* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO 220 Chapter 8 lecture outline Vocabulary Central dogma of
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Biomolecular engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA-encoded chemical library wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
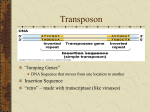
BIO 220 Chapter 8 lecture outline Vocabulary Central dogma of biology More vocabulary Prokaryotic chromosome Horizontal vs. vertical gene transfer DNA replication Review of DNA structure Semiconservative replication Prokaryotic protein synthesis Transcription Translation Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic differences Control of gene expression Constitutive Pre-transcriptional control Inducible operons lac operon Repressible operons trp operon Positive control lac operon Epigenetic control Post-transcriptional control microRNA Changes in genetic material Mutations Types Silent Base substitution (point mutation) Missense Nonsense Frameshift Mugatens Nitrous acid Nucleoside analogs Aflatoxin Radiation Identification of mutants Positive and negative selection Ames test Horizonal gene transfer Transformation Conjugation Transduction Plasmids & transposons Objective questions 1. Be able to define all of the vocabulary used in lecture. 2. What is the central dogma of biology? Who proposed this theory? 3. What is the difference between the terms genotype and phenotype? Are bacteria typically diploid or haploid? What do diploid and haploid mean? 4. How many chromosomes does the typical bacterial cell have? In what form do these chromosomes exist? Are they associated with histone proteins? 5. What is horizontal gene transfer? Vertical gene transfer? 6. Describe the basic structure of a DNA molecule. The strands of nucleotides in a DNA molecule are antiparallel. What does that mean? What are the 5’ and 3’ ends of a DNA strand? 7. Describe the process of DNA replication. What enzymes are involved? What do they contribute to the process? What does semiconservative replication mean? What are the leading and lagging strands of DNA? 8. Describe the process of prokaryotic transcription and translation. How does this compare to protein synthesis occurring in eukaryotic cells? 9. What is meant by the “degeneracy” of the genetic code? 10. What does it mean when a gene is constitutively expressed? 11. Describe the operation of the lac and trp operons. 12. What is the function of microRNAs? 13. What is a mutation? Are mutations always deleterious? 14. Differentiate between different types of mutations. 15. Describe the mode of action for mutagens discussed in lecture. 16. How can positive and negative selection be used to identify mutants? What is replica plating? 17. What is the purpose of the Ames test? How does it work? 18. Describe bacterial transformation, conjugation, and transduction. 19. What are plasmids? Identify different types of plasmids. What are transposons?