Gene Section ATF1 (activating transcription factor 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537-42 ...
... encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537-42 ...
Feb 26
... 5’-TATAAT-3’ determines exact start site: bound by s factor 2)” -35 region” : 5’-TTGACA-3’ : bound by s factor 3) UP element : -57: bound by a factor ...
... 5’-TATAAT-3’ determines exact start site: bound by s factor 2)” -35 region” : 5’-TTGACA-3’ : bound by s factor 3) UP element : -57: bound by a factor ...
Biological networks and network motifs
... Cells need to react to their environment Reaction is by synthesizing task-specific proteins, on demand. The solution – regulated transcription network ...
... Cells need to react to their environment Reaction is by synthesizing task-specific proteins, on demand. The solution – regulated transcription network ...
Chapter 17- Transcription and Translation
... 1) Complete the following table by filling in the appropriate description of each property associated with prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes. Property Prokaryote Size of Genome (large or small) ...
... 1) Complete the following table by filling in the appropriate description of each property associated with prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes. Property Prokaryote Size of Genome (large or small) ...
4.7.08 105 lecture
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase promoter – the genetic information in the DNA that tells where, when, and how much the gene should be expressed. ------------------------------coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the codi ...
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase promoter – the genetic information in the DNA that tells where, when, and how much the gene should be expressed. ------------------------------coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the codi ...
DNA Control Mechanisms
... D. Heterochromatin - This refers to DNA that remains condensed even during interphase. – It is NOT active. 1. This CANNOT do transcription so it is inactivated. (“hetero” means “different”) E. Euchromatin - This refers to DNA that IS loose during interphase. – It IS active. 1. It CAN do transcriptio ...
... D. Heterochromatin - This refers to DNA that remains condensed even during interphase. – It is NOT active. 1. This CANNOT do transcription so it is inactivated. (“hetero” means “different”) E. Euchromatin - This refers to DNA that IS loose during interphase. – It IS active. 1. It CAN do transcriptio ...
Problem 3: Why do pre-mRNAs get smaller during RNA processing?
... The primary RNA transcript of the chicken ovalbumin gene is 7700 nucleotides long, but the mature mRNA that is translated on the ribosome is 1872 nucleotides long. This size difference occurs primarily as a result of: A. capping B. cleavage of polycistronic mRNA C. removal of poly A tails D. reverse ...
... The primary RNA transcript of the chicken ovalbumin gene is 7700 nucleotides long, but the mature mRNA that is translated on the ribosome is 1872 nucleotides long. This size difference occurs primarily as a result of: A. capping B. cleavage of polycistronic mRNA C. removal of poly A tails D. reverse ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
... The left half of the figure represents the state of several proteins and mRNAs under normal conditions, the right half shows the activation of the UPR in response to an overload of the ER with unfolded or malfolded proteins. Under normal conditions the three effector proteins of the UPR (PERK, IRE1 ...
... The left half of the figure represents the state of several proteins and mRNAs under normal conditions, the right half shows the activation of the UPR in response to an overload of the ER with unfolded or malfolded proteins. Under normal conditions the three effector proteins of the UPR (PERK, IRE1 ...
401Lecture6Sp2013post
... expression in vivo? One method: transgenic mouse Introduce “reporter gene” controlled by potential regulatory elements into a mouse transgenic mouse animation Distinct from reporter gene assay which is performed in cell culture ...
... expression in vivo? One method: transgenic mouse Introduce “reporter gene” controlled by potential regulatory elements into a mouse transgenic mouse animation Distinct from reporter gene assay which is performed in cell culture ...
Document
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
Gene Section TFE3 (transcription factor E3) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Online updated version : http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Genes/TFE3ID86.html ...
... Online updated version : http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Genes/TFE3ID86.html ...
Section 7.2: Transcription: DNA
... 3. (a) The role of the promoter in transcription is to prepare a site where RNA polymerase can access and bind to the DNA strand. (b) The role of RNA polymerase is to read the DNA code and create a complementary RNA molecule. (c) The role of spliceosomes is to take part in eukaryotic post-transcript ...
... 3. (a) The role of the promoter in transcription is to prepare a site where RNA polymerase can access and bind to the DNA strand. (b) The role of RNA polymerase is to read the DNA code and create a complementary RNA molecule. (c) The role of spliceosomes is to take part in eukaryotic post-transcript ...
Aim: What is positive feedback of bacterial operons?
... pathways, digesting nutrients to simpler molecules. (lactose metabolism). Both repressible and inducible operons demonstrate negative control because active repressors can only have negative effects on transcription. ...
... pathways, digesting nutrients to simpler molecules. (lactose metabolism). Both repressible and inducible operons demonstrate negative control because active repressors can only have negative effects on transcription. ...
GENE EXPRESSION CHAPTER 11
... known commonly for their illegal use by athletes, anabolic steroids are used medically to treat growth abnormalities, anemia, leukemia, kidney failure, and other medical problems. ...
... known commonly for their illegal use by athletes, anabolic steroids are used medically to treat growth abnormalities, anemia, leukemia, kidney failure, and other medical problems. ...
Lecture slides
... After a receptor notices a change: 1. Cascade message to nucleus 2. Open chromatin & bind transcription factors 3. Recruit RNA polymerase and transcribe 4. Splice mRNA and send to cytoplasm ...
... After a receptor notices a change: 1. Cascade message to nucleus 2. Open chromatin & bind transcription factors 3. Recruit RNA polymerase and transcribe 4. Splice mRNA and send to cytoplasm ...
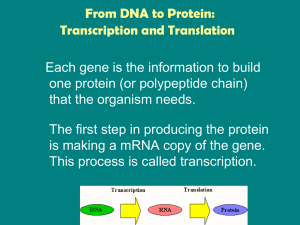
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation
... • mRNA has the nitrogen base uracil instead of thymine. ...
... • mRNA has the nitrogen base uracil instead of thymine. ...
Bio 313 worksheet 14 - Iowa State University
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
Cellular Control miniQUIZ
... b) Are plant homeobox genes homologous to the homeobox genes in the fruit fly? 17. Apoptosis is important during development. Define the meaning of apoptosis and give an example. ...
... b) Are plant homeobox genes homologous to the homeobox genes in the fruit fly? 17. Apoptosis is important during development. Define the meaning of apoptosis and give an example. ...
Using bioinformatics for better understanding of genes amplify
... How this project using DOGMA will help me teaching my genetics course The next time I teach the part of genomes and proteomes in my genetics course, in the explanation of comparative genomics, I can show similarities between different genomes and introduce them the evolutionary relationships betwee ...
... How this project using DOGMA will help me teaching my genetics course The next time I teach the part of genomes and proteomes in my genetics course, in the explanation of comparative genomics, I can show similarities between different genomes and introduce them the evolutionary relationships betwee ...
Objectives 7 - u.arizona.edu
... 2) Distinguish the differences between a promoter, a response element, and an enhancer. Promoters are the sites where RNA polymerase must bind to the DNA in order to initiate transcription. Response elements are DNA sequences that coordinately regulate the expression of groups of genes and are locat ...
... 2) Distinguish the differences between a promoter, a response element, and an enhancer. Promoters are the sites where RNA polymerase must bind to the DNA in order to initiate transcription. Response elements are DNA sequences that coordinately regulate the expression of groups of genes and are locat ...
Control of Gene Expression Control of Gene Expression Regulatory
... • Control of transcription initiation can be: – positive control – increases transcription when activators bind DNA – negative control – reduces transcription when repressors bind to DNA regulatory regions ...
... • Control of transcription initiation can be: – positive control – increases transcription when activators bind DNA – negative control – reduces transcription when repressors bind to DNA regulatory regions ...
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor (sometimes called a sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA. Transcription factors perform this function alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA polymerase (the enzyme that performs the transcription of genetic information from DNA to RNA) to specific genes.A defining feature of transcription factors is that they contain one or more DNA-binding domains (DBDs), which attach to specific sequences of DNA adjacent to the genes that they regulate. Additional proteins such as coactivators, chromatin remodelers, histone acetylases, deacetylases, kinases, and methylases, while also playing crucial roles in gene regulation, lack DNA-binding domains, and, therefore, are not classified as transcription factors.