The Code of Life: Topic 3
... • Gene expression! • You have 23 pairs of chromosomes. • In each pair you get one from your mother and one from your father. • Each chromosome in a pair holds all the same genes as the other. • So what determines which gene is expressed when you develop? • ie how do you get your mother's eyes or you ...
... • Gene expression! • You have 23 pairs of chromosomes. • In each pair you get one from your mother and one from your father. • Each chromosome in a pair holds all the same genes as the other. • So what determines which gene is expressed when you develop? • ie how do you get your mother's eyes or you ...
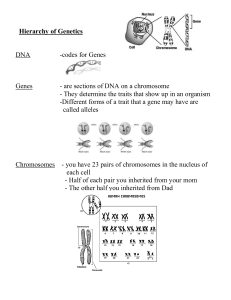
Hierarchy of Genetics
... - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
... - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
Gene Regulation
... Some genes are regulated (turned off and on) by repressor proteins While others use proteins that enhance the rate of transcription. Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the la ...
... Some genes are regulated (turned off and on) by repressor proteins While others use proteins that enhance the rate of transcription. Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the la ...
2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clot _____________________________________ (e) the ability to read _____________________________________ ...
... (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clot _____________________________________ (e) the ability to read _____________________________________ ...
Functional Characterization of Soybean Transcription Factor
... INTRODUCTION: Transcription factors are proteins that regulate gene expression by binding to specific sequences in DNA. Transcription factors are among the major targets to increase the tolerance of plants to stresses, since these proteins control the expression of several genes simultaneously. Memb ...
... INTRODUCTION: Transcription factors are proteins that regulate gene expression by binding to specific sequences in DNA. Transcription factors are among the major targets to increase the tolerance of plants to stresses, since these proteins control the expression of several genes simultaneously. Memb ...
Notes from Lecture 1 - Tufts Computer Science
... 20 types of ”beads” called amino acids. Amino acids differ from eachother based on what ”hangs off” the standard chemical backbone. We use letters represent the alphabet of all amino acids. ...
... 20 types of ”beads” called amino acids. Amino acids differ from eachother based on what ”hangs off” the standard chemical backbone. We use letters represent the alphabet of all amino acids. ...
CentralDogmaNotes
... • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation ...
... • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation ...
國立嘉義大學九十七學年度
... (3) Which of the following statements are correct? For the incorrect statements, correct them specifically (hint: the correction should not be simply from “can” to “cannot”, or from “is” to “isn’t”). (10%) (i) Restriction endonucleases cut DNA at specific sites that always located between genes. (ii ...
... (3) Which of the following statements are correct? For the incorrect statements, correct them specifically (hint: the correction should not be simply from “can” to “cannot”, or from “is” to “isn’t”). (10%) (i) Restriction endonucleases cut DNA at specific sites that always located between genes. (ii ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... In some cases this shape change will help RNA polymerase to bind to DNA, and in other cases it will prevent it from doing so. ...
... In some cases this shape change will help RNA polymerase to bind to DNA, and in other cases it will prevent it from doing so. ...
AP Biology
... 12. What are some ways in which posttranscriptional and posttranslational modifications may alter protein structure and function? ...
... 12. What are some ways in which posttranscriptional and posttranslational modifications may alter protein structure and function? ...
Chapter 3 Section 4
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be pr ...
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be pr ...
Microorganisms in Biotechnology
... depositing the new gene in the chromosome of that cell • The gene is then passed on to daughter cells as the cell divides ...
... depositing the new gene in the chromosome of that cell • The gene is then passed on to daughter cells as the cell divides ...
Genetic Engineering Short Notes
... Definitions: 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can repli ...
... Definitions: 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can repli ...
Given the following two evolutionary conserved eukaryotic genes A
... Gene A and B are transcription factors. One is a repressor of transcription and one is an activator of transcription, but you don’t know which is which. Both bind to DNA: protein A binds to DNA element AA and protein B binds to DNA element BB. Each DNA binding portion, activation portion and repress ...
... Gene A and B are transcription factors. One is a repressor of transcription and one is an activator of transcription, but you don’t know which is which. Both bind to DNA: protein A binds to DNA element AA and protein B binds to DNA element BB. Each DNA binding portion, activation portion and repress ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression ppt
... Have a nuclear envelope Many are multicellular with specialized cells All cells have full sets of chromosomes Not all genes need to be turned on (expressed) ...
... Have a nuclear envelope Many are multicellular with specialized cells All cells have full sets of chromosomes Not all genes need to be turned on (expressed) ...
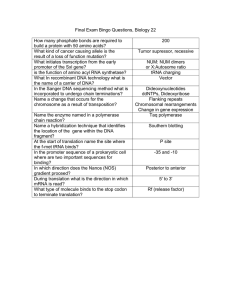
How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...