Study Guide- DNA, Protein Synthesis, Mitosis and Meiosis
... 1) Outline the scientists and the experiments that lead to the discovery of DNA, and later, it’s structure. Include: Meischer, Griffith, Avery, Hershey and Chase, Watson and Crick and Rosalind Franklin. 2) Discuss the structure and chemical composition of bacteriophages. 3) Be able to describe in de ...
... 1) Outline the scientists and the experiments that lead to the discovery of DNA, and later, it’s structure. Include: Meischer, Griffith, Avery, Hershey and Chase, Watson and Crick and Rosalind Franklin. 2) Discuss the structure and chemical composition of bacteriophages. 3) Be able to describe in de ...
DNA Transcription / Translation
... A. RNA polymerase moves along the DNA strand that is oriented in the 5’ to 3’ direction. B. RNA polymerase must first bind to a promoter sequence. C. Transcription is always initiated at the start codon. D. The 3’ end of the RNA molecule is produced first. ...
... A. RNA polymerase moves along the DNA strand that is oriented in the 5’ to 3’ direction. B. RNA polymerase must first bind to a promoter sequence. C. Transcription is always initiated at the start codon. D. The 3’ end of the RNA molecule is produced first. ...
apbio ch 17 test
... A) The tRNA that was in the A site moves into the P site. B) The tRNA that was in the P site moves into the A site. C) The tRNA that was in the A site moves to the E site and is released. D) The tRNA that was in the A site departs from the ribosome via a tunnel. E) The polypeptide enters the E site. ...
... A) The tRNA that was in the A site moves into the P site. B) The tRNA that was in the P site moves into the A site. C) The tRNA that was in the A site moves to the E site and is released. D) The tRNA that was in the A site departs from the ribosome via a tunnel. E) The polypeptide enters the E site. ...
Slide 1
... Genes defined as regions of the genome that encode RNA that are translated into proteins. Estimated >100,000 proteins from 35,000 genes (only 1.5% of the genome are “genes”) Each gene can encode multiple proteins due to “alternative splicing”. ...
... Genes defined as regions of the genome that encode RNA that are translated into proteins. Estimated >100,000 proteins from 35,000 genes (only 1.5% of the genome are “genes”) Each gene can encode multiple proteins due to “alternative splicing”. ...
Players in the protein game
... • Are tightly wound coils of DNA. Chromosomes can be seen in a light microscope but in order to see the DNA you have to have a high powered mircroscope ...
... • Are tightly wound coils of DNA. Chromosomes can be seen in a light microscope but in order to see the DNA you have to have a high powered mircroscope ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... The Sugar is a ______Carbon Sugar called ___________________________ To each Deoxyribose, there is a _____________________________________ connected. The Rungs are connected by weak ___________________________________ ...
... The Sugar is a ______Carbon Sugar called ___________________________ To each Deoxyribose, there is a _____________________________________ connected. The Rungs are connected by weak ___________________________________ ...
DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... 23. Transcription and Translation for the following Strand of DNA. DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa_____________________ ...
... 23. Transcription and Translation for the following Strand of DNA. DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa_____________________ ...
rnalabreport_1
... Currency - Look for publication or copyright dates associated with the site; the more current the better. Links - What links does the site contain? A reliable website will offer links to other reliable websites, not to "junk" sites. ...
... Currency - Look for publication or copyright dates associated with the site; the more current the better. Links - What links does the site contain? A reliable website will offer links to other reliable websites, not to "junk" sites. ...
Ch 11 homework
... A) adjacent to the gene that they regulate. B) required to turn on gene expression when transcription factors are in short supply. C) the site on DNA to which activators bind. D) required to facilitate the binding of DNA polymerases. E) the products of transcription factors. 8. Outline the 4 ways ge ...
... A) adjacent to the gene that they regulate. B) required to turn on gene expression when transcription factors are in short supply. C) the site on DNA to which activators bind. D) required to facilitate the binding of DNA polymerases. E) the products of transcription factors. 8. Outline the 4 ways ge ...
GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES AND EUKARYOTES
... mRNA must be exported from the nucleus before it can be translated. This means that other factors being equal, protein synthesis in a prokaryote can be faster than in a eukaryote. It also means that the primary mRNA transcript can be processed before it is exported from the nucleus, with translation ...
... mRNA must be exported from the nucleus before it can be translated. This means that other factors being equal, protein synthesis in a prokaryote can be faster than in a eukaryote. It also means that the primary mRNA transcript can be processed before it is exported from the nucleus, with translation ...
What is RNA splicing?
... Genetic information is transferred from genes to the proteins they encode via a “messenger” RNA ...
... Genetic information is transferred from genes to the proteins they encode via a “messenger” RNA ...
DNA - TeacherWeb
... DNA unzips and replicates new base pairs to match the existing ones on each strand ...
... DNA unzips and replicates new base pairs to match the existing ones on each strand ...
Transcription Worksheet
... 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of mRNA called?___________________________________________ 4. ...
... 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of mRNA called?___________________________________________ 4. ...
Chapter 3 Section 4
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be pr ...
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be pr ...
Transcription Worksheet
... 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of mRNA called?___________________________________________ 4. ...
... 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of mRNA called?___________________________________________ 4. ...
DNA Jeopardy Review
... 2. Prokaryotes: the polymerase binds to promoter directly in eukaryotes the polymerase requires transcription factors for binding a promoter (TATA) 3. In termination prokaryotic transcription hits a terminator sequence, but in eukaryotes the pre-mRNA is cleaved from the growing RNA chain ...
... 2. Prokaryotes: the polymerase binds to promoter directly in eukaryotes the polymerase requires transcription factors for binding a promoter (TATA) 3. In termination prokaryotic transcription hits a terminator sequence, but in eukaryotes the pre-mRNA is cleaved from the growing RNA chain ...
MCDB 1030
... 3. Describe the principle events that occur in the life cycle of a + strand RNA virus. ...
... 3. Describe the principle events that occur in the life cycle of a + strand RNA virus. ...
genetics i - Indian School Al Wadi Al Kabir
... Infer any 3 properties of genetic code with examples from the above information 14. i) Why does DNA replication occur in small replication occur in small replication forks and not in its entire length? ii) Why is DNA replication continuous and discontinuous in a replication fork? iii) Explain the im ...
... Infer any 3 properties of genetic code with examples from the above information 14. i) Why does DNA replication occur in small replication occur in small replication forks and not in its entire length? ii) Why is DNA replication continuous and discontinuous in a replication fork? iii) Explain the im ...
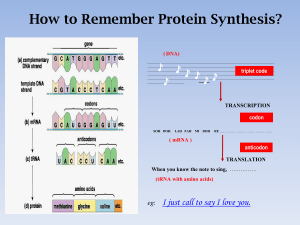
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... _________________________________________________ one amino acid transcription ribosome cytoplasm ...
... _________________________________________________ one amino acid transcription ribosome cytoplasm ...
DNA and Gene Expression
... In eukaryotes, transcription occurs inside the nucleus in a two step sequence of events. ...
... In eukaryotes, transcription occurs inside the nucleus in a two step sequence of events. ...
INS Biology Name: Winter Quarter Midterm
... neutrons; therefore, they are more radioactive. e. Amino acids (and thus proteins) also have nitrogen atoms; thus, the radioactivity would not distinguish between DNA and proteins. 2. Which of the following is true for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene expression? a. After transcription, a 3' pol ...
... neutrons; therefore, they are more radioactive. e. Amino acids (and thus proteins) also have nitrogen atoms; thus, the radioactivity would not distinguish between DNA and proteins. 2. Which of the following is true for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene expression? a. After transcription, a 3' pol ...
Translation RNA Single stranded Does not contain thymine but has
... – Pre-mRNA includes both introns and exons for the gene. – mRNA is only the coding portion (exons). ...
... – Pre-mRNA includes both introns and exons for the gene. – mRNA is only the coding portion (exons). ...
1 Biology 20 Protein Synthesis DNA: How is this linear information
... The proteins produced are in the 1˚ level of protein structure, which the genes determine Some proteins are modified further before they do their specific jobs What are some of the possible roles for these proteins? The following tRNA has the anticodon UAC. What is the DNA base code for this tRNA? W ...
... The proteins produced are in the 1˚ level of protein structure, which the genes determine Some proteins are modified further before they do their specific jobs What are some of the possible roles for these proteins? The following tRNA has the anticodon UAC. What is the DNA base code for this tRNA? W ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.