MCAS Review Booklet
... Describe species as reproductively distinct groups of organisms. Recognize that species are further classified into a hierarchical taxonomic system (kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species) based on morphological, behavioral, and molecular similarities. Describe the role that geographi ...
... Describe species as reproductively distinct groups of organisms. Recognize that species are further classified into a hierarchical taxonomic system (kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species) based on morphological, behavioral, and molecular similarities. Describe the role that geographi ...
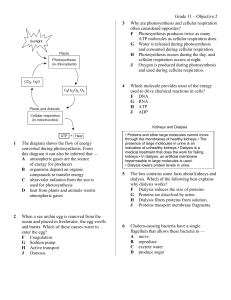
Grade 11 – Objective 2 1 The diagram shows the flow
... H White-eyed flies have many phenotypes for eye color. J This trait is carried only on the X chromosome. ...
... H White-eyed flies have many phenotypes for eye color. J This trait is carried only on the X chromosome. ...
NEW Biology Part II CPR
... Meetings: 180 days Course Description The Biology course is designed to provide students with a detailed understanding of living systems. Emphasis continues to be placed on the skills necessary to examine alternative scientific explanations, actively conduct controlled experiments, analyze and commu ...
... Meetings: 180 days Course Description The Biology course is designed to provide students with a detailed understanding of living systems. Emphasis continues to be placed on the skills necessary to examine alternative scientific explanations, actively conduct controlled experiments, analyze and commu ...
3 | biological macromolecules
... relative to the next one resulting in a linear, fibrous structure. ...
... relative to the next one resulting in a linear, fibrous structure. ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Stern - Introductory Plant Biology: 9th Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies ...
... Stern - Introductory Plant Biology: 9th Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies ...
1강 - KOCW
... • Chromosomes contain most of a cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) • DNA is the substance of genes • Genes are the units of inheritance that transmit information from parents to offspring • The ability of cells to divide is the basis of all reproduction, growth, and r ...
... • Chromosomes contain most of a cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) • DNA is the substance of genes • Genes are the units of inheritance that transmit information from parents to offspring • The ability of cells to divide is the basis of all reproduction, growth, and r ...
Biology EOCEP Review - Teacher Copy
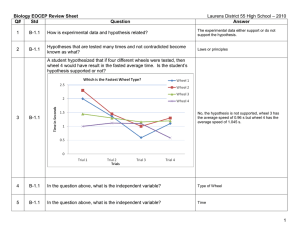
... The process of items moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, down its concentration gradient, without energy is called? ...
... The process of items moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, down its concentration gradient, without energy is called? ...
Question paper - Unit F215/01 - Control, genomes and
... Fig. 3.2 (on the next page) shows the end parts of the sequences of seven of these different length fragments, labelled 1 to 7. The end parts of the sequences for fragments 1 to 4 are complete but those for fragments 5 to 7 are not. These seven fragments correspond to the last seven peaks on the rig ...
... Fig. 3.2 (on the next page) shows the end parts of the sequences of seven of these different length fragments, labelled 1 to 7. The end parts of the sequences for fragments 1 to 4 are complete but those for fragments 5 to 7 are not. These seven fragments correspond to the last seven peaks on the rig ...
Biology - PCMBToday
... 14. Aleurone layer with cells possessing dense cytoplasm filled with aleurone or protein grain is found on the outside of endosperm. 15. Leaves of dicotyledonous plants generally possess parallel venation, while reticulate venation is the characteristic feature of monocotyledonous plants. 16. Th ...
... 14. Aleurone layer with cells possessing dense cytoplasm filled with aleurone or protein grain is found on the outside of endosperm. 15. Leaves of dicotyledonous plants generally possess parallel venation, while reticulate venation is the characteristic feature of monocotyledonous plants. 16. Th ...
Bio Frames - Lee County School District
... Define a problem based on a specific body of knowledge for example: biology, chemistry, physics, and earth/space science and do the following: (DOK High) (1) pose quesons about the natural world, (2) conduct systemic observa ons, (3) examine books and other sources of informa on to see what is already ...
... Define a problem based on a specific body of knowledge for example: biology, chemistry, physics, and earth/space science and do the following: (DOK High) (1) pose quesons about the natural world, (2) conduct systemic observa ons, (3) examine books and other sources of informa on to see what is already ...
Unit Four : Classification of Living Organisms
... pH and the enzymes activity You know that the enzymes are protein substances. They contain acidic carboxylic groups COOH-, and basic amino groups NH2. So, the enzymes are affected by the changing of pH value. Each enzyme has a pH value working at it with a maximum efficiency called the optimal pH. I ...
... pH and the enzymes activity You know that the enzymes are protein substances. They contain acidic carboxylic groups COOH-, and basic amino groups NH2. So, the enzymes are affected by the changing of pH value. Each enzyme has a pH value working at it with a maximum efficiency called the optimal pH. I ...
TOPIC 5 Energy for biological processes 5.1 Cellular respiration
... Krebs cycle is longer with a more complex series of reactions; glycolysis has to expend ATP to move reduced NAD into the mitochondria to reach the electron transport chain; 1 hydrogen removed from each 3C sugar in glycolysis while 5 hydrogen atoms are passed into the electron transport chain from ea ...
... Krebs cycle is longer with a more complex series of reactions; glycolysis has to expend ATP to move reduced NAD into the mitochondria to reach the electron transport chain; 1 hydrogen removed from each 3C sugar in glycolysis while 5 hydrogen atoms are passed into the electron transport chain from ea ...
Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems
... polynucleotides is very specific, and its complementarity allows for a precise replication of the DNA molecule. The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of the biomolecules (RNA molecules and proteins) involved in protein synthesis. While every cell in a m ...
... polynucleotides is very specific, and its complementarity allows for a precise replication of the DNA molecule. The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of the biomolecules (RNA molecules and proteins) involved in protein synthesis. While every cell in a m ...
Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems
... polynucleotides is very specific, and its complementarity allows for a precise replication of the DNA molecule. The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of the biomolecules (RNA molecules and proteins) involved in protein synthesis. While every cell in a m ...
... polynucleotides is very specific, and its complementarity allows for a precise replication of the DNA molecule. The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of the biomolecules (RNA molecules and proteins) involved in protein synthesis. While every cell in a m ...
Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems
... polynucleotides is very specific, and its complementarity allows for a precise replication of the DNA molecule. The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of the biomolecules (RNA molecules and proteins) involved in protein synthesis. While every cell in a m ...
... polynucleotides is very specific, and its complementarity allows for a precise replication of the DNA molecule. The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of the biomolecules (RNA molecules and proteins) involved in protein synthesis. While every cell in a m ...
Biology High School Release Item Document MCAS 2014
... were long and very cold, with deep snow. Over the past 50 years the climate in Yellowstone has become warmer and snowfall amounts have decreased. More elk have been surviving the winters, but populations of scavengers have been decreasing. Scavengers feed on the carcasses of animals. The reintroduct ...
... were long and very cold, with deep snow. Over the past 50 years the climate in Yellowstone has become warmer and snowfall amounts have decreased. More elk have been surviving the winters, but populations of scavengers have been decreasing. Scavengers feed on the carcasses of animals. The reintroduct ...
Chapter 9
... – one strand is synthesised continuously (leading strand) – the other (lagging strand) is synthesised discontinuously as the replication fork moves along the template strand – primases attach a series of primers along the template strand – DNA polymerase extends the primers away from the replication ...
... – one strand is synthesised continuously (leading strand) – the other (lagging strand) is synthesised discontinuously as the replication fork moves along the template strand – primases attach a series of primers along the template strand – DNA polymerase extends the primers away from the replication ...
Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems
... polynucleotides is very specific, and its complementarity allows for a precise replication of the DNA molecule. The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of the biomolecules (RNA molecules and proteins) involved in protein synthesis. While every cell in a m ...
... polynucleotides is very specific, and its complementarity allows for a precise replication of the DNA molecule. The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of the biomolecules (RNA molecules and proteins) involved in protein synthesis. While every cell in a m ...
Assignments Handbook - Independence High
... What is phenylketonuria? Phenylketonuria (commonly known as PKU) is an inherited disorder that increases the levels of a substance called phenylalanine in the blood. Phenylalanine (an amino acid) is a building block of proteins that is obtained through the diet. It is found in all proteins and in so ...
... What is phenylketonuria? Phenylketonuria (commonly known as PKU) is an inherited disorder that increases the levels of a substance called phenylalanine in the blood. Phenylalanine (an amino acid) is a building block of proteins that is obtained through the diet. It is found in all proteins and in so ...
Unit 1 - West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District
... ● Construct an explanation based on observations from microscopic slides to identify patterns that relate the structure of bone to its function (HS-LS1-1) ● Differentiate between the types of osseous tissue in the body using the differences in structural features present in each type of tissue (HS-L ...
... ● Construct an explanation based on observations from microscopic slides to identify patterns that relate the structure of bone to its function (HS-LS1-1) ● Differentiate between the types of osseous tissue in the body using the differences in structural features present in each type of tissue (HS-L ...
7. Biology Glossary
... growth. Acinar cell: A cell from the pancreas. It produces enzymes that are used in digestion. Acrosome, Acrosome reaction: An organelle in the head of a sperm that contains digestive enzymes. When fertilisation takes place, the membrane surrounding these enzymes bursts. The enzymes digest the folli ...
... growth. Acinar cell: A cell from the pancreas. It produces enzymes that are used in digestion. Acrosome, Acrosome reaction: An organelle in the head of a sperm that contains digestive enzymes. When fertilisation takes place, the membrane surrounding these enzymes bursts. The enzymes digest the folli ...
PRACTICE TEST 1
... grain fertilizes an egg cell to form a diploid zygote, while a second sperm cell from the same pollen grain combines with two fused nuclei in the embryo sac, resulting in the formation of a triploid endosperm nucleus. (D) One sperm cell from a single pollen grain fertilizes an egg cell to form a hap ...
... grain fertilizes an egg cell to form a diploid zygote, while a second sperm cell from the same pollen grain combines with two fused nuclei in the embryo sac, resulting in the formation of a triploid endosperm nucleus. (D) One sperm cell from a single pollen grain fertilizes an egg cell to form a hap ...
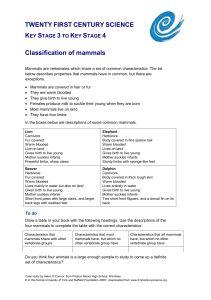
worksheet: classifying mammals
... hair colour, height, weight, sex and blood group are examples of characteristics which are determined by genes. We human beings have about 30,000 genes, but simpler organisms have a lot fewer genes. The more genes that humans have in common, the more similar they are. It follows that the more genes ...
... hair colour, height, weight, sex and blood group are examples of characteristics which are determined by genes. We human beings have about 30,000 genes, but simpler organisms have a lot fewer genes. The more genes that humans have in common, the more similar they are. It follows that the more genes ...
XVIII. Biology, High School - Massachusetts Department of
... Lions and tigers do not usually interact in the wild, but in captivity a lion and a tiger may mate with each other and produce offspring. These offspring do not generally live long and cannot typically reproduce. ...
... Lions and tigers do not usually interact in the wild, but in captivity a lion and a tiger may mate with each other and produce offspring. These offspring do not generally live long and cannot typically reproduce. ...