Biology Professor, Robert Osuna, Receives National Science
... transcription initiation sites (i.e. promoters), and several other transcription factors (including DksA itself). The dksA gene expression was also found to be controlled at the level of translation (i.e. protein synthesis), and this control required a specific portion of the dksA mRNA referred to a ...
... transcription initiation sites (i.e. promoters), and several other transcription factors (including DksA itself). The dksA gene expression was also found to be controlled at the level of translation (i.e. protein synthesis), and this control required a specific portion of the dksA mRNA referred to a ...
DNA Control Mechanisms
... D. Heterochromatin - This refers to DNA that remains condensed even during interphase. – It is NOT active. 1. This CANNOT do transcription so it is inactivated. (“hetero” means “different”) E. Euchromatin - This refers to DNA that IS loose during interphase. – It IS active. 1. It CAN do transcriptio ...
... D. Heterochromatin - This refers to DNA that remains condensed even during interphase. – It is NOT active. 1. This CANNOT do transcription so it is inactivated. (“hetero” means “different”) E. Euchromatin - This refers to DNA that IS loose during interphase. – It IS active. 1. It CAN do transcriptio ...
AS 90715 version 2 Describe the role of DNA in relation to gene
... gene-environment interactions: Gene-environment interactions include examples of modification of phenotype by environment, eg determination of sex in crocodile hatchlings by temperature. mutations: selected from o gene mutations o chromosomal mutations the control of metabolic pathways by gene ...
... gene-environment interactions: Gene-environment interactions include examples of modification of phenotype by environment, eg determination of sex in crocodile hatchlings by temperature. mutations: selected from o gene mutations o chromosomal mutations the control of metabolic pathways by gene ...
Study Guide Unit 4 - Mrs. Wolodkowicz`s Biological Realm
... Approximate Unit Length: 4 Weeks Unit Developer/Teacher: Susan Wolodkowicz ...
... Approximate Unit Length: 4 Weeks Unit Developer/Teacher: Susan Wolodkowicz ...
Slide 1
... Figure 1 Genes used to study RNA-mediated genetic interference in C.elegans. Intron–exon structure for genes used to test RNA-mediated inhibition are shown (grey and filled boxes, exons; open boxes, introns; patterned and striped boxes, 5' and 3' untranslated regions. unc-22. ref. 9, unc-54, ref. 1 ...
... Figure 1 Genes used to study RNA-mediated genetic interference in C.elegans. Intron–exon structure for genes used to test RNA-mediated inhibition are shown (grey and filled boxes, exons; open boxes, introns; patterned and striped boxes, 5' and 3' untranslated regions. unc-22. ref. 9, unc-54, ref. 1 ...
Document
... is higher after drug treatment Red -- expression of the gene is lower after drug treatment ...
... is higher after drug treatment Red -- expression of the gene is lower after drug treatment ...
Genetic Engineering
... pancreas of cows and pigs (limited production) • Today, most human insulin comes from human insulin-making genes transferred into simple cells such as bacteria or baker’s yeast (unlimited supply) – Identical to insulin made by the human pancreas ...
... pancreas of cows and pigs (limited production) • Today, most human insulin comes from human insulin-making genes transferred into simple cells such as bacteria or baker’s yeast (unlimited supply) – Identical to insulin made by the human pancreas ...
genetics science learning center – internet lesson
... using the top toolbar. WHAT IS DNA? 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four bases found in the DNA molecule. ...
... using the top toolbar. WHAT IS DNA? 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four bases found in the DNA molecule. ...
Genetics Quiz- Matching, Short answer
... 1. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. For example, if I have brown eyes what would the allele look like. ...
... 1. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. For example, if I have brown eyes what would the allele look like. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 13. _______ inversion in which the rearrangement of genes is confined to single arm of the chromosome 14. ----------------- introns are located in the protein encoding genes of the nucleus. 15. ----------------- discovered that new species arise as a result of natural selection. IV. Answer all, each ...
... 13. _______ inversion in which the rearrangement of genes is confined to single arm of the chromosome 14. ----------------- introns are located in the protein encoding genes of the nucleus. 15. ----------------- discovered that new species arise as a result of natural selection. IV. Answer all, each ...
File
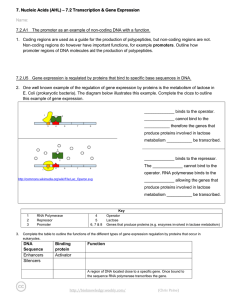
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation STUDY GUIDE
... Be able to make a complementary base sequence to A C C G T A T for DNA. Be able to make a RNA nucleotide sequence that would be complementary to a G T A G T C A DNA strand Who discovered/made a model of the double helix structure? What holds base pairs together? The process that makes an exact copy ...
... Be able to make a complementary base sequence to A C C G T A T for DNA. Be able to make a RNA nucleotide sequence that would be complementary to a G T A G T C A DNA strand Who discovered/made a model of the double helix structure? What holds base pairs together? The process that makes an exact copy ...
Recombinant DNA Technologies
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
INSERT A-3c
... Explanation/Answer: If all of the DNA is present and the breakage for the translocation did not occur within a gene, then the phenotype of the individual can be normal. However, when that individual’s sex cells undergo meiosis, some of the resulting gametes will not contain the normal amount of DNA. ...
... Explanation/Answer: If all of the DNA is present and the breakage for the translocation did not occur within a gene, then the phenotype of the individual can be normal. However, when that individual’s sex cells undergo meiosis, some of the resulting gametes will not contain the normal amount of DNA. ...
rec07
... exhibit similarities at the sequence level. These include very short “motifs”, such as: • Gene splice sites • DNA regulatory binding sites (bound by transcription factors) ...
... exhibit similarities at the sequence level. These include very short “motifs”, such as: • Gene splice sites • DNA regulatory binding sites (bound by transcription factors) ...
Biology 105
... synthesis Usually single stranded Has Uracil instead of Thymine (still pairs with adenine) ...
... synthesis Usually single stranded Has Uracil instead of Thymine (still pairs with adenine) ...
DNA Test Review
... 1. What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which goes with which? 2. Describe the Central Dogma of molecular biology. 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. ...
... 1. What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which goes with which? 2. Describe the Central Dogma of molecular biology. 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. ...
Leaving Cert Biology Notes - Genetics Definitions
... Manipulation or alteration / of genes or of genotypes ...
... Manipulation or alteration / of genes or of genotypes ...
TwoQuestions Darwin Could Not Answer
... • Chemical markers act as “on/off switches” • Genes need instructions for what to do & where & when to do it • Changes gene expression/activity, but not the DNA itself ...
... • Chemical markers act as “on/off switches” • Genes need instructions for what to do & where & when to do it • Changes gene expression/activity, but not the DNA itself ...
Gene Regulation
... • Inducible enzymes catabolic pathways – Break down larger molecules – Turn on in the presence of starting product ...
... • Inducible enzymes catabolic pathways – Break down larger molecules – Turn on in the presence of starting product ...