ExamView - SUPERVOCAB PRETESTLISTS1THRU17.tst
... The stage of cellular respiration that produce 2 ATP and occur in the matrix of the mitochondria ...
... The stage of cellular respiration that produce 2 ATP and occur in the matrix of the mitochondria ...
Worksheets - cloudfront.net
... Scientists think of nature as a single system controlled by natural laws. By discovering natural laws, scientists strive to increase their understanding of the natural world. Laws of nature are expressed as scientific laws. A scientific law is a statement that describes what always happens under cer ...
... Scientists think of nature as a single system controlled by natural laws. By discovering natural laws, scientists strive to increase their understanding of the natural world. Laws of nature are expressed as scientific laws. A scientific law is a statement that describes what always happens under cer ...
Prentice hall Biology Worksheets
... 1–3 Studying Life Although living things vary greatly, all living things share eight characteristics: 1. Living things are made up of units called cells. Cells are the smallest units of an organism that can be considered alive. 2. Living things reproduce. In sexual reproduction, cells from two diffe ...
... 1–3 Studying Life Although living things vary greatly, all living things share eight characteristics: 1. Living things are made up of units called cells. Cells are the smallest units of an organism that can be considered alive. 2. Living things reproduce. In sexual reproduction, cells from two diffe ...
Workbook biology dragonfly text
... 1–3 Studying Life Although living things vary greatly, all living things share eight characteristics: 1. Living things are made up of units called cells. Cells are the smallest units of an organism that can be considered alive. 2. Living things reproduce. In sexual reproduction, cells from two diffe ...
... 1–3 Studying Life Although living things vary greatly, all living things share eight characteristics: 1. Living things are made up of units called cells. Cells are the smallest units of an organism that can be considered alive. 2. Living things reproduce. In sexual reproduction, cells from two diffe ...
Preview Sample 3
... Outline the path of a cancer from initial occurrence through benign growth, malignancy, and finally the death of the individual. Compare and contrast oncogenes and tumor-supressor genes. Explain how a mutation in a gene can lead to cancer. Describe cancer in terms of cell cycle control. List causes ...
... Outline the path of a cancer from initial occurrence through benign growth, malignancy, and finally the death of the individual. Compare and contrast oncogenes and tumor-supressor genes. Explain how a mutation in a gene can lead to cancer. Describe cancer in terms of cell cycle control. List causes ...
The Mid-Missouri Area Health Education Center Science Resource
... Center Science Resource Library was created to provide resources for educators and students in rural and underserved areas of the 23 counties we serve who might not otherwise have access to quality science and health materials. Refer to the map on the back cover for counties served. We have selected ...
... Center Science Resource Library was created to provide resources for educators and students in rural and underserved areas of the 23 counties we serve who might not otherwise have access to quality science and health materials. Refer to the map on the back cover for counties served. We have selected ...
Section Summaries With IPC Review • Concise two
... from Integrated Physics and Chemistry (IPC) that will be tested on the TAKS, in grade 10 and grade 11. In addition, there are • vocabulary terms from IPC and • key formulas from IPC, with practice in using each of the formulas. Section Summaries A two-page summary for each chapter in Prentice Hall B ...
... from Integrated Physics and Chemistry (IPC) that will be tested on the TAKS, in grade 10 and grade 11. In addition, there are • vocabulary terms from IPC and • key formulas from IPC, with practice in using each of the formulas. Section Summaries A two-page summary for each chapter in Prentice Hall B ...
Assessments
... an educated guess. a guess about how or why something happens. a statement that describes what always happens under certain conditions in nature. an explanation for events that are generally accepted as true. ...
... an educated guess. a guess about how or why something happens. a statement that describes what always happens under certain conditions in nature. an explanation for events that are generally accepted as true. ...
earth science - Augusta County Public Schools
... Genetic information encoded in the DNA molecules provides instructions for assembling protein molecules. The genetic code is the same for all life forms. The double helix model explained how hereditary information is passed on, and provided the basis for an explosion of scientific research in molecu ...
... Genetic information encoded in the DNA molecules provides instructions for assembling protein molecules. The genetic code is the same for all life forms. The double helix model explained how hereditary information is passed on, and provided the basis for an explosion of scientific research in molecu ...
Chapter 22 Gas Exchange
... C) Hot, dry weather, and strong winds. D) Sunrise on a clear morning. E) A cool night is setting in. Answer: D 18) If a plant is kept in the dark, A) the stomata continue their daily rhythm of opening and closing. B) the stomata will remain closed the entire time that the plant is in the dark. C) th ...
... C) Hot, dry weather, and strong winds. D) Sunrise on a clear morning. E) A cool night is setting in. Answer: D 18) If a plant is kept in the dark, A) the stomata continue their daily rhythm of opening and closing. B) the stomata will remain closed the entire time that the plant is in the dark. C) th ...
Biology For Dummies, 2nd Edition - The Official Site
... For general information on our other products and services, please contact our Customer Care Department within the U.S. at 877-762-2974, outside the U.S. at 317-572-3993, or fax 317-572-4002. For technical support, please visit www.wiley.com/techsupport. Wiley also publishes its books in a variety o ...
... For general information on our other products and services, please contact our Customer Care Department within the U.S. at 877-762-2974, outside the U.S. at 317-572-3993, or fax 317-572-4002. For technical support, please visit www.wiley.com/techsupport. Wiley also publishes its books in a variety o ...
PC_Biology_Macomb_April08
... Students describe the general structure and function of cells. They can explain that all living systems are composed of cells and that organisms may be unicellular or multi-cellular. They understand that cells are composed of biological macromolecules and that the complex processes of the cell allow ...
... Students describe the general structure and function of cells. They can explain that all living systems are composed of cells and that organisms may be unicellular or multi-cellular. They understand that cells are composed of biological macromolecules and that the complex processes of the cell allow ...
Biology - Tutor
... organisms into three domains (domain Archaea, domain Bacteria, and domain Eukarya). Domain Eukarya is further categorized into four kingdoms. Here’s an explanation of each: 1. Domain Archaea is made up of prokaryotic, unicellular organisms that live in extreme habitats, such as deep ocean steam vent ...
... organisms into three domains (domain Archaea, domain Bacteria, and domain Eukarya). Domain Eukarya is further categorized into four kingdoms. Here’s an explanation of each: 1. Domain Archaea is made up of prokaryotic, unicellular organisms that live in extreme habitats, such as deep ocean steam vent ...
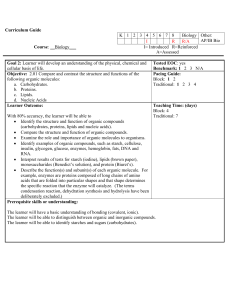
Curriculum Guide Template DRAFT
... • Examine the role and importance of organic molecules to organisms. • Identify examples of organic compounds, such as starch, cellulose, insulin, glycogen, glucose, enzymes, hemoglobin, fats, DNA and RNA. • Interpret results of tests for starch (iodine), lipids (brown paper), monosaccharides (Bened ...
... • Examine the role and importance of organic molecules to organisms. • Identify examples of organic compounds, such as starch, cellulose, insulin, glycogen, glucose, enzymes, hemoglobin, fats, DNA and RNA. • Interpret results of tests for starch (iodine), lipids (brown paper), monosaccharides (Bened ...
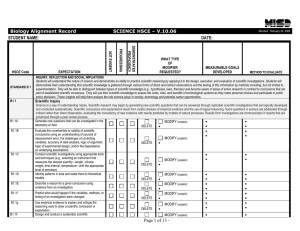
Keystone Exams: Biology - Standards Aligned System
... Module: The Assessment Anchors are organized into two thematic modules for each of the Keystone Exams. The module title appears at the top of each page. The module level is important because the Keystone Exams are built using a module format, with each of the Keystone Exams divided into two equally ...
... Module: The Assessment Anchors are organized into two thematic modules for each of the Keystone Exams. The module title appears at the top of each page. The module level is important because the Keystone Exams are built using a module format, with each of the Keystone Exams divided into two equally ...
AP Biology
... Differentiate between dominant and recessive alleles Differentiate between homozygous and heterozygous Distinguish between a genotype and a phenotype Perform a test cross to predict genotypes and phenotypes Describe the law of independent assortment Distinguish between incomplete and complete domina ...
... Differentiate between dominant and recessive alleles Differentiate between homozygous and heterozygous Distinguish between a genotype and a phenotype Perform a test cross to predict genotypes and phenotypes Describe the law of independent assortment Distinguish between incomplete and complete domina ...
4.7 SYBSC Zoology Syllabus
... Note -The practicals may be conducted by using specimens authorised by the wildlife and such other regulating authorities though it is strongly recommended that the same should be taught by using photographs/audio-visual aids/ simulations / models, etc. as recommended by the UGC and as envisaged in ...
... Note -The practicals may be conducted by using specimens authorised by the wildlife and such other regulating authorities though it is strongly recommended that the same should be taught by using photographs/audio-visual aids/ simulations / models, etc. as recommended by the UGC and as envisaged in ...
Syllabus / Pacing Guide page 2
... The student will know, or be able to do the following. - The difference between a solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. - The three subatomic particles. - The difference between an atom and an element. - The difference between a compound and a mixture - How to use the periodic table. - How to draw atoms u ...
... The student will know, or be able to do the following. - The difference between a solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. - The three subatomic particles. - The difference between an atom and an element. - The difference between a compound and a mixture - How to use the periodic table. - How to draw atoms u ...
biology syllabus
... State that karyotyping is performed using cells collected by chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis, for pre-natal diagnosis of chromosome abnormalities. ...
... State that karyotyping is performed using cells collected by chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis, for pre-natal diagnosis of chromosome abnormalities. ...
4.7 S.Y.B.Sc. Zoology Syllabus
... To Introduce basic terms of genetics To study Mendelian principles of inheritance and other forms pattern of inheritance Desired outcomes : Understand and apply the principles of inheritance. Understand the concept of multiple alleles, linkage and crossing over. Introduction to genetics De ...
... To Introduce basic terms of genetics To study Mendelian principles of inheritance and other forms pattern of inheritance Desired outcomes : Understand and apply the principles of inheritance. Understand the concept of multiple alleles, linkage and crossing over. Introduction to genetics De ...
Chapter (25): Excretion
... D) They have a poor blood supply. E) Like lungs, they have an exhale/inhale function. Answer: A 7) In the countercurrent exchange system of fish gills, المعاكس نظام الصرف من خياشيم األسماك A) blood and water flow in the same direction. B) blood and water flow in opposite directions. الدم وتدفق ال ...
... D) They have a poor blood supply. E) Like lungs, they have an exhale/inhale function. Answer: A 7) In the countercurrent exchange system of fish gills, المعاكس نظام الصرف من خياشيم األسماك A) blood and water flow in the same direction. B) blood and water flow in opposite directions. الدم وتدفق ال ...
Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell)
... D) They have a poor blood supply. E) Like lungs, they have an exhale/inhale function. Answer: A 7) In the countercurrent exchange system of fish gills, المعاكس نظام الصرف من خياشيم األسماك A) blood and water flow in the same direction. B) blood and water flow in opposite directions. الدم وتدفق ال ...
... D) They have a poor blood supply. E) Like lungs, they have an exhale/inhale function. Answer: A 7) In the countercurrent exchange system of fish gills, المعاكس نظام الصرف من خياشيم األسماك A) blood and water flow in the same direction. B) blood and water flow in opposite directions. الدم وتدفق ال ...
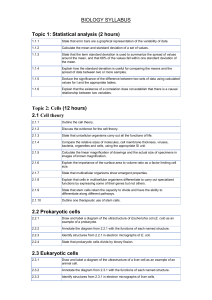
Life Science - SC3206 IC Scope and Sequence
... Identify and describe the steps of meiosis. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Analyze the process of sexual reproduction. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. Examine the different types of asexual reproduction. Identify the advantages and disadvantages of both asexual and sexual repr ...
... Identify and describe the steps of meiosis. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Analyze the process of sexual reproduction. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. Examine the different types of asexual reproduction. Identify the advantages and disadvantages of both asexual and sexual repr ...
Now - Lachoo Memorial College
... Unit I: Membrane Structure and Function:Structural models; Composition and dynamics; Transport of ions and macromolecules; Pumps, carriers and channels; Endo- and Exocytosis; Membrane carbohydrates and their significance in cellular recognition. Unit II: Nucleus – Structure and function of nuclear ...
... Unit I: Membrane Structure and Function:Structural models; Composition and dynamics; Transport of ions and macromolecules; Pumps, carriers and channels; Endo- and Exocytosis; Membrane carbohydrates and their significance in cellular recognition. Unit II: Nucleus – Structure and function of nuclear ...
Discover Fall 2007
... culture system where more complex experiments can be conducted. At the most detailed level, ciliary function in isolated cilia, which have been removed from their cell moorings, are studied in a cell-free system. “We have discovered that nitric oxide is located in the cilia basal at all three levels ...
... culture system where more complex experiments can be conducted. At the most detailed level, ciliary function in isolated cilia, which have been removed from their cell moorings, are studied in a cell-free system. “We have discovered that nitric oxide is located in the cilia basal at all three levels ...