BIOL 222 - philipdarrenjones.com
... 11) From the following list, which is the first event in translation in eukaryotes? A) elongation of the polypeptide B) base pairing of methionine-tRNA to AUG (start codon) of the messenger RNA C) the larger ribosomal subunit binds to smaller ribosomal subunits D) covalent bonding between the first ...
... 11) From the following list, which is the first event in translation in eukaryotes? A) elongation of the polypeptide B) base pairing of methionine-tRNA to AUG (start codon) of the messenger RNA C) the larger ribosomal subunit binds to smaller ribosomal subunits D) covalent bonding between the first ...
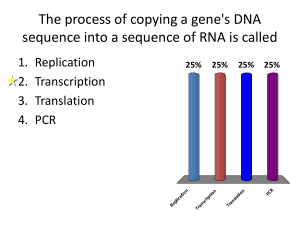
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... to both DNA replication and transcription? 1. Nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the newly ...
... to both DNA replication and transcription? 1. Nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the newly ...
aa + aa + aa + aa aa – aa – aa – aa
... (working) protein. The protein will not work unless it is folded up. 4. Most amino acids look exactly the same except for the _____ group or ________________ group. 5. There are _______ different functional groups that give each amino acid different properties. Forming a polypeptide 6. aa=__________ ...
... (working) protein. The protein will not work unless it is folded up. 4. Most amino acids look exactly the same except for the _____ group or ________________ group. 5. There are _______ different functional groups that give each amino acid different properties. Forming a polypeptide 6. aa=__________ ...
trp operon – a repressible system
... Gene regulation in eukaryotes is more complex than it is in prokaryotes because of: – the larger amount of DNA – the organization of chromatin – larger number of chromosomes – spatial separation of transcription and translation – mRNA processing – RNA stability – cellular differentiation in eukar ...
... Gene regulation in eukaryotes is more complex than it is in prokaryotes because of: – the larger amount of DNA – the organization of chromatin – larger number of chromosomes – spatial separation of transcription and translation – mRNA processing – RNA stability – cellular differentiation in eukar ...
Lab Instructions - Translation Please
... Purpose: To help students understand the role of DNA, mRNA, tRNA, and amino acids in the role of protein synthesis. This activity will also introduce the concept of mutations. Procedure: 1. You will be working in 3 person teams. 2. The teacher’s desk is the nucleus and the DNA templates cannot leave ...
... Purpose: To help students understand the role of DNA, mRNA, tRNA, and amino acids in the role of protein synthesis. This activity will also introduce the concept of mutations. Procedure: 1. You will be working in 3 person teams. 2. The teacher’s desk is the nucleus and the DNA templates cannot leave ...
Remember, transcription copies the DNA into mRNA
... This is an enzyme that attaches amino acids to tRNAs (that is how it uses the tRNA). ...
... This is an enzyme that attaches amino acids to tRNAs (that is how it uses the tRNA). ...
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
... Translation- cellular process that converts the mRNA codons into amino acids to build proteins. First let’s practice reading the mRNA into amino acids and then I will outline the process of how it’s done step by step. Look at the sequence of mRNA below and the chart in Fig. ___ on page _____. ...
... Translation- cellular process that converts the mRNA codons into amino acids to build proteins. First let’s practice reading the mRNA into amino acids and then I will outline the process of how it’s done step by step. Look at the sequence of mRNA below and the chart in Fig. ___ on page _____. ...
From Gene to Protein Protein Synthesis
... http://vcell.ndsu.edu/animations/transcription/movie.htm ...
... http://vcell.ndsu.edu/animations/transcription/movie.htm ...
Protein Synthesis
... Three Main Types of RNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) - Carries copies of instructions for the assembly of amino acids into proteins from DNA to the rest of the cell (serve as “messenger”) 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – Makes up the major part of ribosomes, which is where proteins are made. 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA ...
... Three Main Types of RNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) - Carries copies of instructions for the assembly of amino acids into proteins from DNA to the rest of the cell (serve as “messenger”) 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – Makes up the major part of ribosomes, which is where proteins are made. 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA ...
Slide 1
... How 24,000 genes in the human genome encode more than 100,000 proteins. How information flows through Transcription and Translation. 4 points of information control in the cell. Explain RNA splicing with respect to Exons and Introns. Explain the difference between a Haploid and a Diploid Cell. ...
... How 24,000 genes in the human genome encode more than 100,000 proteins. How information flows through Transcription and Translation. 4 points of information control in the cell. Explain RNA splicing with respect to Exons and Introns. Explain the difference between a Haploid and a Diploid Cell. ...
File
... RNA splicing – removal of introns so that only exons remain (exons = mRNA that exits nucleus (includes leader and trailer )) Roberts and Sharp 1977 RNA polymerase II transcribes whole transcription unit (DNA that is transcribed), but many nucleotides need to be spliced to form true mRNA from primary ...
... RNA splicing – removal of introns so that only exons remain (exons = mRNA that exits nucleus (includes leader and trailer )) Roberts and Sharp 1977 RNA polymerase II transcribes whole transcription unit (DNA that is transcribed), but many nucleotides need to be spliced to form true mRNA from primary ...
From Gene to Protein
... Stop codon sequence that signifies the end of a polypeptide chain Sequences are UAG, UAA, and UGA Don’t code for AA’s Polypeptide cleaved from last tRNA (P site) and leaves the ...
... Stop codon sequence that signifies the end of a polypeptide chain Sequences are UAG, UAA, and UGA Don’t code for AA’s Polypeptide cleaved from last tRNA (P site) and leaves the ...
Protein Synthesis - OpotikiCollegeBiology
... and proteins are built out of amino acids. • How does the chromosome alphabet get changed into structures that join up to make proteins? ...
... and proteins are built out of amino acids. • How does the chromosome alphabet get changed into structures that join up to make proteins? ...
Complete the blank spaces in the following chart:
... Part A: Circle the correct choice within the parenthesis for 1-8. 1. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucleus. 2. mRNA is made during (transcription/translation). 3. mRNA is made in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 4. DNA is located in the (nucleus/cytoplasm) 5. (Translation/Transcription) converts DNA into mRNA. 6. ...
... Part A: Circle the correct choice within the parenthesis for 1-8. 1. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucleus. 2. mRNA is made during (transcription/translation). 3. mRNA is made in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 4. DNA is located in the (nucleus/cytoplasm) 5. (Translation/Transcription) converts DNA into mRNA. 6. ...
Transcription and Translation Candy Activity
... Get your original DNA model or rebuild it using the pictures from the DNA structure and replication lab. Transcription is the process of copying the genetic information from DNA into a usable copy of mRNA. Make a model clearly indicating this process make sure to include in your model representation ...
... Get your original DNA model or rebuild it using the pictures from the DNA structure and replication lab. Transcription is the process of copying the genetic information from DNA into a usable copy of mRNA. Make a model clearly indicating this process make sure to include in your model representation ...
Transcrip_Translation
... 3. Send the copy out of the Nucleus to be read off of, so that proteins can be made ...
... 3. Send the copy out of the Nucleus to be read off of, so that proteins can be made ...
Topic 7 The Discovery of DNA & Its Roles
... cell is the ribosome Amino acids are carried to the growing ...
... cell is the ribosome Amino acids are carried to the growing ...
DNA to Protein Synthesis Internet Quest
... 7. Click and read slides 9 – 14. Using slide 14, illustrate how the mRNA molecule is “read” and used to build a polypeptide chain (protein) during translation. Label the following terms: ribosome, mRNA ...
... 7. Click and read slides 9 – 14. Using slide 14, illustrate how the mRNA molecule is “read” and used to build a polypeptide chain (protein) during translation. Label the following terms: ribosome, mRNA ...
Biology Topics, Venn diagrams
... • Start with one diploid cell and result in four haploid cells • Produces gametes • Cells produced are not identical • Two rounds to produce daughter cells • Homologs pair in prophase 1 ...
... • Start with one diploid cell and result in four haploid cells • Produces gametes • Cells produced are not identical • Two rounds to produce daughter cells • Homologs pair in prophase 1 ...
Gene Expression
... anitcodon UAC, will bind to AUG • The tRNA carries the animo acid specific to the mRNA sequence AUG, which is methionine ...
... anitcodon UAC, will bind to AUG • The tRNA carries the animo acid specific to the mRNA sequence AUG, which is methionine ...
Unit 7 Study Guide ANSWERS 2014
... 14. Generally, mutations that affect a single gene occur during cell replication (Meiosis and Mitosis) 15. Mutations that can affect the offspring of an organism occur in what cell type? Germ/Sex Cells 16. Give an example of a mutagen? UV light, radiation 17. Define gene. A segment of DNA that conta ...
... 14. Generally, mutations that affect a single gene occur during cell replication (Meiosis and Mitosis) 15. Mutations that can affect the offspring of an organism occur in what cell type? Germ/Sex Cells 16. Give an example of a mutagen? UV light, radiation 17. Define gene. A segment of DNA that conta ...
MTC19: transcription and gene expression 02/10/07
... A gene in transcription can be defined as a segment of DNA extending from the site of initiation to the site of termination Genes consist of exons (sequences to be subsequently translated into proteins) separated by introns, which can contain other control regions or even other genes to allow more c ...
... A gene in transcription can be defined as a segment of DNA extending from the site of initiation to the site of termination Genes consist of exons (sequences to be subsequently translated into proteins) separated by introns, which can contain other control regions or even other genes to allow more c ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.