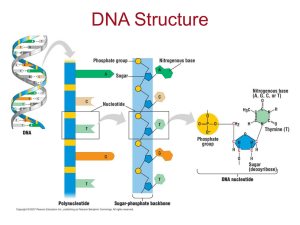
BCH 401G Lecture 44 Eukaryotic gene expression Andres
... nucleus, and translation, which occurs in the cytoplasm, means that certain forms of regulation found in prokaryotes are not possible in eukaryotes (mechanisms such as attenuation). ...
... nucleus, and translation, which occurs in the cytoplasm, means that certain forms of regulation found in prokaryotes are not possible in eukaryotes (mechanisms such as attenuation). ...
Study Questions for Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... RNA splicing takes out sections of mRNA that are not coding for a section of the protein; introns are spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biolog ...
... RNA splicing takes out sections of mRNA that are not coding for a section of the protein; introns are spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biolog ...
G19S Amino Acid code
... 1. Complete column B by writing the correct mRNA codon for each sequence of DNA bases listed in the column marked DNA Base Sequence. Use the letters A, U, C, or G 2. Identify the process responsible by writing its mane below the arrow in Column A. 3. Identify the process responsible by writing its n ...
... 1. Complete column B by writing the correct mRNA codon for each sequence of DNA bases listed in the column marked DNA Base Sequence. Use the letters A, U, C, or G 2. Identify the process responsible by writing its mane below the arrow in Column A. 3. Identify the process responsible by writing its n ...
Athena, Jen and Natalie`s Powerpt
... Upstream from a gene, template strand of DNA, This enzyme is called RNA polymerase It binds to a site packed with adenine and thymine It’s not transcribed but unwinding is very easy Between these bases are only 2 hydrogen bonds; This promoter region’s bonds are not as strong RNA polymerase unwinds t ...
... Upstream from a gene, template strand of DNA, This enzyme is called RNA polymerase It binds to a site packed with adenine and thymine It’s not transcribed but unwinding is very easy Between these bases are only 2 hydrogen bonds; This promoter region’s bonds are not as strong RNA polymerase unwinds t ...
DNA to Protein Name____________ Period______ DNA Location
... 1. DNA is contained in the nucleus of eukaryotes (plants/animals) 2. DNA mRNA The DNA message gets copied into mRNA. This is called transcription. 3. The mRNA leaves nucleus and sticks to ribosomes. (The ribosomes can be floating in cytoplasm (free) or stuck to rough endoplasmic reticulum.) 4. Ribo ...
... 1. DNA is contained in the nucleus of eukaryotes (plants/animals) 2. DNA mRNA The DNA message gets copied into mRNA. This is called transcription. 3. The mRNA leaves nucleus and sticks to ribosomes. (The ribosomes can be floating in cytoplasm (free) or stuck to rough endoplasmic reticulum.) 4. Ribo ...
Central Dogma of Cell Biology
... How do we know what to transcribe? • Start and stop codons – What are codons? ...
... How do we know what to transcribe? • Start and stop codons – What are codons? ...
Lecture TandT
... from DNA to RNA to Protein – DNA functions as the inherited directions for a cell or organism. ...
... from DNA to RNA to Protein – DNA functions as the inherited directions for a cell or organism. ...
DNA Transcription – A Simulation using Corticon
... fatal consequences. For example, the inherited disease, sickle cell anemia, results from a single incorrect amino acid at the 6th position of the beta - protein chain out of 146. Hemoglobin consists of four protein chains - two beta and two alpha. See the graphic on the right for the sequences. This ...
... fatal consequences. For example, the inherited disease, sickle cell anemia, results from a single incorrect amino acid at the 6th position of the beta - protein chain out of 146. Hemoglobin consists of four protein chains - two beta and two alpha. See the graphic on the right for the sequences. This ...
Gene Expression and Gene Regulation
... • Transcription – Transfer of genetic information from the base sequence of DNA to the base sequence of RNA, mediated by RNA synthesis ...
... • Transcription – Transfer of genetic information from the base sequence of DNA to the base sequence of RNA, mediated by RNA synthesis ...
How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50
... incorporated to undergo chain terminations? Name a change that occurs for the chromosome as a result of transposition? Name the enzyme named in a polymerase chain reaction? Name a hybridization technique that identifies the location of the gene within the DNA fragment? At the start of translation na ...
... incorporated to undergo chain terminations? Name a change that occurs for the chromosome as a result of transposition? Name the enzyme named in a polymerase chain reaction? Name a hybridization technique that identifies the location of the gene within the DNA fragment? At the start of translation na ...
Protien Synthesis
... RNA 3 Types: 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) Carries a copy of the protein building instructions from the nucleus (DNA) to the cytoplasm ...
... RNA 3 Types: 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) Carries a copy of the protein building instructions from the nucleus (DNA) to the cytoplasm ...
8.5
... are made up of twenty types of amino acids. The mRNA message is read as a series of non-overlapping codons, a sequence of three nucleotides that code for an amino acid. Many amino acids are coded for by more than one codon. In general, codons that code for the same amino acid share the same first tw ...
... are made up of twenty types of amino acids. The mRNA message is read as a series of non-overlapping codons, a sequence of three nucleotides that code for an amino acid. Many amino acids are coded for by more than one codon. In general, codons that code for the same amino acid share the same first tw ...
Lecture 5
... - Protein: one or more polypeptide chains joined and folded in a 3D configuration (folds occur due to electrical charges of amino acids) - Codon: 3 letter nucleotide sequence in messenger RNA that codes for an amino acid (can also refer to a 3 letter sequence in DNA as well) ...
... - Protein: one or more polypeptide chains joined and folded in a 3D configuration (folds occur due to electrical charges of amino acids) - Codon: 3 letter nucleotide sequence in messenger RNA that codes for an amino acid (can also refer to a 3 letter sequence in DNA as well) ...
DNA Quiz Review - OG-Science
... There are 20 amino acids and they can be combined in all different combinations to create every protein in your body Everything in you is made OF or BY ...
... There are 20 amino acids and they can be combined in all different combinations to create every protein in your body Everything in you is made OF or BY ...
Protein Synthesis
... code for all the necessary amino acids. • The same amino acid is often specified by more than one codon. However, the reverse is never true. • that is, any one codon only specifies ONE amino acid ...
... code for all the necessary amino acids. • The same amino acid is often specified by more than one codon. However, the reverse is never true. • that is, any one codon only specifies ONE amino acid ...
Reading the Blueprint of Life Chromosome DNA Gene Transcription
... Reading the Blueprint of Life: Translation 1. mRNA must be decoded by the ribosome Message from DNA the Gene! Instructions to ribosome on how to assemble a protein mRNA Code words are called Codons Codons are 3 base pairs long Every message has a start codon Every message has a stop cod ...
... Reading the Blueprint of Life: Translation 1. mRNA must be decoded by the ribosome Message from DNA the Gene! Instructions to ribosome on how to assemble a protein mRNA Code words are called Codons Codons are 3 base pairs long Every message has a start codon Every message has a stop cod ...
Regulation of gene expression: Eukaryotic
... Termination of Transcription in Prokaryotes • A specific nucleotide sequence acts as a termination signal, about 40 base pairs in length • Sometimes a special protein called termination factor, rho is required for termination • At termination, RNA dissociates from DNA and enzyme (RNA polymerase) fa ...
... Termination of Transcription in Prokaryotes • A specific nucleotide sequence acts as a termination signal, about 40 base pairs in length • Sometimes a special protein called termination factor, rho is required for termination • At termination, RNA dissociates from DNA and enzyme (RNA polymerase) fa ...
The Genetic Code and Translation
... – There are 64 different codons, but only 20 amino acids. (So, there may be more than one codon for an amino acid.) – AUG codes for methionine (the “start” codon) • Signals the beginning of protein production ...
... – There are 64 different codons, but only 20 amino acids. (So, there may be more than one codon for an amino acid.) – AUG codes for methionine (the “start” codon) • Signals the beginning of protein production ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations - Mrs. Gracie Gonzalez Biology Class
... Transcription: (writing mRNA = the message of how to make proteins); occurs in Nucleus of cell 1. Part of DNA unwinds and creates mRNA (messenger) in the nucleus with the help of RNA polymerase. 2. When transcribing from DNA to RNA, Thymine is replaced by Uracil. 3. Only one side of the DNA i ...
... Transcription: (writing mRNA = the message of how to make proteins); occurs in Nucleus of cell 1. Part of DNA unwinds and creates mRNA (messenger) in the nucleus with the help of RNA polymerase. 2. When transcribing from DNA to RNA, Thymine is replaced by Uracil. 3. Only one side of the DNA i ...
AP Lesson #50 After transcription, do prokaryotes need to modify
... – Protein coding gene is colinear with the mRNA – mRNA is ready to be translated into a protein ...
... – Protein coding gene is colinear with the mRNA – mRNA is ready to be translated into a protein ...
Protein Synthesis PowerPoint
... or Fiction: All living things have ribosomes to make protein? o ...
... or Fiction: All living things have ribosomes to make protein? o ...
AP Biology - Naber Biology
... 35. Write a paragraph to describe the process by which mRNA is formed. Use these terms correctly in your essay, and highlight (or underline) each one: TATA box, gene, terminator, promoter, elongation, 5’ to 3’, termination, ignition RNA, polymerase RNA nucleotides, template, start point, termination ...
... 35. Write a paragraph to describe the process by which mRNA is formed. Use these terms correctly in your essay, and highlight (or underline) each one: TATA box, gene, terminator, promoter, elongation, 5’ to 3’, termination, ignition RNA, polymerase RNA nucleotides, template, start point, termination ...
Gene Regulation: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
... (a) Tryptophan absent, repressor inactive, operon on. RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA at the promoter and transcribes the operon’s genes. ...
... (a) Tryptophan absent, repressor inactive, operon on. RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA at the promoter and transcribes the operon’s genes. ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.