Research Questions
... methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp).Hydrophobic amino have side-chains that do not like to reside in an aqueous environment. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion of the membrane. Hydrophilic amino aci ...
... methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp).Hydrophobic amino have side-chains that do not like to reside in an aqueous environment. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion of the membrane. Hydrophilic amino aci ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... – Histone acetylation- acetyl groups are added to amino acids of histone proteins, making the chromatin less tightly packaged, encouraging transcription. ...
... – Histone acetylation- acetyl groups are added to amino acids of histone proteins, making the chromatin less tightly packaged, encouraging transcription. ...
Problem 3: Why do pre-mRNAs get smaller during RNA processing?
... The primary RNA transcript of the chicken ovalbumin gene is 7700 nucleotides long, but the mature mRNA that is translated on the ribosome is 1872 nucleotides long. This size difference occurs primarily as a result of: A. capping B. cleavage of polycistronic mRNA C. removal of poly A tails D. reverse ...
... The primary RNA transcript of the chicken ovalbumin gene is 7700 nucleotides long, but the mature mRNA that is translated on the ribosome is 1872 nucleotides long. This size difference occurs primarily as a result of: A. capping B. cleavage of polycistronic mRNA C. removal of poly A tails D. reverse ...
Genetic engineering - Mad River Local Schools
... lives. As a gene therapist, you'll treat human patients with genetic illnesses. Otherwise, you might work in a non-medical environment as a biochemist or biophysicist, exploring living organisms such as plants used as food crops. You'll typically work full-time with a ...
... lives. As a gene therapist, you'll treat human patients with genetic illnesses. Otherwise, you might work in a non-medical environment as a biochemist or biophysicist, exploring living organisms such as plants used as food crops. You'll typically work full-time with a ...
2D Barcode Quiz
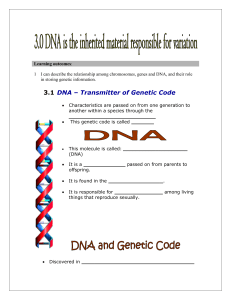
... Thymine, Guanine, Adenine and Cytosine are the four bases or ‘nucleotides’ that make up DNA Adenine and Guanine are Pyrimidines (6-point ring), Cytosine and Thymine are Purines (fused 5- and 6-point rings) DNA has a triple helix structure Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine ...
... Thymine, Guanine, Adenine and Cytosine are the four bases or ‘nucleotides’ that make up DNA Adenine and Guanine are Pyrimidines (6-point ring), Cytosine and Thymine are Purines (fused 5- and 6-point rings) DNA has a triple helix structure Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine ...
BIO 220 Chapter 8 lecture outline Vocabulary Central dogma of
... 1. Be able to define all of the vocabulary used in lecture. 2. What is the central dogma of biology? Who proposed this theory? 3. What is the difference between the terms genotype and phenotype? Are bacteria typically diploid or haploid? What do diploid and haploid mean? 4. How many chromosomes does ...
... 1. Be able to define all of the vocabulary used in lecture. 2. What is the central dogma of biology? Who proposed this theory? 3. What is the difference between the terms genotype and phenotype? Are bacteria typically diploid or haploid? What do diploid and haploid mean? 4. How many chromosomes does ...
REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION, TRANSLATION TAKS
... 14 Part of a DNA strand is represented in the diagram above. In order for DNA to replicate, the strand must separate at which of the following locations? F Between every phosphate-sugar pair G Between the eight sugar-base pairs H* Between the four nitrogenous base pairs J Between any two chemical bo ...
... 14 Part of a DNA strand is represented in the diagram above. In order for DNA to replicate, the strand must separate at which of the following locations? F Between every phosphate-sugar pair G Between the eight sugar-base pairs H* Between the four nitrogenous base pairs J Between any two chemical bo ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(student notes)
... Activity: How DNA is organized! Create a project that explains to the class how DNA is organized. Ex: Kids book, A comparison, a 3-D diorama ...
... Activity: How DNA is organized! Create a project that explains to the class how DNA is organized. Ex: Kids book, A comparison, a 3-D diorama ...
Ch 16-17 Practice Quiz
... 1. What are the 2 pyrimidines? ____________, and the 2 purines? __________, which is a double ring structure and which is a single ring? ___________________ What are Chargaff’s rules? ______________ 2. How many H bonds are there between A and T? ______ and how many between C and G? ________ 3. Which ...
... 1. What are the 2 pyrimidines? ____________, and the 2 purines? __________, which is a double ring structure and which is a single ring? ___________________ What are Chargaff’s rules? ______________ 2. How many H bonds are there between A and T? ______ and how many between C and G? ________ 3. Which ...
Vocabulary 7
... • When one of the 4 base pairs is : –(substitution) “replaced” or –(insertion) “added” or –(deletion) “removed” ...
... • When one of the 4 base pairs is : –(substitution) “replaced” or –(insertion) “added” or –(deletion) “removed” ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... causes a genetic disorder. In gene therapy, an absent or faulty gene is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
... causes a genetic disorder. In gene therapy, an absent or faulty gene is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
Chapter 10 Protein Synthesis Test Study Guide THERE WILL BE 21
... 12. Transcribe the following DNA sequence CCCGAGTAACAT. (p. 206) 13. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC. 14. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence AUGGACAAUUC ...
... 12. Transcribe the following DNA sequence CCCGAGTAACAT. (p. 206) 13. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC. 14. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence AUGGACAAUUC ...
consumer perceptions of food biotechnology
... Genome is the collection of all base pairs within the cell Human Genome project started in 1980s ...
... Genome is the collection of all base pairs within the cell Human Genome project started in 1980s ...
Genetic Engineering
... Polymerase Chain Reaction • Used to make millions of copies of select section of DNA • When small amount of DNA are found but large amounts are needed for analysis • Semen, blood, other tissues, long-dead specimens – DNA from all can be amplified • Thermus aquaticus – hot springs bacterium • http:/ ...
... Polymerase Chain Reaction • Used to make millions of copies of select section of DNA • When small amount of DNA are found but large amounts are needed for analysis • Semen, blood, other tissues, long-dead specimens – DNA from all can be amplified • Thermus aquaticus – hot springs bacterium • http:/ ...
Introduction to Genetics Klug 8th Edition
... Mendel is the starting point for Genetics (the study of heredity and variation) 1860’s used garden peas Identified patterns of inheritance His work was ignored until Correns in 1900’s ...
... Mendel is the starting point for Genetics (the study of heredity and variation) 1860’s used garden peas Identified patterns of inheritance His work was ignored until Correns in 1900’s ...
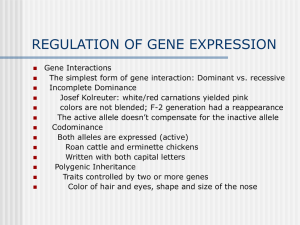
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
... a cluster of genes working together a region of the chromosome near the cluster: operator a region of the chromosome next to the operator: promotor products that initiates the production of enzymes are inducers ...
... a cluster of genes working together a region of the chromosome near the cluster: operator a region of the chromosome next to the operator: promotor products that initiates the production of enzymes are inducers ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
... a. Kary Mullis invented PCR to harness the power of and direct DNA replication to massproduce selected genes. b. RNAi technology uses short synthetic RNA molecules to squelch gene expression. c. Gene targeting through homologous recombination swaps in pieces of DNA into their location in the genome. ...
... a. Kary Mullis invented PCR to harness the power of and direct DNA replication to massproduce selected genes. b. RNAi technology uses short synthetic RNA molecules to squelch gene expression. c. Gene targeting through homologous recombination swaps in pieces of DNA into their location in the genome. ...
Recombinant DNA
... Cut DNA into pieces Insert DNA into vectors that can replicate in bacteria Transform (introduce) DNA into host cell Plate cells and select those with vectors Each colony has one chunk of DNA The whole set is a library of human DNA ...
... Cut DNA into pieces Insert DNA into vectors that can replicate in bacteria Transform (introduce) DNA into host cell Plate cells and select those with vectors Each colony has one chunk of DNA The whole set is a library of human DNA ...
Human Genome Project, Gene Therapy, and Cloning
... 1. Isolate the normal sequence for a gene and package it into a virus (vector). 2. Infect a target cell, usually the one with the illness, such as a liver or lung. 3. The virus uses the normal sequence to produce the missing protein and the cell returns to normal. ...
... 1. Isolate the normal sequence for a gene and package it into a virus (vector). 2. Infect a target cell, usually the one with the illness, such as a liver or lung. 3. The virus uses the normal sequence to produce the missing protein and the cell returns to normal. ...
Plant Transformation
... • DNA repair enzymes recognize the mismatches between the targeted gene and the chimeric oligonucleotide • During the repair process, the altered DNA is incorporated into the plant genome • detected phenotypically • similar to conventional mutagenesis and selection procedures ...
... • DNA repair enzymes recognize the mismatches between the targeted gene and the chimeric oligonucleotide • During the repair process, the altered DNA is incorporated into the plant genome • detected phenotypically • similar to conventional mutagenesis and selection procedures ...