dsRNA synthesis RNAi (Howard Clarke)
... Chose an exon-rich region of genomic DNA 300bp in length (>500 is better, and 3’ UTR sequence is fine). Alternatively, cDNA clones or first-strand cDNA generated by RT-PCR can be used as template (see protocol “Oligo d(T) primed cDNA synthesis”). cDNA templates are recommended for genes that have on ...
... Chose an exon-rich region of genomic DNA 300bp in length (>500 is better, and 3’ UTR sequence is fine). Alternatively, cDNA clones or first-strand cDNA generated by RT-PCR can be used as template (see protocol “Oligo d(T) primed cDNA synthesis”). cDNA templates are recommended for genes that have on ...
Slide 1
... Figure 1 Genes used to study RNA-mediated genetic interference in C.elegans. Intron–exon structure for genes used to test RNA-mediated inhibition are shown (grey and filled boxes, exons; open boxes, introns; patterned and striped boxes, 5' and 3' untranslated regions. unc-22. ref. 9, unc-54, ref. 1 ...
... Figure 1 Genes used to study RNA-mediated genetic interference in C.elegans. Intron–exon structure for genes used to test RNA-mediated inhibition are shown (grey and filled boxes, exons; open boxes, introns; patterned and striped boxes, 5' and 3' untranslated regions. unc-22. ref. 9, unc-54, ref. 1 ...
Document
... • RNA interference: limits the invasion of foreign genes and censors the expression of their own genes • Antisense RNA: single-stranded RNA molecules that bind to mRNA and inhibit translation • siRNA and microRNAs: doubled-stranded RNA that regulate gene expression by a process called RNA interferen ...
... • RNA interference: limits the invasion of foreign genes and censors the expression of their own genes • Antisense RNA: single-stranded RNA molecules that bind to mRNA and inhibit translation • siRNA and microRNAs: doubled-stranded RNA that regulate gene expression by a process called RNA interferen ...
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are one of the most abundant groups of
... The areas we are working on are several – miRNA, plant viroids, DNA markers, plant biotech etc. One subject we are most interested is the Bioinformatics, where I have a small but a capable group. The specific reason I write to you concerns one of the topics we work on – miRNA and gene regulation. As ...
... The areas we are working on are several – miRNA, plant viroids, DNA markers, plant biotech etc. One subject we are most interested is the Bioinformatics, where I have a small but a capable group. The specific reason I write to you concerns one of the topics we work on – miRNA and gene regulation. As ...
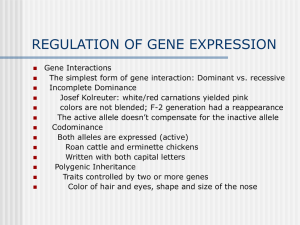
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
... a cluster of genes working together a region of the chromosome near the cluster: operator a region of the chromosome next to the operator: promotor products that initiates the production of enzymes are inducers ...
... a cluster of genes working together a region of the chromosome near the cluster: operator a region of the chromosome next to the operator: promotor products that initiates the production of enzymes are inducers ...
24.8 brief comms MH - Department of Entomology
... Figure 1 | Kin discrimination during social development in the amoeba Dictyostelium purpureum. a, Scatter plot showing the proportion of fluorescently labelled spores in individual fruiting bodies formed at high amoeba density for isolates 13 and 18 (see text; bold, fluorescently labelled isolate). ...
... Figure 1 | Kin discrimination during social development in the amoeba Dictyostelium purpureum. a, Scatter plot showing the proportion of fluorescently labelled spores in individual fruiting bodies formed at high amoeba density for isolates 13 and 18 (see text; bold, fluorescently labelled isolate). ...
Problem 3: Why do pre-mRNAs get smaller during RNA processing?
... Problem 3: Why do pre-mRNAs get smaller during RNA processing? The primary RNA transcript of the chicken ovalbumin gene is 7700 nucleotides long, but the mature mRNA that is translated on the ribosome is 1872 nucleotides long. This size difference occurs primarily as a result of: A. capping B. cleav ...
... Problem 3: Why do pre-mRNAs get smaller during RNA processing? The primary RNA transcript of the chicken ovalbumin gene is 7700 nucleotides long, but the mature mRNA that is translated on the ribosome is 1872 nucleotides long. This size difference occurs primarily as a result of: A. capping B. cleav ...
BIO CH 13 Test Review
... 32. the operator (O) or “O-site” is where a DNA-binding protein known as the lac repressor can bind to DNA. 33. By binding DNA sequences in the regulatory regions of eukaryotic genes, transcription factors control the expression of those genes. 34. Blocking gene expression by means of an miRNA silen ...
... 32. the operator (O) or “O-site” is where a DNA-binding protein known as the lac repressor can bind to DNA. 33. By binding DNA sequences in the regulatory regions of eukaryotic genes, transcription factors control the expression of those genes. 34. Blocking gene expression by means of an miRNA silen ...
Chapter 10 - Power Point Presentation
... before making the protein. The portions that remain and ARE used are called exons So, eukaryotes undergo RNA splicing This is one way a gene can have some variability in its outcome ...
... before making the protein. The portions that remain and ARE used are called exons So, eukaryotes undergo RNA splicing This is one way a gene can have some variability in its outcome ...
Piwi-interacting RNAs and the role of RNA interference
... family, which are defined as having a PAZ and PIWI domains. A schematic of the structure of RISC is shown in Figure 2.3 The Argonaute PAZ domain most likely holds the 3' end of siRNA, providing the proper orientation for recognition and cleavage of mRNA. PIWI contains the active site for cleaving th ...
... family, which are defined as having a PAZ and PIWI domains. A schematic of the structure of RISC is shown in Figure 2.3 The Argonaute PAZ domain most likely holds the 3' end of siRNA, providing the proper orientation for recognition and cleavage of mRNA. PIWI contains the active site for cleaving th ...
Earth`s Early History 10-2
... the origin of life. Discuss the hypothesis that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells. ...
... the origin of life. Discuss the hypothesis that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells. ...
Review for Molecular Genetics Quest
... 20. Label with either tRNA, mRNA, rRNA: a. Carries the DNA code from nucleus to cytoplasm b. Made by the nucleolus c. Adds the correct amino acid to the growing protein chain d. Combines with proteins to form ribosomes e. Has a CODON region f. Has an ANTICODON region g. ...
... 20. Label with either tRNA, mRNA, rRNA: a. Carries the DNA code from nucleus to cytoplasm b. Made by the nucleolus c. Adds the correct amino acid to the growing protein chain d. Combines with proteins to form ribosomes e. Has a CODON region f. Has an ANTICODON region g. ...
Section 5-4
... • The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins – A gene is a section of DNA – DNA is made of four nitrogen bases • Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) • Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C) ...
... • The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins – A gene is a section of DNA – DNA is made of four nitrogen bases • Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) • Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C) ...
Poster
... Human cells have the remarkable capability to regulate protein production by degrading target mRNA by two pathways: RNA interference (RNAi) and micro RNA (miRNA). Central to these pathways is the protein Argonaute-2 (Ago-2). In the RNAi pathway, small RNAs derived from viruses are used by Ago-2 to s ...
... Human cells have the remarkable capability to regulate protein production by degrading target mRNA by two pathways: RNA interference (RNAi) and micro RNA (miRNA). Central to these pathways is the protein Argonaute-2 (Ago-2). In the RNAi pathway, small RNAs derived from viruses are used by Ago-2 to s ...
Ch. 13.3 13.4 notes mutations
... A _______________________________ in the Hox genes of fruit flies has yielded wings or legs in areas that they otherwise would not be ...
... A _______________________________ in the Hox genes of fruit flies has yielded wings or legs in areas that they otherwise would not be ...
Document
... • Only about 1.5% of the human genome codes for proteins. (This is also true of many other multicellular eukaryotes.) • Another small fraction of DNA consists of genes for ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA. • A flood of recent data suggests that a significant amount of the remaining genome is transcrib ...
... • Only about 1.5% of the human genome codes for proteins. (This is also true of many other multicellular eukaryotes.) • Another small fraction of DNA consists of genes for ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA. • A flood of recent data suggests that a significant amount of the remaining genome is transcrib ...
DNA to Proteins
... you see in organisms. • Proteins are chemical triggers and messengers for cell processes. • An organism may have thousands for genes that code for thousands of proteins ...
... you see in organisms. • Proteins are chemical triggers and messengers for cell processes. • An organism may have thousands for genes that code for thousands of proteins ...
Eat to Regulate Your Genes?
... messenger RNA, which then is (or may be) “translated” into protein. The entire process is broadly known as “gene expression.” However, one of the hottest fields of research in molecular biology over the past decade or two has to do with DNA regions that produce a wide assortment of nonprotein-coding ...
... messenger RNA, which then is (or may be) “translated” into protein. The entire process is broadly known as “gene expression.” However, one of the hottest fields of research in molecular biology over the past decade or two has to do with DNA regions that produce a wide assortment of nonprotein-coding ...
Joining the Dots: Network Analysis of Gene Perturbation Screens
... “What I cannot break, I do not understand.” ...
... “What I cannot break, I do not understand.” ...
rna interference
... sometimes DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), which covalently modify histones in the immediate region. This process eventually causes heterochromatin formation and spreading; in some cases the RITS complex can induce DNA methylation. As a result, gene expression can be silenced over long periods to lim ...
... sometimes DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), which covalently modify histones in the immediate region. This process eventually causes heterochromatin formation and spreading; in some cases the RITS complex can induce DNA methylation. As a result, gene expression can be silenced over long periods to lim ...
Moderately Repetitive Sequences Code for rRNA Structure and
... Eukaryotic Transcription & Translation are Compartmentalized ...
... Eukaryotic Transcription & Translation are Compartmentalized ...
Silencing unhealthy alleles naturally
... In C. elegans, one can introduce long dsRNAs by several different means to initiate RNAi. However, in most mammalian cells, long dsRNAs trigger the interferon response, which effectively shuts down all gene expression, making the specific targeting of a gene irrelevant. Two general methods for getti ...
... In C. elegans, one can introduce long dsRNAs by several different means to initiate RNAi. However, in most mammalian cells, long dsRNAs trigger the interferon response, which effectively shuts down all gene expression, making the specific targeting of a gene irrelevant. Two general methods for getti ...
Biology Ch 10 How Proteins are Made
... • DNA is unwound and unzipped at the site of the gene to be expressed (promoter) • RNA polymerase adds the complementary nucleotides to the exposed DNA nucleotides – Every three mRNA bases is called a codon ...
... • DNA is unwound and unzipped at the site of the gene to be expressed (promoter) • RNA polymerase adds the complementary nucleotides to the exposed DNA nucleotides – Every three mRNA bases is called a codon ...
Chapter 17 - Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
... 5. Regulation of RNA processing, RNA stability, and translation a. Alternative splicing regulates which exons occur in an RNA transcript, allowing different polypeptides to be made from the same structural gene b. The stability of mRNA influences mRNA concentration c. Double-stranded RNA can silence ...
... 5. Regulation of RNA processing, RNA stability, and translation a. Alternative splicing regulates which exons occur in an RNA transcript, allowing different polypeptides to be made from the same structural gene b. The stability of mRNA influences mRNA concentration c. Double-stranded RNA can silence ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.