Protein Synthesis Is a Major Function of Cells
... sequence of a gene into a mRNA transcript • Takes place in the nucleus 2. Translation is the process of copying the mRNA transcript into a sequence of amino acids which will eventually become a protein • The mRNA than moves to a ribosome, either attached or free • Free ribosomes are found in the cel ...
... sequence of a gene into a mRNA transcript • Takes place in the nucleus 2. Translation is the process of copying the mRNA transcript into a sequence of amino acids which will eventually become a protein • The mRNA than moves to a ribosome, either attached or free • Free ribosomes are found in the cel ...
DNA to Protein Synthesis
... DNA must be copied to messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA goes from nucleus to the ribosomes in cytoplasm mRNA complements known as codons ...
... DNA must be copied to messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA goes from nucleus to the ribosomes in cytoplasm mRNA complements known as codons ...
Protein Synthesis - Madison County Schools
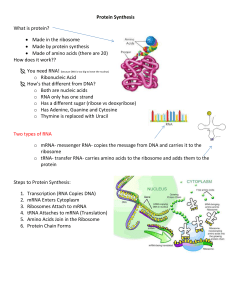
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
DNA WebQuest NAME
... A. Go to: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP1302 Read the animation page by page – just click the “next” button when you are ready to move on. ...
... A. Go to: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP1302 Read the animation page by page – just click the “next” button when you are ready to move on. ...
Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
... Ribosome– The “workbench” where translation takes place. Catalyzes the formation of __________ bonds between amino acids to form the polypeptide chain. Made of ________ and rRNA. ...
... Ribosome– The “workbench” where translation takes place. Catalyzes the formation of __________ bonds between amino acids to form the polypeptide chain. Made of ________ and rRNA. ...
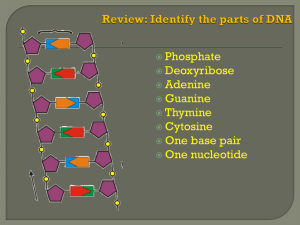
DNA
... • Why: DNA can’t leave the nucleus but the message must get to the ribosome • You are now using U’s no T’s. • RNA polymerase – Enzyme that brings in RNA nucleotides to match up with DNA ...
... • Why: DNA can’t leave the nucleus but the message must get to the ribosome • You are now using U’s no T’s. • RNA polymerase – Enzyme that brings in RNA nucleotides to match up with DNA ...
DNA - Transcription & Translation
... complementary base pairs with the tRNA anticodon The ribosome moves from codon to codon along the mRNA. Amino acids are added one by one ...
... complementary base pairs with the tRNA anticodon The ribosome moves from codon to codon along the mRNA. Amino acids are added one by one ...
Chapter 16 Quiz - Home - Union Academy Charter School
... b. Genetic codes based on sequences of bases c. A nitrogenous base known as uracil d. Double-stranded polymers ...
... b. Genetic codes based on sequences of bases c. A nitrogenous base known as uracil d. Double-stranded polymers ...
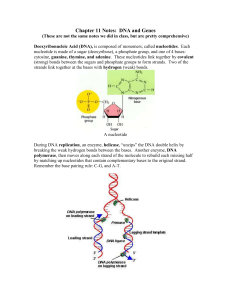
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
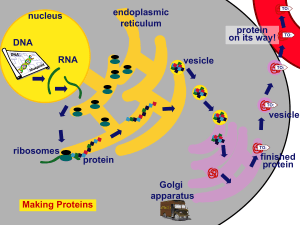
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
A Bioinformatics Tool for Analyzing G
... A hybrid of information sciences and biology Similar, but not the same as computational biology Enlists the help of databases and tools to analyze large masses of data to find patterns that are not easily discernable by the human eye ...
... A hybrid of information sciences and biology Similar, but not the same as computational biology Enlists the help of databases and tools to analyze large masses of data to find patterns that are not easily discernable by the human eye ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Transcription=part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence of RNA. 1. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to and unzips the DNA. It uses 1 strand as a template. 2. A single strand of mRNA is made. (U) replaces (T). 3. mRNA breaks off from the DNA, leaves the nucleus an ...
... Transcription=part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence of RNA. 1. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to and unzips the DNA. It uses 1 strand as a template. 2. A single strand of mRNA is made. (U) replaces (T). 3. mRNA breaks off from the DNA, leaves the nucleus an ...
sample genetic code exercises
... Given the following DNA sequences, derive the (a) complementary mRNA, and the (b) resulting protein: 1. 5’ TTTCATGCCCCGATAUGTACCC 3’ a. to derive the complementary RNA, we simply take note of the pairing rules (A with T/U, and C with G). Also, the DNA and RNA strands must be antiparallel (i.e. 5’ an ...
... Given the following DNA sequences, derive the (a) complementary mRNA, and the (b) resulting protein: 1. 5’ TTTCATGCCCCGATAUGTACCC 3’ a. to derive the complementary RNA, we simply take note of the pairing rules (A with T/U, and C with G). Also, the DNA and RNA strands must be antiparallel (i.e. 5’ an ...
Answers section 4
... portion of the promoter – this recruits the general transcription factors that bind to the basal promoter and recruit RNA polymerase; RNA polymerase synthesizes the mRNA - the first general transcription factor to bind is TBP, which recruits the remaining factors; this complex recruits RNA polymeras ...
... portion of the promoter – this recruits the general transcription factors that bind to the basal promoter and recruit RNA polymerase; RNA polymerase synthesizes the mRNA - the first general transcription factor to bind is TBP, which recruits the remaining factors; this complex recruits RNA polymeras ...
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics
... • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than one codon sequence. ...
... • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than one codon sequence. ...
PP-Protein Synthesis
... Proteins have MANY different functions Enzymes to help control/speed up chemical reactions Help to build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
... Proteins have MANY different functions Enzymes to help control/speed up chemical reactions Help to build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
Study Guide to Chapter 5 Ð DNA
... template to make a strand of ___________________ a) mRNA b) tRNA. This occurs in __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is called __________________ a) transcription b) translation. The molecule of ___________ ...
... template to make a strand of ___________________ a) mRNA b) tRNA. This occurs in __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is called __________________ a) transcription b) translation. The molecule of ___________ ...
second of Chapter 10: RNA processing
... molecules were larger than predicted, based on protein structure. • In 1977, internal, non-coding sequences were discovered. • These internal, non-coding sequences are called introns. ...
... molecules were larger than predicted, based on protein structure. • In 1977, internal, non-coding sequences were discovered. • These internal, non-coding sequences are called introns. ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... What Codes For A Protein? A. The genetic code allows for almost an infinite amount of different proteins. B. Every 3 bases of DNA (or mRNA) is referred to as a CODON. - Each codon codes for 1 amino acid. ...
... What Codes For A Protein? A. The genetic code allows for almost an infinite amount of different proteins. B. Every 3 bases of DNA (or mRNA) is referred to as a CODON. - Each codon codes for 1 amino acid. ...
Energy Unit SG Key
... The structure and function of a protein is determined by the order of the amino acids and their chemical properties. ...
... The structure and function of a protein is determined by the order of the amino acids and their chemical properties. ...
Translation
... In order for a cell to make a protein, DNA must be transcribed into ____________ and the mRNA must then be translated into _____________. The processes of transcription and translation together are called _________________________. The process of transcription occurs in the ____________ of a cell. T ...
... In order for a cell to make a protein, DNA must be transcribed into ____________ and the mRNA must then be translated into _____________. The processes of transcription and translation together are called _________________________. The process of transcription occurs in the ____________ of a cell. T ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.