Determining the Transcription Factor Genes Populating a Fruit Fly
... metabolism have been identified (Wittkopp et al., 2003). The enzymes encoded by two genes have been identified as being necessary in forming black tergite pigmentation. The gene yellow is necessary to produce the black melanin pigment, most noticeably seen in the A5 and A6 segments of Drosophila mel ...
... metabolism have been identified (Wittkopp et al., 2003). The enzymes encoded by two genes have been identified as being necessary in forming black tergite pigmentation. The gene yellow is necessary to produce the black melanin pigment, most noticeably seen in the A5 and A6 segments of Drosophila mel ...
A computational approach to map nucleosome positions and
... ends of the nucleosome when averaged over the genome and population. The biological variation at individual nucleosomes could generate large shifts in read midpoints due to length differences in nucleosomes (likely by multiples of 10 bp due to the unwrapping of each helical turn of DNA), and could b ...
... ends of the nucleosome when averaged over the genome and population. The biological variation at individual nucleosomes could generate large shifts in read midpoints due to length differences in nucleosomes (likely by multiples of 10 bp due to the unwrapping of each helical turn of DNA), and could b ...
Understanding the Regulation of Metabolic Enzyme Acetylation in E
... Global protein acetylation is a newly discovered phenomenon in bacteria. Of the more than 250 acetylations reported in E. coli, many are of metabolic enzymes [1-3]. Thus, acetylation could represent a novel posttranslational mechanism of metabolic control. Yet, almost nothing is known about the regu ...
... Global protein acetylation is a newly discovered phenomenon in bacteria. Of the more than 250 acetylations reported in E. coli, many are of metabolic enzymes [1-3]. Thus, acetylation could represent a novel posttranslational mechanism of metabolic control. Yet, almost nothing is known about the regu ...
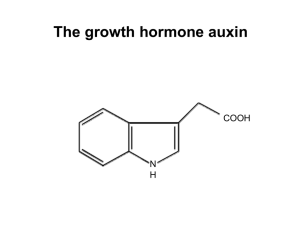
The growth hormone auxin
... The AUX/IAA genes • Transcription is rapidly induced by auxin • Independent of protein synthesis - primary response • Induced by cycloheximide • Unstable nuclear proteins • Large gene family (29 in Arabidopsis) AUX/IAA proteins probably serve as negative regulators ...
... The AUX/IAA genes • Transcription is rapidly induced by auxin • Independent of protein synthesis - primary response • Induced by cycloheximide • Unstable nuclear proteins • Large gene family (29 in Arabidopsis) AUX/IAA proteins probably serve as negative regulators ...
genetic variability, twin hybrids and constant hybrids, in a case of
... nal form. I n other words, there exists in beaded stack a sort of variation that is purely somatic, which is caused by external influences. Secondly, DEXTERfound that beaded is linked to pink eyes and to ebony body color, and a factor for beaded must therefore lie somewhere in the third chromosome, ...
... nal form. I n other words, there exists in beaded stack a sort of variation that is purely somatic, which is caused by external influences. Secondly, DEXTERfound that beaded is linked to pink eyes and to ebony body color, and a factor for beaded must therefore lie somewhere in the third chromosome, ...
Transvection Is Common Throughout the Drosophila
... integration of transgenes is becoming increasingly common, as it provides the opportunity to control for and minimize genomic position effects (Markstein et al. 2008; Pfeiffer et al. 2010). Given the use of multiple transgenes in many crossing schemes, it is common to use two transgenes that have be ...
... integration of transgenes is becoming increasingly common, as it provides the opportunity to control for and minimize genomic position effects (Markstein et al. 2008; Pfeiffer et al. 2010). Given the use of multiple transgenes in many crossing schemes, it is common to use two transgenes that have be ...
Genetic interactions between scribbler, Atrophin and
... presence and activity of specific regulatory transcription factors which bind in a sequencespecific manner to adjacent cis-regulatory elements. These regulatory transcription factors can act either as activators and promote transcription or as repressors and inhibit it. To function as repressors, th ...
... presence and activity of specific regulatory transcription factors which bind in a sequencespecific manner to adjacent cis-regulatory elements. These regulatory transcription factors can act either as activators and promote transcription or as repressors and inhibit it. To function as repressors, th ...
Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2 Transcription Factors in Heart
... are highly-regulated by signaling cascades that control MEF2’s function as a transcriptional switch. We highlight the many signaling pathways and kinases that regulate MEF2-HDAC interactions, MEF2 post-translational modification, and how these pathways influence MEF2 activity. We also discuss the ge ...
... are highly-regulated by signaling cascades that control MEF2’s function as a transcriptional switch. We highlight the many signaling pathways and kinases that regulate MEF2-HDAC interactions, MEF2 post-translational modification, and how these pathways influence MEF2 activity. We also discuss the ge ...
Gene Section ATF4 (activating transcription factor 4 (tax responsive enhancer element B67)) -
... is unstable and structured into several domains/motifs that are essential for ATF4 homo/heterodimerization, DNA binding, and the regulation of ATF4 at the protein stability level. The organization of the motifs modulating ATF4 protein stability is potentially essential for the regulation of ATF4 sta ...
... is unstable and structured into several domains/motifs that are essential for ATF4 homo/heterodimerization, DNA binding, and the regulation of ATF4 at the protein stability level. The organization of the motifs modulating ATF4 protein stability is potentially essential for the regulation of ATF4 sta ...
Identity elements in tRNA-mediated transcription
... and hence to the specificity and efficacy of the regulatory response. ...
... and hence to the specificity and efficacy of the regulatory response. ...
Identity elements in tRNA-mediated transcription
... and hence to the specificity and efficacy of the regulatory response. ...
... and hence to the specificity and efficacy of the regulatory response. ...
Factor IXHollywood
... this mutation. Churucferizof ion ofjucfor /X,,” protein. Approximately 5 mg of factor IX,,, protein was isolated from 5 L of the patient’s plasma. The results of SDS gel electrophoretic analysis of the purified factor IX,,, are shown in Fig I A . For comparison, SIX gels of factor IX, arc also depic ...
... this mutation. Churucferizof ion ofjucfor /X,,” protein. Approximately 5 mg of factor IX,,, protein was isolated from 5 L of the patient’s plasma. The results of SDS gel electrophoretic analysis of the purified factor IX,,, are shown in Fig I A . For comparison, SIX gels of factor IX, arc also depic ...
Perspectives in Diabetes Glucokinase Gene Structure
... site between the first and second exons of the hepatic glucokinase transcription unit (12,25). This finding indicated that the hepatic and p-cell glucokinase transcription units utilized different first exons and therefore also utilized different transcription control regions. Figure 1 illustrates t ...
... site between the first and second exons of the hepatic glucokinase transcription unit (12,25). This finding indicated that the hepatic and p-cell glucokinase transcription units utilized different first exons and therefore also utilized different transcription control regions. Figure 1 illustrates t ...
SPT4, a gene important for tr
... and spt6 null mutants, which are inviable, spt4 null mutants are viable and have an Spt- phenotype. The DNA sequence of the SPT4 gene predicts a protein product of 102 amino acids that contains four cysteine residues positioned similarly to those of zinc binding proteins. Mutational analysis suggest ...
... and spt6 null mutants, which are inviable, spt4 null mutants are viable and have an Spt- phenotype. The DNA sequence of the SPT4 gene predicts a protein product of 102 amino acids that contains four cysteine residues positioned similarly to those of zinc binding proteins. Mutational analysis suggest ...
709_2010_211_MOESM2_ESM - Springer Static Content Server
... pattern and is involved in vascular strand development in the leaf, control of leaf shape, size and symmetry, male gametophyte development and ovule specification and function. Anthers of double mutants (bam1bam2) appeared abnormal at a very early stage and lack the endothecium, middle, and tapetum ...
... pattern and is involved in vascular strand development in the leaf, control of leaf shape, size and symmetry, male gametophyte development and ovule specification and function. Anthers of double mutants (bam1bam2) appeared abnormal at a very early stage and lack the endothecium, middle, and tapetum ...
Cold-induced silencing by long antisense transcripts of an
... treatments, but change independently in cold-treated plants. Prolonged cold epigenetically silences FLC in a Polycombmediated process called vernalization2. Our data indicate that upregulation of long non-coding antisense transcripts covering the entire FLC locus may be part of the cold-sensing mech ...
... treatments, but change independently in cold-treated plants. Prolonged cold epigenetically silences FLC in a Polycombmediated process called vernalization2. Our data indicate that upregulation of long non-coding antisense transcripts covering the entire FLC locus may be part of the cold-sensing mech ...
+ΔFosB
... - Nave is the mean N value for the control - Ctave is the mean Ct value for the control. - Fold differences (stress ChIP relative to control ChIP) were then determined by raising 2 to the Ct power. Input : One hundred microliters of the pre-immunoprecipitated lysate Control ChIP : samples were immun ...
... - Nave is the mean N value for the control - Ctave is the mean Ct value for the control. - Fold differences (stress ChIP relative to control ChIP) were then determined by raising 2 to the Ct power. Input : One hundred microliters of the pre-immunoprecipitated lysate Control ChIP : samples were immun ...
View PDF - OSU Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
... required for appendage formation, encodes a homeobox transcription factor and is one of the high-level executives regulated by Hox proteins. The area of Dll expression in the embryo (shown as grey patches) corresponds to sites where in the course of development imaginal discs and, subsequently, appe ...
... required for appendage formation, encodes a homeobox transcription factor and is one of the high-level executives regulated by Hox proteins. The area of Dll expression in the embryo (shown as grey patches) corresponds to sites where in the course of development imaginal discs and, subsequently, appe ...
Genome Biology - Department of Computer Science and
... hierarchy, and in a number of additional features, indicating possible differences in their transcriptional regulation mechanisms. ...
... hierarchy, and in a number of additional features, indicating possible differences in their transcriptional regulation mechanisms. ...
RNA PCR Kit (AMV)
... change the annealing temperature (55 - 65℃) depending on the targets. It may be necessary to determine the optimal annealing temperature experimentally in the range of 45 - 65℃. ・Extension time The extension time depends on the target length. Usually, TaKaRa Ex Taq HS extends DNA at 1 kb per minute ...
... change the annealing temperature (55 - 65℃) depending on the targets. It may be necessary to determine the optimal annealing temperature experimentally in the range of 45 - 65℃. ・Extension time The extension time depends on the target length. Usually, TaKaRa Ex Taq HS extends DNA at 1 kb per minute ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... proteins encoded by these related genes and MITF can form stable dimeric combinations among each other but not with other bHLH-LZ or bHLH proteins (34,35), and, together, constitute the MITF-TFE subfamily of bHLH-LZ proteins (35). In both mouse and humans, Mitf transcription is initiated from at lea ...
... proteins encoded by these related genes and MITF can form stable dimeric combinations among each other but not with other bHLH-LZ or bHLH proteins (34,35), and, together, constitute the MITF-TFE subfamily of bHLH-LZ proteins (35). In both mouse and humans, Mitf transcription is initiated from at lea ...
ARTICLES - Weizmann Institute of Science
... nucleosomes and move them to new locations whenever needed. Another view, however, is that remodelling factors do not themselves ...
... nucleosomes and move them to new locations whenever needed. Another view, however, is that remodelling factors do not themselves ...
Cormack et al, 1991 Cell
... not the divergent N-terminal regions. The N-terminal region Is unimportant for the essential function(s) of yeast TFIID because expression of the core domain permits eff icient cell growth. Analysis of yeast-human hybrid TFllDs indicates that several regions within the conserved core account for the ...
... not the divergent N-terminal regions. The N-terminal region Is unimportant for the essential function(s) of yeast TFIID because expression of the core domain permits eff icient cell growth. Analysis of yeast-human hybrid TFllDs indicates that several regions within the conserved core account for the ...
Isolation and characterization of an RNA that binds with high affinity
... Since the Tat protein has various functions in the life cycle of HIV-1, as well as in viral proliferation, it is an important and attractive target in efforts to develop weapons against HIV. Several genetic strategies have been tested, in the past, in attempts to repress the proliferation of HIV. Tr ...
... Since the Tat protein has various functions in the life cycle of HIV-1, as well as in viral proliferation, it is an important and attractive target in efforts to develop weapons against HIV. Several genetic strategies have been tested, in the past, in attempts to repress the proliferation of HIV. Tr ...
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor (sometimes called a sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA. Transcription factors perform this function alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA polymerase (the enzyme that performs the transcription of genetic information from DNA to RNA) to specific genes.A defining feature of transcription factors is that they contain one or more DNA-binding domains (DBDs), which attach to specific sequences of DNA adjacent to the genes that they regulate. Additional proteins such as coactivators, chromatin remodelers, histone acetylases, deacetylases, kinases, and methylases, while also playing crucial roles in gene regulation, lack DNA-binding domains, and, therefore, are not classified as transcription factors.