PROTEIN SYNTHESIS - Gull Lake Community Schools / Overview
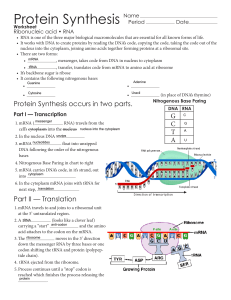
... of the DNA strand ….breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the nitrogenous bases together (the “steps” of the ladder) at the promoter site. Unattached RNA (free) nucleotides bind to their complimentary bases on the DNA strand to form a molecule of mRNA (messenger RNA); RNA polymerase works like a “train ...
... of the DNA strand ….breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the nitrogenous bases together (the “steps” of the ladder) at the promoter site. Unattached RNA (free) nucleotides bind to their complimentary bases on the DNA strand to form a molecule of mRNA (messenger RNA); RNA polymerase works like a “train ...
Proteins
... hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase ...
... hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase ...
TRANSLATION NOTES - Randolph High School
... The ribosome has 2 slots for tRNAs to fit into tRNAs come in and their anticodon pairs complementary to the codon on the mRNA The amino acids (carried on the top of the tRNA) bond together and start forming a protein Everything shifts over one slot and a new tRNA comes in – this continues until a st ...
... The ribosome has 2 slots for tRNAs to fit into tRNAs come in and their anticodon pairs complementary to the codon on the mRNA The amino acids (carried on the top of the tRNA) bond together and start forming a protein Everything shifts over one slot and a new tRNA comes in – this continues until a st ...
DNA to Protein - Seabreeze High School
... Things to think About & Discuss 1. What if a mutation occurs in the DNA? Explain how could that affect the organism’s protein? 2. What if a mutation occurs in 3rd base of the codon? Will it always code for a different amino acid? Explain. ...
... Things to think About & Discuss 1. What if a mutation occurs in the DNA? Explain how could that affect the organism’s protein? 2. What if a mutation occurs in 3rd base of the codon? Will it always code for a different amino acid? Explain. ...
A20-Protein Synthesis
... reads it 3 bases at a time, and matches these with bases on tRNA attached to an amino acid. An amino acid chain is formed from many peptide bonds. ...
... reads it 3 bases at a time, and matches these with bases on tRNA attached to an amino acid. An amino acid chain is formed from many peptide bonds. ...
Chapter 17 Power Point
... • Allows for different combinations of exons • This results in more than one protein per gene • This explains why we have fewer genes in our genome than what was expected • The human genome contains about 21,000 protein-encoding genes, but the total number of proteins in human cells is estimated to ...
... • Allows for different combinations of exons • This results in more than one protein per gene • This explains why we have fewer genes in our genome than what was expected • The human genome contains about 21,000 protein-encoding genes, but the total number of proteins in human cells is estimated to ...
Protein Synthesis - Issaquah Connect
... 4. Nitrogenous Base Paring in chart to right 5. mRNA carries DNA’s code, in it’s strand, out into cytoplasm 6. In the cytoplasm mRNA joins with tRNA for next step, translation ...
... 4. Nitrogenous Base Paring in chart to right 5. mRNA carries DNA’s code, in it’s strand, out into cytoplasm 6. In the cytoplasm mRNA joins with tRNA for next step, translation ...
The DNA Song
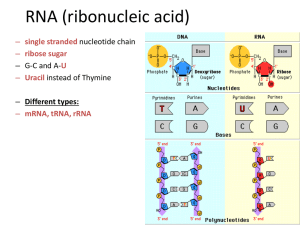
... made of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of 4 bases: cytosine, guanine, thymine, and adenine. These nucleotides link together by covalent (strong) bonds between the sugars and phosphate groups to form strands. Two of the strands link together at the bases with hydrogen (weak) bonds. ...
... made of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of 4 bases: cytosine, guanine, thymine, and adenine. These nucleotides link together by covalent (strong) bonds between the sugars and phosphate groups to form strands. Two of the strands link together at the bases with hydrogen (weak) bonds. ...
Name Class ______ Date ______ The Genetic Code 1. Genetic
... Name _____________________________ Class __________ Date __________ 9. A researcher identifies the nucleotide sequence AAC in a long strand of RNA inside a nucleus. In the genetic code, AAC codes for the amino acid asparagine. When the RNA becomes involved in protein synthesis, will asparagines nec ...
... Name _____________________________ Class __________ Date __________ 9. A researcher identifies the nucleotide sequence AAC in a long strand of RNA inside a nucleus. In the genetic code, AAC codes for the amino acid asparagine. When the RNA becomes involved in protein synthesis, will asparagines nec ...
protein synthesis - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... During transcription, the DNA double helix “unzips”. As the hydrogen bonds between the two strands break, nucleotides floating in the nucleus line up next to the nucleotides of one DNA strand (“master strand”) to form mRNA. (Remember that uracil replaces thymine in the RNA formation; therefore, urac ...
... During transcription, the DNA double helix “unzips”. As the hydrogen bonds between the two strands break, nucleotides floating in the nucleus line up next to the nucleotides of one DNA strand (“master strand”) to form mRNA. (Remember that uracil replaces thymine in the RNA formation; therefore, urac ...
RNA-Unit 6 cont.
... 61 code for amino acids (20 possibilities) 1 codes to start = AUG = methionine ...
... 61 code for amino acids (20 possibilities) 1 codes to start = AUG = methionine ...
Central Dogma PPT
... • Code for ALL life! • Code is redundant – several codons for each amino acid ...
... • Code for ALL life! • Code is redundant – several codons for each amino acid ...
Biology: Protein Synthesis, Extra Credit Name: Place these
... Place these events in the correct order defining protein synthesis. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. ...
... Place these events in the correct order defining protein synthesis. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. ...
2009 WH Freeman and Company
... Eukaryotic cells contain far more DNA than is required to encode proteins. Nuclear RNAs undergo some type of change before they are exported to the cytoplasm. Regions of DNA might not be transcribed. ...
... Eukaryotic cells contain far more DNA than is required to encode proteins. Nuclear RNAs undergo some type of change before they are exported to the cytoplasm. Regions of DNA might not be transcribed. ...
BIO 103 - Genes
... specifies a particular amino acid (64 possible codons) stop codons: (UUA, UGA, UAG) used to terminate translation start codon: (AUG) used to start translation ...
... specifies a particular amino acid (64 possible codons) stop codons: (UUA, UGA, UAG) used to terminate translation start codon: (AUG) used to start translation ...
Transcription_12_Teacher
... and the passage of mRNA into the cytoplasm Genes may play roles in multiple proteins, introns may enable a gene to be diverse in function May increase recombination of genetic material (easier to cut and paste) ...
... and the passage of mRNA into the cytoplasm Genes may play roles in multiple proteins, introns may enable a gene to be diverse in function May increase recombination of genetic material (easier to cut and paste) ...
CENTRAL DOGMA AND GENE REGULATION
... 1. Transcription :: the information on DNA is copied onto a length of mRNA (DNA mRNA) 2. Translation ; the polypeptide chain is formed (RNA protein) Transcription occurs in the nucleus. The transfer of information from DNA to RNA is through complimentary base pairing. Transcription uses the enzyme ...
... 1. Transcription :: the information on DNA is copied onto a length of mRNA (DNA mRNA) 2. Translation ; the polypeptide chain is formed (RNA protein) Transcription occurs in the nucleus. The transfer of information from DNA to RNA is through complimentary base pairing. Transcription uses the enzyme ...
Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... Nitrogen Base: A,C,G,Uracil (instead of thymine) Single stranded (vs. DNA double stranded) ...
... Nitrogen Base: A,C,G,Uracil (instead of thymine) Single stranded (vs. DNA double stranded) ...
File - Mrs. Badger`s Honors Biology Class
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes f ...
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes f ...
Protein Synthesis – Level 1
... 3. What anticodons will the tRNAs have for this mRNA? (Remember, there is no tRNA anticodon for a stop codon) ...
... 3. What anticodons will the tRNAs have for this mRNA? (Remember, there is no tRNA anticodon for a stop codon) ...
Genetics Practice Questions C 1. Describe transcription
... than one amino acid, the proper sequence of amino acids by which a protein is made could not be created. ・Redundance・・・・Most amino acids are encoded by more than one codon. This is important because even if one of the four bases is in short supply, the letters still have the possibility to make the ...
... than one amino acid, the proper sequence of amino acids by which a protein is made could not be created. ・Redundance・・・・Most amino acids are encoded by more than one codon. This is important because even if one of the four bases is in short supply, the letters still have the possibility to make the ...
DNA Transcription
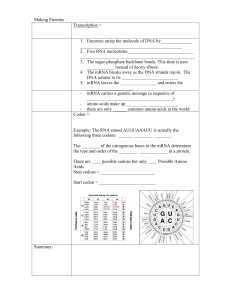
... The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA attaches to the ________________. 2. A ___________ molecule brings the first amino acid to the mRNA strand that is ...
... The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA attaches to the ________________. 2. A ___________ molecule brings the first amino acid to the mRNA strand that is ...
MS Word worksheet
... Be able to use the codon table to construct the genetic code for a polypeptide chain (assuming you are given the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide). ...
... Be able to use the codon table to construct the genetic code for a polypeptide chain (assuming you are given the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide). ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.