Central Dogma
... • In bacteria: polymerase stops transcription at end of terminator (nucleotide sequence) • In eukaryotes: polymerase continues transcription after pre-mRNA is cut polymerase eventually falls off DNA ...
... • In bacteria: polymerase stops transcription at end of terminator (nucleotide sequence) • In eukaryotes: polymerase continues transcription after pre-mRNA is cut polymerase eventually falls off DNA ...
Glossary
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) :【伝令 RNA】Protein-coding RNA that encodes and carries information from DNA to sites of protein synthesis to undergo translation. The mRNA bears the 5´ m7G cap structure (a specially altered nucleotide) and the 3´ poly(A) tail (a long sequence of adenine nucleotides), both of whic ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) :【伝令 RNA】Protein-coding RNA that encodes and carries information from DNA to sites of protein synthesis to undergo translation. The mRNA bears the 5´ m7G cap structure (a specially altered nucleotide) and the 3´ poly(A) tail (a long sequence of adenine nucleotides), both of whic ...
013368718X_CH13_193
... DNA template is RNA polymerase. 6. The region of DNA where the production of an RNA strand begins is called the intron. 7. Exons are spliced together in forming messenger RNA. For Questions 8–16, match the term with its definition. ...
... DNA template is RNA polymerase. 6. The region of DNA where the production of an RNA strand begins is called the intron. 7. Exons are spliced together in forming messenger RNA. For Questions 8–16, match the term with its definition. ...
HERE
... • Three bases make up the base sequence. • The three bases are called the CODON. • Scientists use tables to determine the correct match of codon to amino acids. • There are 21 amino acids in the body. ...
... • Three bases make up the base sequence. • The three bases are called the CODON. • Scientists use tables to determine the correct match of codon to amino acids. • There are 21 amino acids in the body. ...
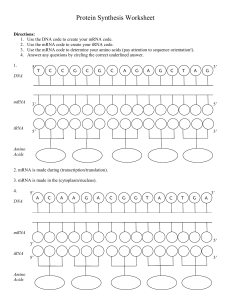
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 13. tRNA uses (anticodons/codons) to match to the mRNA. 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in t ...
... 13. tRNA uses (anticodons/codons) to match to the mRNA. 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in t ...
Chapter 17 - Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
... a. Insulators may act as a barrier to changes in chromatin structure or block the effects of neighboring enhancers b. Insulators may promote the formation of loops that block the effects of nearby enhancers 5. Regulation of RNA processing, RNA stability, and translation a. Alternative splicing regul ...
... a. Insulators may act as a barrier to changes in chromatin structure or block the effects of neighboring enhancers b. Insulators may promote the formation of loops that block the effects of nearby enhancers 5. Regulation of RNA processing, RNA stability, and translation a. Alternative splicing regul ...
RNA Transcription
... polymerase bumps into the assemblage and is then held there by binding to it. ...
... polymerase bumps into the assemblage and is then held there by binding to it. ...
DNA Test Review
... 1. What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which goes with which? 2. Describe the Central Dogma of molecular biology. 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. ...
... 1. What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which goes with which? 2. Describe the Central Dogma of molecular biology. 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. ...
Chapter 9 – Genetically Modified Organisms
... coded for by a particular codon can be determined using the genetic code • What is the relationship between the genetic code and genetic modification? ...
... coded for by a particular codon can be determined using the genetic code • What is the relationship between the genetic code and genetic modification? ...
Transcription and Translation
... • RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence and separates the DNA strands • Complementary ribonucleotides align opposite complementary base pairs • RNA polymerase joins the ribonucleotides together with covalent bonds • The transcription process stops when a termination sequence is reached ...
... • RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence and separates the DNA strands • Complementary ribonucleotides align opposite complementary base pairs • RNA polymerase joins the ribonucleotides together with covalent bonds • The transcription process stops when a termination sequence is reached ...
Lecture 16: Expression of genetic information
... To outline the flow of genetic information from DNA to protein synthesis. To identify the different types of RNA To compare, the structure of DNA & RNA. To outline the general characteristics of genetic code & transcription process. To explain the importance of tRNA, mRNA & rRNA. To diagram the proc ...
... To outline the flow of genetic information from DNA to protein synthesis. To identify the different types of RNA To compare, the structure of DNA & RNA. To outline the general characteristics of genetic code & transcription process. To explain the importance of tRNA, mRNA & rRNA. To diagram the proc ...
Translation - Net Start Class
... On translation notes: Glue the copy of the codon keys into your notes. Use the key for the following: Identify the three amino acids being coded for by the strand of mRNA. Copy the mRNA into your notebook and ...
... On translation notes: Glue the copy of the codon keys into your notes. Use the key for the following: Identify the three amino acids being coded for by the strand of mRNA. Copy the mRNA into your notebook and ...
6-Premedical-From-Gene-to
... • Information is simply copied from one to another according to complementarity of bases • enzyme RNA polymerase (RNAP) • beginning = promotor with initial code • Initiation, elongation, termination phases with specific ...
... • Information is simply copied from one to another according to complementarity of bases • enzyme RNA polymerase (RNAP) • beginning = promotor with initial code • Initiation, elongation, termination phases with specific ...
Mutation
... Review of Last Lecture I. tRNA and the genetic code II. Transcription - prokaryotes ...
... Review of Last Lecture I. tRNA and the genetic code II. Transcription - prokaryotes ...
protein synthesis
... There are 4 bases (A, T, C, G) Thus 4 3 (64) possible combinations of codons There are 20 amino acids Code is redundant (2 or more codons code for same amino acid) but not ambiquous (no codon codes fro more than 1 amino acid) ...
... There are 4 bases (A, T, C, G) Thus 4 3 (64) possible combinations of codons There are 20 amino acids Code is redundant (2 or more codons code for same amino acid) but not ambiquous (no codon codes fro more than 1 amino acid) ...
Gene to Protein
... nucleotides through the coding region Termination – Ends at the termination sequence. mRNA is now complete ...
... nucleotides through the coding region Termination – Ends at the termination sequence. mRNA is now complete ...
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... Composed of nucleotides, but differs from DNA in three ways. 1. Single strand of nucleotides instead of double stranded 2. Has uracil instead of thymine 3. Contains ribose instead of deoxyribose ...
... Composed of nucleotides, but differs from DNA in three ways. 1. Single strand of nucleotides instead of double stranded 2. Has uracil instead of thymine 3. Contains ribose instead of deoxyribose ...
Gene Expression Vocabulary
... 2. Uracil: one of the four nitrogen bases for RNA that pairs up with adenine; it replaces the bases thymine 3. Gene expression: the process of information from DNA to proteins 4. Transcription: the information in DNA is transferred to mRNA 5. Translation: the information in mRNA is used to make a pr ...
... 2. Uracil: one of the four nitrogen bases for RNA that pairs up with adenine; it replaces the bases thymine 3. Gene expression: the process of information from DNA to proteins 4. Transcription: the information in DNA is transferred to mRNA 5. Translation: the information in mRNA is used to make a pr ...
Science 103: Outline 17
... A single-stranded RNA copy of the DNA is made by RNA polymerase: (i) RNA pol binds to and moves down the DNA, separating the strands. (ii) As it goes, it pairs complementary nucleotides with ONE strand, the template strand (*NOT coding strand as in the book!) making a copy of the information in th ...
... A single-stranded RNA copy of the DNA is made by RNA polymerase: (i) RNA pol binds to and moves down the DNA, separating the strands. (ii) As it goes, it pairs complementary nucleotides with ONE strand, the template strand (*NOT coding strand as in the book!) making a copy of the information in th ...
Protein Synthesis Quick Questions
... of the cell – the instructions tell the cell how to assemble the amino acids for making proteins ...
... of the cell – the instructions tell the cell how to assemble the amino acids for making proteins ...
Lecture outlines: RNA to proteins
... rRNA and tRNA generally called “stable RNAs” (have long half-lives) while mRNAs are degraded fairly rapidly (in E. coli, typical mRNA with half-life of a few minutes). Generally, do not see processing of mRNAs in bacterial cells (as seen in eukaryotes; Fig. 8.12). Exception to this are the RNAs tran ...
... rRNA and tRNA generally called “stable RNAs” (have long half-lives) while mRNAs are degraded fairly rapidly (in E. coli, typical mRNA with half-life of a few minutes). Generally, do not see processing of mRNAs in bacterial cells (as seen in eukaryotes; Fig. 8.12). Exception to this are the RNAs tran ...
Protein Synthesis
... RNA is needed to produce proteins. It is so similar to DNA that it serves as a temporary copy of a DNA sequence. Three different types of RNA are involved in the making of a protein. 1. mRNA (messenger RNA): mRNA creates a complementary strand from DNA and carries it out of the nucleus into the cyt ...
... RNA is needed to produce proteins. It is so similar to DNA that it serves as a temporary copy of a DNA sequence. Three different types of RNA are involved in the making of a protein. 1. mRNA (messenger RNA): mRNA creates a complementary strand from DNA and carries it out of the nucleus into the cyt ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... If a strand of DNA says this: T C G G A C T A A A G C C U G A U U What will the strand of mRNA say? – Congratulations! You just did a process called transcription ! ...
... If a strand of DNA says this: T C G G A C T A A A G C C U G A U U What will the strand of mRNA say? – Congratulations! You just did a process called transcription ! ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.