RNA polymerase: (i) RNA pol binds to and moves down the DNA, separating the strands. (ii) As it goes, it pairs compleme ...
... (a) Transcription (b) Translation 2. Transcription (a) Overall Process Gene (DNA) (b) Functions (i) (ii) (c) Location (d) Process A single-stranded RNA copy of the DNA is made by RNA polymerase: (i) RNA pol binds to and moves down the DNA, separating the strands. (ii) As it goes, it pairs compleme ...
Document
... Alternative RNA splicing --- One exon codes for one domain of a protein (p. 336) Introns allow for more crossing over without disrupting domain coding = new proteins sequences. ...
... Alternative RNA splicing --- One exon codes for one domain of a protein (p. 336) Introns allow for more crossing over without disrupting domain coding = new proteins sequences. ...
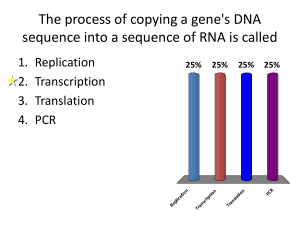
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
... true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
Chapter 10 Lesson 1
... a. One nucleotide is substituted for another. This only changes one a.acid B. Mutagen 1. Def – External agents that cause mutations a. Ex: radiation, high temp, chemicals, environmental factors C. Mutations 1. Body cells – only cause problems in person 2. Sex cells – problems are passed from generat ...
... a. One nucleotide is substituted for another. This only changes one a.acid B. Mutagen 1. Def – External agents that cause mutations a. Ex: radiation, high temp, chemicals, environmental factors C. Mutations 1. Body cells – only cause problems in person 2. Sex cells – problems are passed from generat ...
Lecture
... both to synthesize the chips (ordering thousands of primers or 70mers) and to buy the dyes to label the cDNA for each experiment Genes should be spotted in duplicate or triplicate Need to do reverse label experiments to confirm results ...
... both to synthesize the chips (ordering thousands of primers or 70mers) and to buy the dyes to label the cDNA for each experiment Genes should be spotted in duplicate or triplicate Need to do reverse label experiments to confirm results ...
CH. 13 - Weebly
... • Separates the DNA strands and helps assemble nucleotides to DNA template • Template: ...
... • Separates the DNA strands and helps assemble nucleotides to DNA template • Template: ...
Study Guide
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
Protein Synthesis
... The ribosome is made of protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). All cells need proteins, DNA, and ribosomes. Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes have ribosomes. ...
... The ribosome is made of protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). All cells need proteins, DNA, and ribosomes. Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes have ribosomes. ...
Chapter 4 Section 4 – The DNA Connection
... from a gene on a chromosome to produce a specific protein. Protein synthesis takes place on the ribosome in the cytoplasm of the cell. ...
... from a gene on a chromosome to produce a specific protein. Protein synthesis takes place on the ribosome in the cytoplasm of the cell. ...
In vitro RNA-peptide co-evolution system for screening ATP
... structural organization through reproduction of molecules. Whereas “evolvability” of the biological system is maintained by replicable nucleotide polymers that undergo Darwinian evolution. Here Functional RNA-protein complexes (RNPs) represent perhaps the oldest conserved molecular assemblies in cel ...
... structural organization through reproduction of molecules. Whereas “evolvability” of the biological system is maintained by replicable nucleotide polymers that undergo Darwinian evolution. Here Functional RNA-protein complexes (RNPs) represent perhaps the oldest conserved molecular assemblies in cel ...
Lecture 18
... iv. All of DNA is double stranded v. RNA can be double or single stranded vi. Evidence for model that RNA precedes DNA 1. RNA involved in synthesis of both itself and DNA 2. DNA cannot synthesize itself, it only provides the encoding 3. Diagram of templates 4. RNA ubiquitous in all DNA functions 5. ...
... iv. All of DNA is double stranded v. RNA can be double or single stranded vi. Evidence for model that RNA precedes DNA 1. RNA involved in synthesis of both itself and DNA 2. DNA cannot synthesize itself, it only provides the encoding 3. Diagram of templates 4. RNA ubiquitous in all DNA functions 5. ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.