5. Protein Synthesis
... Protein Synthesis Makeup Study Guide 1. In DNA: a. C pairs with ______ b. A pairs with ______ c. ...
... Protein Synthesis Makeup Study Guide 1. In DNA: a. C pairs with ______ b. A pairs with ______ c. ...
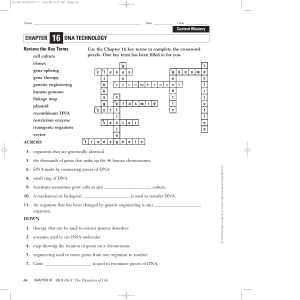
chapter dna technology - Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
... 8. small ring of DNA 9. Scientists sometimes grow cells in a(n) ______________________ culture. 10. A mechanical or biological ______________________ is used to transfer DNA. 11. An organism that has been changed by genetic engineering is a(n) ______________________ organism. DOWN 1. therapy that ca ...
... 8. small ring of DNA 9. Scientists sometimes grow cells in a(n) ______________________ culture. 10. A mechanical or biological ______________________ is used to transfer DNA. 11. An organism that has been changed by genetic engineering is a(n) ______________________ organism. DOWN 1. therapy that ca ...
Document
... 18a) Can all CDS’ be said to contain an ORF? (yes, no-circle one) 18b) Can all ORFs be said to contain a CDS? (yes, no-circle one) ...
... 18a) Can all CDS’ be said to contain an ORF? (yes, no-circle one) 18b) Can all ORFs be said to contain a CDS? (yes, no-circle one) ...
Virtual DNA Lab
... 1. Where can the instructions be found that provide information needed to grow? _______________ 2. Which molecule acts as a blueprint for building cell parts? _______________________________ 3. a. What is the shape of DNA called? ...
... 1. Where can the instructions be found that provide information needed to grow? _______________ 2. Which molecule acts as a blueprint for building cell parts? _______________________________ 3. a. What is the shape of DNA called? ...
Quiz 3-DNA.doc
... ____, and G always pairs with ______ a. C, U b. U, T c. C, T d. T, C 4. During DNA replication, what pulls apart DNA? a. Protease b. Helicase c. Primase d. Ligase 5. The amino acid’s ____________ determines what protein is created: a. size b. order c. color d. ribosome e. ribosomal RNA ...
... ____, and G always pairs with ______ a. C, U b. U, T c. C, T d. T, C 4. During DNA replication, what pulls apart DNA? a. Protease b. Helicase c. Primase d. Ligase 5. The amino acid’s ____________ determines what protein is created: a. size b. order c. color d. ribosome e. ribosomal RNA ...
Genetic Engineering
... – Knowledge of full sequence not required – Can produce large amount of copies from >minute quantity of target DNA >Partially damaged DNA ...
... – Knowledge of full sequence not required – Can produce large amount of copies from >minute quantity of target DNA >Partially damaged DNA ...
Protein Synthesis
... The amino acids called for in the DNA recipe are linked together in a long chain called a polypeptide The polypeptide is folded into a specific shape The shape determines what protein it is The protein will become a part of the cell or part of an organelle ...
... The amino acids called for in the DNA recipe are linked together in a long chain called a polypeptide The polypeptide is folded into a specific shape The shape determines what protein it is The protein will become a part of the cell or part of an organelle ...
Pre-AP Biology 2009
... 7. What are the three types of RNA and what are their functions? Review Figure 12-18 to note these differences. What is difference between an exon and an intron? 8. What is the purpose of transcription? What is the role of RNA in this process? ...
... 7. What are the three types of RNA and what are their functions? Review Figure 12-18 to note these differences. What is difference between an exon and an intron? 8. What is the purpose of transcription? What is the role of RNA in this process? ...
ALE #7
... polymerase binds to a promoter, transcription occurs e. Enhancers – these are sections of DNA that play a role in the regulation of gene expression. When activator proteins bind to enhancers, they assist other transcription factors to bind to RNA polymerase. This helps to promote transcription 2. Pl ...
... polymerase binds to a promoter, transcription occurs e. Enhancers – these are sections of DNA that play a role in the regulation of gene expression. When activator proteins bind to enhancers, they assist other transcription factors to bind to RNA polymerase. This helps to promote transcription 2. Pl ...
Players in the protein game
... language of genes, into amino acids, the language of proteins. They also match nucleic acids with their partner ...
... language of genes, into amino acids, the language of proteins. They also match nucleic acids with their partner ...
Paradigm Shifts in Biomedical Research
... and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
... and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
Genetics Science Learning Center
... What is DNA? 2. What does DNA stand for? __________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? __________________________________________________________ 4. The "twisted ladder" shape of the DNA molecule is called a _________________________________ 5. Name the four ba ...
... What is DNA? 2. What does DNA stand for? __________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? __________________________________________________________ 4. The "twisted ladder" shape of the DNA molecule is called a _________________________________ 5. Name the four ba ...
SW describe how techniques such as DNA
... Sex-influenced traits are those that are expressed differently in the two sexes. Such traits are autosomal, which means that the genes responsible for their expression are not carried on the sex chromosomes. ...
... Sex-influenced traits are those that are expressed differently in the two sexes. Such traits are autosomal, which means that the genes responsible for their expression are not carried on the sex chromosomes. ...
Major Functions
... A gene is a stretch of DNA that contains the information to produce a particular product (usually a protein). ...
... A gene is a stretch of DNA that contains the information to produce a particular product (usually a protein). ...
View a technical slide presentation
... • The ZFP design platform is robust and highly specific. ZFPs can be designed and validated to bind to almost any sequence. • Because plant genomes are complex and highly redundant, a priori knowledge of target gene sequence and genome representation is critical. • Expression of ZFNs is necessary an ...
... • The ZFP design platform is robust and highly specific. ZFPs can be designed and validated to bind to almost any sequence. • Because plant genomes are complex and highly redundant, a priori knowledge of target gene sequence and genome representation is critical. • Expression of ZFNs is necessary an ...
No Slide Title
... nuc1 and nuc2. • Acetylation leads to recruitment of co-activators, chromatin remodeling complex, and RNA pol II. ...
... nuc1 and nuc2. • Acetylation leads to recruitment of co-activators, chromatin remodeling complex, and RNA pol II. ...
Unit 7 Review – DNA Replication, Gene Expression, and Gene
... location of various processes, molecules and enzymes involved, the role of basepairing rules, etc. How do we go from a gene to the expression of a phenotypic trait in a living organism? ...
... location of various processes, molecules and enzymes involved, the role of basepairing rules, etc. How do we go from a gene to the expression of a phenotypic trait in a living organism? ...
Ch 11 homework
... A) exons together. B) polymerase to the promotor. C) nucleotides together. D) introns together. E) an intron to an exon. ...
... A) exons together. B) polymerase to the promotor. C) nucleotides together. D) introns together. E) an intron to an exon. ...