Biology - The Roblesite
... 20. Additionally a _____ _______ and a tail are added to opposite ends of the mRNA piece. (Know what these two end sections do.) ...
... 20. Additionally a _____ _______ and a tail are added to opposite ends of the mRNA piece. (Know what these two end sections do.) ...
Protein Synthesis (Translation)
... mRNA is a message that codes for a protein Proteins are made in the cytoplasm and then work to keep the cell alive Translation (protein synthesis): Process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
... mRNA is a message that codes for a protein Proteins are made in the cytoplasm and then work to keep the cell alive Translation (protein synthesis): Process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
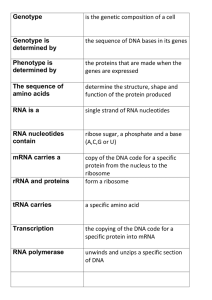
The sequence of amino acids
... copy of the DNA code for a specific protein from the nucleus to the ...
... copy of the DNA code for a specific protein from the nucleus to the ...
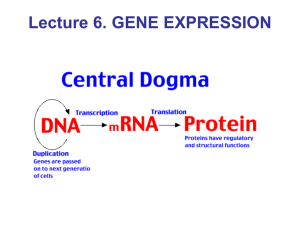
DNA -> RNA -> Proteins
... molecules, it does not travel well, so when it wants to make a protein it makes and mRNA copy of the instructions ...
... molecules, it does not travel well, so when it wants to make a protein it makes and mRNA copy of the instructions ...
Gene Expression Jeopardy
... What is the difference in premRNA and mRNS Pre-mRNA includes the introns ...
... What is the difference in premRNA and mRNS Pre-mRNA includes the introns ...
Genes and How they work!
... forming a 5’ cap. Protects end from degradation by nucleases and phosphotases. • 3’ end contain AAUAAA, poly A polymerase adds about 250 A’s to 3’ end long A tail. Needed to prevent degradation. ...
... forming a 5’ cap. Protects end from degradation by nucleases and phosphotases. • 3’ end contain AAUAAA, poly A polymerase adds about 250 A’s to 3’ end long A tail. Needed to prevent degradation. ...
How do we get proteins? - Sebastian Charter Junior High
... Ribosomal RNA= ribosome that reads the mRNA Transfer RNA= transfers the amino acid from the code ...
... Ribosomal RNA= ribosome that reads the mRNA Transfer RNA= transfers the amino acid from the code ...
Protein Synthesis - Beaver Local High School
... tRNA and Anticodons Anticodon- a region of tRNA consisting of three bases complementary to the codon of mRNA Amino acids floating freely in the cytosol are transported to the ribosomes by tRNA ...
... tRNA and Anticodons Anticodon- a region of tRNA consisting of three bases complementary to the codon of mRNA Amino acids floating freely in the cytosol are transported to the ribosomes by tRNA ...
DNA Function II - Complete Vocab with
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
4TH 6 WEEKS EXAM REVIEW!
... “B” is pointing to the first 3 bases of ________, which is the _________ codon. ...
... “B” is pointing to the first 3 bases of ________, which is the _________ codon. ...
TRANSCRIPTION TRANSLATION
... by mRNA is called translation. Involves: (i) charging of the tRNA with the specific amino acids and (ii) synthesis of polypeptide chain by the ribosomes. ...
... by mRNA is called translation. Involves: (i) charging of the tRNA with the specific amino acids and (ii) synthesis of polypeptide chain by the ribosomes. ...
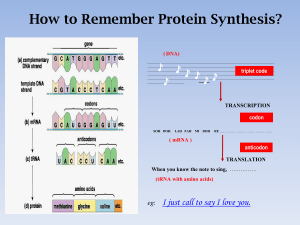
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
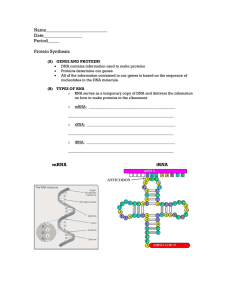
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... Protein Synthesis (A) GENES AND PROTEINS DNA contains information used to make proteins ...
... Protein Synthesis (A) GENES AND PROTEINS DNA contains information used to make proteins ...
Transcription/Translation foldable
... DNA and making mRNA. • Location? Nucleus • Why? DNA cannot leave the nucleus, so the messenger RNA has to take the nucleotide sequence to the ribosome to make proteins. Cut out the picture below. Label and color the DNA blue and the mRNA red. ...
... DNA and making mRNA. • Location? Nucleus • Why? DNA cannot leave the nucleus, so the messenger RNA has to take the nucleotide sequence to the ribosome to make proteins. Cut out the picture below. Label and color the DNA blue and the mRNA red. ...
CentralDogmaNotes
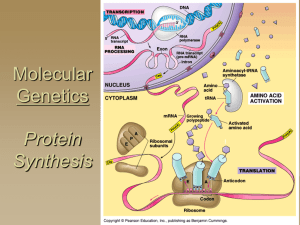
... • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation ...
... • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations Review Sheet 2014
... Protein Synthesis and Mutations Review Sheet Directions: Write the answers to each of the questions on a separate sheet of paper or flash cards. For the terms, either use them in your answers or separately define or describe their relation to the concepts of protein synthesis or mutations. Protein S ...
... Protein Synthesis and Mutations Review Sheet Directions: Write the answers to each of the questions on a separate sheet of paper or flash cards. For the terms, either use them in your answers or separately define or describe their relation to the concepts of protein synthesis or mutations. Protein S ...
2. Where does translation take place
... 5. What is the role of ribosomes in protein production? 6. Below you’ll be given an mRNA codon. Write down the tRNA anticodon and the corresponding amino acid that the codon codes for. You will need the handout Genetic Code. mRNA codon tRNA anticodon Amino acid (AA) UAC CGU AUG UUC AAA AUU AAC CCA ...
... 5. What is the role of ribosomes in protein production? 6. Below you’ll be given an mRNA codon. Write down the tRNA anticodon and the corresponding amino acid that the codon codes for. You will need the handout Genetic Code. mRNA codon tRNA anticodon Amino acid (AA) UAC CGU AUG UUC AAA AUU AAC CCA ...
Biology Ch 10 How Proteins are Made
... • Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules deliver the proper amino acids to the ribosome • Each codon codes for a specific amino acid • tRNA molecules have an anti-codon that matches the codon • The delivered AA attaches to the chain adding to the polymer (protein) ...
... • Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules deliver the proper amino acids to the ribosome • Each codon codes for a specific amino acid • tRNA molecules have an anti-codon that matches the codon • The delivered AA attaches to the chain adding to the polymer (protein) ...
Chapter 10 Protein Synthesis Test Study Guide THERE WILL BE 21
... What is the relationship between a cell, DNA and protein? Explain. (p. 204) List the three types of RNA and their functions. (p. 205) List the four ways RNA differs from DNA. (p. 205) In RNA, the base adenine is complementary to the base ______________. (p. 205) How are DNA replication and transcrip ...
... What is the relationship between a cell, DNA and protein? Explain. (p. 204) List the three types of RNA and their functions. (p. 205) List the four ways RNA differs from DNA. (p. 205) In RNA, the base adenine is complementary to the base ______________. (p. 205) How are DNA replication and transcrip ...
LEARNING GOALS - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Main Idea
... 1. The enzyme RNA-polymerase reads the DNA molecule in the 3’ to 5’ direction and synthesizes complementary mRNA molecules that determine the order of amino acids in the polypeptide. 2. In eukaryotic cells the mRNA transcript undergoes a series of enzymeregulated modifications. Examples include o Ad ...
... 1. The enzyme RNA-polymerase reads the DNA molecule in the 3’ to 5’ direction and synthesizes complementary mRNA molecules that determine the order of amino acids in the polypeptide. 2. In eukaryotic cells the mRNA transcript undergoes a series of enzymeregulated modifications. Examples include o Ad ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.