Chapter 13- RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Some mutations are caused by physical agents in the environment, called mutagens The effects of mutations can have little/no effect, or can negatively disrupt gene function ...
... Some mutations are caused by physical agents in the environment, called mutagens The effects of mutations can have little/no effect, or can negatively disrupt gene function ...
Section 18.1 Summary – pages 475-483
... • The species specific characteristic of viruses is significant for controlling the spread of viral diseases. For example, smallpox was easier to eradicate because it only affects humans and since it is a DNA virus does not mutate very often. (unlike the bird flu and West Nile that affect several t ...
... • The species specific characteristic of viruses is significant for controlling the spread of viral diseases. For example, smallpox was easier to eradicate because it only affects humans and since it is a DNA virus does not mutate very often. (unlike the bird flu and West Nile that affect several t ...
Control of gene expression in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
... Gene expression is transcription of DNA to make RNA and then using the RNA to make proteins. This process can’t be left on indefinitely. The turning on and off of genes is critical to the development of an organism and the organism functioning properly throughout its life. Eukaryotic control Pretran ...
... Gene expression is transcription of DNA to make RNA and then using the RNA to make proteins. This process can’t be left on indefinitely. The turning on and off of genes is critical to the development of an organism and the organism functioning properly throughout its life. Eukaryotic control Pretran ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... 3.Transfer RNA (tRNA)—transfers each amino acid and anticodon to the appropriate place on the mRNA strand. ...
... 3.Transfer RNA (tRNA)—transfers each amino acid and anticodon to the appropriate place on the mRNA strand. ...
Non-coding RNA | Principles of Biology from Nature Education
... work from a distance — they are sometimes located in regions of DNA far upstream or downstream from transcription sites and can even be on a different chromosome. New research points out that many of these enhancer sites are transcribed into eRNAs. eRNA was discovered in mouse neuron cells. When res ...
... work from a distance — they are sometimes located in regions of DNA far upstream or downstream from transcription sites and can even be on a different chromosome. New research points out that many of these enhancer sites are transcribed into eRNAs. eRNA was discovered in mouse neuron cells. When res ...
TARBP2 mediated post-transcriptional regulation of gene
... Role of DICER cofactors during post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in vivo ...
... Role of DICER cofactors during post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in vivo ...
Clark: Biotechnology, 2nd Edition Chapter 2: DNA, RNA, and Protein
... 21. All of these are differences in translation between eukaryotes and prokaryotes EXCEPT: *a. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic genetic codes are different from each other. b. Each organism has its own codon bias, certain codons but not other codons are used more often for the same amino acid. c. They are ...
... 21. All of these are differences in translation between eukaryotes and prokaryotes EXCEPT: *a. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic genetic codes are different from each other. b. Each organism has its own codon bias, certain codons but not other codons are used more often for the same amino acid. c. They are ...
Central Dogma
... 2. If the number of bacteria continued to increase at the same rate as the pond continued to warm, what would the measurement be at 30 degrees? A. 400 B. 640 C. 860 D. 1270 3. Based on the information presented, the number of which of the following substances is not determined by the pond's temperat ...
... 2. If the number of bacteria continued to increase at the same rate as the pond continued to warm, what would the measurement be at 30 degrees? A. 400 B. 640 C. 860 D. 1270 3. Based on the information presented, the number of which of the following substances is not determined by the pond's temperat ...
Nucleic acid recognition from prokaryotes to eukaryotes: Case
... ‘Nucleic acid recognition from prokaryotes to eukaryotes: Case studies of a redox-sensing repressor and a pre-mRNA splicing factor’ Clara L. Kielkopf, Assistant Professor University of Rochester School of Medicine Proteins regulate gene expression at multiple stages ranging from transcription throug ...
... ‘Nucleic acid recognition from prokaryotes to eukaryotes: Case studies of a redox-sensing repressor and a pre-mRNA splicing factor’ Clara L. Kielkopf, Assistant Professor University of Rochester School of Medicine Proteins regulate gene expression at multiple stages ranging from transcription throug ...
myPresentation
... 1. Network-based identification of candidate cancer genes • Identification of functionally relevant genes in copy number regions • Co-expression and transcriptional analysis 2. Identification of differentially expressed miRNAs and their target genes in the GBM network 3. Identification of prognostic ...
... 1. Network-based identification of candidate cancer genes • Identification of functionally relevant genes in copy number regions • Co-expression and transcriptional analysis 2. Identification of differentially expressed miRNAs and their target genes in the GBM network 3. Identification of prognostic ...
Glimpses of a few literatures on snRNA
... Higher eukaryotes can mount antiviral immune responses induced by dsRNA. This process, called RNA interference, is sequence specific and can therefore be used to target gene expression. Nature Immunology 3, 597 - 599 (2002) doi:10.1038/ni0702-597 ...
... Higher eukaryotes can mount antiviral immune responses induced by dsRNA. This process, called RNA interference, is sequence specific and can therefore be used to target gene expression. Nature Immunology 3, 597 - 599 (2002) doi:10.1038/ni0702-597 ...
1495/Chapter 08
... this chapter to find ways to fight bacterial infections in humans? Write a short report (up to one page) identifying some processes that might be significant in the development of treatments. Could the same processes be applied to fight infections by eukaryotic cells such as yeast? Why or why not? 4 ...
... this chapter to find ways to fight bacterial infections in humans? Write a short report (up to one page) identifying some processes that might be significant in the development of treatments. Could the same processes be applied to fight infections by eukaryotic cells such as yeast? Why or why not? 4 ...
How are protein made in our cells?
... • What are 3 differences between DNA and RNA? What are 3 types of RNA? • What is transcription? What are the steps in this process? • What is translation? What are the steps in this process? • Protein is made up of smaller building blocks called ______ ______. • What is the mRNA sequence for the fol ...
... • What are 3 differences between DNA and RNA? What are 3 types of RNA? • What is transcription? What are the steps in this process? • What is translation? What are the steps in this process? • Protein is made up of smaller building blocks called ______ ______. • What is the mRNA sequence for the fol ...
Describe the operon hypothesis and discuss
... Describe the operon hypothesis and discuss how it explains the control of messenger RNA production and the regulation of protein synthesis in bacterial cells. STANDARDS: BACKGROUND: ...
... Describe the operon hypothesis and discuss how it explains the control of messenger RNA production and the regulation of protein synthesis in bacterial cells. STANDARDS: BACKGROUND: ...
Aliens? - Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
... Another old element, new to science: microRNAs RNA world hypothesis: First “organism” was a strand of RNA that could somehow replicate itself. Eventually RNA used DNA as a more stable storage for genetic material. ...
... Another old element, new to science: microRNAs RNA world hypothesis: First “organism” was a strand of RNA that could somehow replicate itself. Eventually RNA used DNA as a more stable storage for genetic material. ...
RNAi: nature abhors a double-strand György Hutvágner and Phillip
... between the two strands. The stRNA would then bind its target genes, and accumulate, while the other strand is degraded. This third idea suggests that the stability of the initial double-stranded Dicer product determines which pathway a small RNA enters. The distinctions between siRNAs and stRNAs (a ...
... between the two strands. The stRNA would then bind its target genes, and accumulate, while the other strand is degraded. This third idea suggests that the stability of the initial double-stranded Dicer product determines which pathway a small RNA enters. The distinctions between siRNAs and stRNAs (a ...
Review Questions
... cytoplasm? DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA. 2. What is a transcript? A transcript is not a copy of the original but has the same information but stored in a different form. Court reporters make a transcript of courtroom proceedings. They type out what everyone says during a trial. Rather than ...
... cytoplasm? DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA. 2. What is a transcript? A transcript is not a copy of the original but has the same information but stored in a different form. Court reporters make a transcript of courtroom proceedings. They type out what everyone says during a trial. Rather than ...
Genetics Review Questions
... 6. Dominant genes are represented by a capital letter, while a recessive gene is represented by a lowercase letter. 7. PP and pp represent a purebred organism. 8. A hybrid gene pair is also referred to as heterozygous. 9. Offspring inherit one gene from each parent. 10. Pp has genes that are differe ...
... 6. Dominant genes are represented by a capital letter, while a recessive gene is represented by a lowercase letter. 7. PP and pp represent a purebred organism. 8. A hybrid gene pair is also referred to as heterozygous. 9. Offspring inherit one gene from each parent. 10. Pp has genes that are differe ...
Mock Exam 2BY330 Summer 2014 Assume that 4 molecules of
... 2. The cytochrome complexes in the mitochondria have _______________ ions in their core, normally present in the (oxidized, reduced) state. 3. Which of the following proteins can be used to synthesize ribosomal RNA in eukaryotes? Circle all that apply. a). RNA polymerase I b). RNA polymerase II c). ...
... 2. The cytochrome complexes in the mitochondria have _______________ ions in their core, normally present in the (oxidized, reduced) state. 3. Which of the following proteins can be used to synthesize ribosomal RNA in eukaryotes? Circle all that apply. a). RNA polymerase I b). RNA polymerase II c). ...
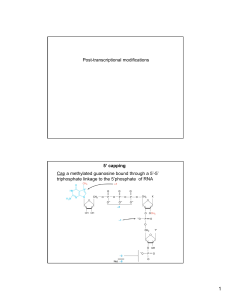
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... targets for ribonucleases, which degrade dsRNAs into small fragments of about 21-25bp. This process appears to be part of the natural defense against viral dsRNAs. Small dsRNAs may serve to target nuclear copies of the gene for methylation, resulting in a feedback mechanism for gene silencing. dsRNA ...
... targets for ribonucleases, which degrade dsRNAs into small fragments of about 21-25bp. This process appears to be part of the natural defense against viral dsRNAs. Small dsRNAs may serve to target nuclear copies of the gene for methylation, resulting in a feedback mechanism for gene silencing. dsRNA ...
From Genes to Proteins
... 1. Determine the sequence of amino acids that will result from the translation of the segment of mRNA above. (Use chart on p. 211.) 2. Determine the anticodon of each tRNA molecule that will bind to this mRNA segment. 3. Determine the sequence of nucleotides in the segment of DNA from which the mRNA ...
... 1. Determine the sequence of amino acids that will result from the translation of the segment of mRNA above. (Use chart on p. 211.) 2. Determine the anticodon of each tRNA molecule that will bind to this mRNA segment. 3. Determine the sequence of nucleotides in the segment of DNA from which the mRNA ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.