GENES
... transcription)in which the introns are removed and the exons are joined. in coding segments exons are part of the 1.5% coding DNA, in non coding segments introns are part of the 98.5% non coding DNA. ...
... transcription)in which the introns are removed and the exons are joined. in coding segments exons are part of the 1.5% coding DNA, in non coding segments introns are part of the 98.5% non coding DNA. ...
From Gene to Protein
... •Called mRNA (messenger RNA) Translation – synthesis of polypeptide from the mRNA In prokaryotes, both happen at same time ...
... •Called mRNA (messenger RNA) Translation – synthesis of polypeptide from the mRNA In prokaryotes, both happen at same time ...
Protein Synthesis Word Scramble
... notebook What does translate mean? Read message and create new message! mRNA to Protein! (the whole goal of PROTEIN synthesis!) ...
... notebook What does translate mean? Read message and create new message! mRNA to Protein! (the whole goal of PROTEIN synthesis!) ...
Transcription andTranslation Flip Book
... enzyme RNA polymerase unzips the DNA molecule at the region of the gene that is being transcribed DNA 2. Free _____________ form base RNA nucleotides A pairs with their complementary T nucleotides on the DNA strand C DNA 3. mRNA threads away and the _____ G strand rejoins nucleus and goes 4. mRNA le ...
... enzyme RNA polymerase unzips the DNA molecule at the region of the gene that is being transcribed DNA 2. Free _____________ form base RNA nucleotides A pairs with their complementary T nucleotides on the DNA strand C DNA 3. mRNA threads away and the _____ G strand rejoins nucleus and goes 4. mRNA le ...
AQA A2 level Biology
... 1 Summarise the differences between protein synthesis in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Protein synthesis is more complex in eukaryotes than in prokaryotes. Eukaryotes must modify the mRNA made during transcription. It must have introns removed and be prepared for the cytoplasm so it does not break dow ...
... 1 Summarise the differences between protein synthesis in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Protein synthesis is more complex in eukaryotes than in prokaryotes. Eukaryotes must modify the mRNA made during transcription. It must have introns removed and be prepared for the cytoplasm so it does not break dow ...
BIOL 241 Nucleic Acids and Gene Expression I. Genes (Overview) A
... 1. come together in cytoplasm at protein-synthesis time 2. mRNA binds to small subunit via its leader sequence 3. small subunit binds to large 4. large subunit has enzymes for amino acid linkage C. Chaperonins 1. prevents premature folding of protein 2. may “escort” protein to destination VIII. Post ...
... 1. come together in cytoplasm at protein-synthesis time 2. mRNA binds to small subunit via its leader sequence 3. small subunit binds to large 4. large subunit has enzymes for amino acid linkage C. Chaperonins 1. prevents premature folding of protein 2. may “escort” protein to destination VIII. Post ...
Protein Synthesis
... 19. How many binding sites do ribosomes have? 20. One site holds the __________ transcript, while the other sites hold __________ with their attached amino acid. 21. Polypeptide formation begins when a ribosome attaches to what mRNA codon? 22. What amino acid does the start codon code for? 23. Amino ...
... 19. How many binding sites do ribosomes have? 20. One site holds the __________ transcript, while the other sites hold __________ with their attached amino acid. 21. Polypeptide formation begins when a ribosome attaches to what mRNA codon? 22. What amino acid does the start codon code for? 23. Amino ...
Chapter 17 - HCC Learning Web
... B) a triplet in the same reading frame as an upstream AUG C) a sequence in tRNA at the 3' end D) a triplet separated spatially from other triplets E) a triplet that has no corresponding amino acid 4) What is a ribozyme? 4) _______ A) an enzyme that synthesizes RNA primers during DNA replication B) a ...
... B) a triplet in the same reading frame as an upstream AUG C) a sequence in tRNA at the 3' end D) a triplet separated spatially from other triplets E) a triplet that has no corresponding amino acid 4) What is a ribozyme? 4) _______ A) an enzyme that synthesizes RNA primers during DNA replication B) a ...
Protein Synthesis
... Transcribe the following DNA strand to an RNA strand: DNA: T A C G G A G T G C T C G C A C G C G A T A C T mRNA: A U G C C U C A C G A G C G U G C G C U A U G A Codons and anticodons consist of 3 nucleotides. How many codons are on the above mRNA strand? 8 Now mRNA can take it’s copy of the DNA code ...
... Transcribe the following DNA strand to an RNA strand: DNA: T A C G G A G T G C T C G C A C G C G A T A C T mRNA: A U G C C U C A C G A G C G U G C G C U A U G A Codons and anticodons consist of 3 nucleotides. How many codons are on the above mRNA strand? 8 Now mRNA can take it’s copy of the DNA code ...
Transcription and Translation
... RNA that encodes information for the synthesis of proteins and carries it to a ribosome from the nucleus ...
... RNA that encodes information for the synthesis of proteins and carries it to a ribosome from the nucleus ...
Protein Synth Notes GO New
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
Part 2 - Latona
... 1. The final step in protein synthesis. a. A stop codon signals the finished polypeptide to be released. b. The polypeptide may or may not join with other chains, then it begins folding into its unique 3-D shape ...
... 1. The final step in protein synthesis. a. A stop codon signals the finished polypeptide to be released. b. The polypeptide may or may not join with other chains, then it begins folding into its unique 3-D shape ...
Select one of your Biology instructors from another class and look
... sequence of four ribonucleotides, all with equal frequency, what is the probability that any three adjacent nucleotides will be a start codon? A stop codon? In an mRNA molecule of random sequence, what is the average distance between stop codons? 8.2 If DNA consisted of only two nucleotides (say, A ...
... sequence of four ribonucleotides, all with equal frequency, what is the probability that any three adjacent nucleotides will be a start codon? A stop codon? In an mRNA molecule of random sequence, what is the average distance between stop codons? 8.2 If DNA consisted of only two nucleotides (say, A ...
From DNA to Protein
... A multistep process in which genetic information is converted into a structural or functional part of a cell or body ...
... A multistep process in which genetic information is converted into a structural or functional part of a cell or body ...
Chapter 3 Protein Synthesis Life Science RNA – Ribonucleic Acid
... How to determine which codon codes for which one of the 20 different amino acids: 1. Find the 1st base on the left side of the table. 2. The middle base is then located on the top of the table. Where they intersect determines the 4 possible outcomes. 3. Find the 3rd base on the right side of the tab ...
... How to determine which codon codes for which one of the 20 different amino acids: 1. Find the 1st base on the left side of the table. 2. The middle base is then located on the top of the table. Where they intersect determines the 4 possible outcomes. 3. Find the 3rd base on the right side of the tab ...
Central Dogma.pptx
... To make a protein (phenotype) the mRNA is translated with the help of the ribosome (rRNA) and tRNA (transfer RNA) which carries amino acids to the mRNARibosome complex. ...
... To make a protein (phenotype) the mRNA is translated with the help of the ribosome (rRNA) and tRNA (transfer RNA) which carries amino acids to the mRNARibosome complex. ...
Transcription
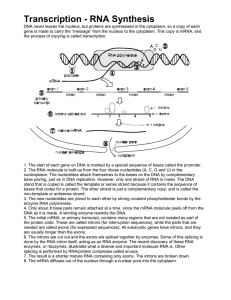
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
Chapter 11: DNA and Genes
... ribosomes for protein manufacturing. In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dn ...
... ribosomes for protein manufacturing. In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dn ...
HL Protein Synthesis Question Sheet
... prevent this. The average lifespan of a eukaryotic mRNA molecule is 10 minutes. In eukaryotes, some of the DNA does not code for polypeptides. Some of these non-coding regions can be found within coding regions, breaking up the code. They are called introns. These non-coding introns are transcribed ...
... prevent this. The average lifespan of a eukaryotic mRNA molecule is 10 minutes. In eukaryotes, some of the DNA does not code for polypeptides. Some of these non-coding regions can be found within coding regions, breaking up the code. They are called introns. These non-coding introns are transcribed ...
Protein Synthesis Practice
... Number the 3-base pair codons in between. A whole protein need to have a series of codons between a start (AUG) and a stop codon (UGA, UAG or UAA). Which strands will build whole proteins? Example: This strand builds a whole protein 7. CGG AUG ...
... Number the 3-base pair codons in between. A whole protein need to have a series of codons between a start (AUG) and a stop codon (UGA, UAG or UAA). Which strands will build whole proteins? Example: This strand builds a whole protein 7. CGG AUG ...
The Central Dogma of Genetics
... chain using anticoding DNA as template. –New RNA nucleotides are added to 3’ end (like DNA) ...
... chain using anticoding DNA as template. –New RNA nucleotides are added to 3’ end (like DNA) ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.