401Lecture6Sp2013post
... • Different enhancers/promoters can control transcription of the same gene in different cell types • Different subsets of transcription factors bind to enhancers of the same gene in different cell types • Enhancers can be located far from transcription start sites ...
... • Different enhancers/promoters can control transcription of the same gene in different cell types • Different subsets of transcription factors bind to enhancers of the same gene in different cell types • Enhancers can be located far from transcription start sites ...
Gene Regulation
... the grandchildren increased, suggesting that this was a transgenerational epigenetic inheritance.[57] The opposite effect was observed for females—the paternal (but not maternal) granddaughters of women who experienced famine while in the womb (and therefore while their eggs were being formed) lived ...
... the grandchildren increased, suggesting that this was a transgenerational epigenetic inheritance.[57] The opposite effect was observed for females—the paternal (but not maternal) granddaughters of women who experienced famine while in the womb (and therefore while their eggs were being formed) lived ...
Review L14 Gene to Protein L15 Gene Reg
... What is the difference between genotype & phenotype? What is gene expression? Why is the phrase “one gene, one protein” inaccurate? Provide a definition for transcription and translation that clearly distinguishes between the two terms. What is a codon? Why is redundancy important in codons? Make a ...
... What is the difference between genotype & phenotype? What is gene expression? Why is the phrase “one gene, one protein” inaccurate? Provide a definition for transcription and translation that clearly distinguishes between the two terms. What is a codon? Why is redundancy important in codons? Make a ...
Write True if the statement is true
... 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme that assembles a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template is RNA polymerase. 6. The region of DNA where the production of an RNA strand begins is called the intron. 7. Exons are spliced toget ...
... 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme that assembles a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template is RNA polymerase. 6. The region of DNA where the production of an RNA strand begins is called the intron. 7. Exons are spliced toget ...
Chapter 17 - Madeira City Schools
... a. introns may play regulatory role in the cell—contain sequences that control gene activity in some way. Splicing process may regulate passage of mRNA from nucleus to cytoplasm. b. many genes give rise to 2 or more different proteins depending on which segments are treated as exons during processin ...
... a. introns may play regulatory role in the cell—contain sequences that control gene activity in some way. Splicing process may regulate passage of mRNA from nucleus to cytoplasm. b. many genes give rise to 2 or more different proteins depending on which segments are treated as exons during processin ...
Quiz 3-DNA.doc
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
1 - gcisd
... a. Find the definition of both and then explain how they are related to each other 10. KNOW ABOUT MRNA’S ROLE IN REPRODUCTION a. Where is it generated or made? The nucleus b. Where does it go after it is made? The cytoplasm c. What is its main job? To make a copy of DNA’s code to build proteins d. H ...
... a. Find the definition of both and then explain how they are related to each other 10. KNOW ABOUT MRNA’S ROLE IN REPRODUCTION a. Where is it generated or made? The nucleus b. Where does it go after it is made? The cytoplasm c. What is its main job? To make a copy of DNA’s code to build proteins d. H ...
Chapter 19: Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
... 4.) What is the gene promoter? In order for RNA Polymerase to gain access to the promoter, what state must chromatin be in? 5.) What are the 3 ways (from lecture) that chromatin can be altered? 6.) What is acetylation? How can does acetylation of histones affect chromatin structure? What enzymes cat ...
... 4.) What is the gene promoter? In order for RNA Polymerase to gain access to the promoter, what state must chromatin be in? 5.) What are the 3 ways (from lecture) that chromatin can be altered? 6.) What is acetylation? How can does acetylation of histones affect chromatin structure? What enzymes cat ...
Eukaryotic Transcription
... – RNA Polymerase I: synthesis of pre-rRNA, which is processed into 28S, 5.8S, and 18S rRNAs – RNA polymerase III: synthesis of tRNA, 18 S rRNA, and small, stable RNAs – RNA polymerase II: synthesis of mRNAs and four small nuclear RNAs that take part in RNA splicing ...
... – RNA Polymerase I: synthesis of pre-rRNA, which is processed into 28S, 5.8S, and 18S rRNAs – RNA polymerase III: synthesis of tRNA, 18 S rRNA, and small, stable RNAs – RNA polymerase II: synthesis of mRNAs and four small nuclear RNAs that take part in RNA splicing ...
Our laboratory studies the regulation of gene expression in
... Our laboratory studies the regulation of gene expression in eukaryotic organisms. The experimental organism used in most of our work is the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which enables us to use a powerful combination of classical genetics, modern biochemistry and genomics/proteomics in our studies ...
... Our laboratory studies the regulation of gene expression in eukaryotic organisms. The experimental organism used in most of our work is the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which enables us to use a powerful combination of classical genetics, modern biochemistry and genomics/proteomics in our studies ...
Bio 220 MiniQuiz 1
... _____1. Organic growth factors include amino acids and vitamins. _____2. Chemoautotrophs use the light from the sun as their primary energy source. _____3. Both chocolate agar and blood agar contain blood. _____4. Transcription refers to the process of DNA synthesis. Multiple choice _____5. An oblig ...
... _____1. Organic growth factors include amino acids and vitamins. _____2. Chemoautotrophs use the light from the sun as their primary energy source. _____3. Both chocolate agar and blood agar contain blood. _____4. Transcription refers to the process of DNA synthesis. Multiple choice _____5. An oblig ...
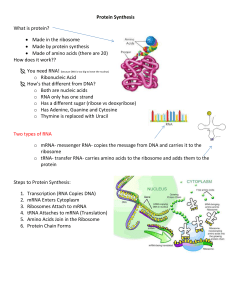
Protein Synthesis - Madison County Schools
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... ______________________________. 21. With restriction enzymes, scientists had a pair of molecular ______________ to ________ DNA molecules. #10- RNA Alternative Splicing ...
... ______________________________. 21. With restriction enzymes, scientists had a pair of molecular ______________ to ________ DNA molecules. #10- RNA Alternative Splicing ...
3687317_mlbio10_Ch13_TestA_3rd.indd
... 2. Which nucleotide in Figure 13–1 indicates the nucleic acid above is RNA? a. uracil c. cytosine b. guanine d. adenine 3. What is produced during transcription? a. RNA molecules c. RNA polymerase b. DNA molecules d. proteins 4. During eukaryotic transcription, the molecule that is formed is a. comp ...
... 2. Which nucleotide in Figure 13–1 indicates the nucleic acid above is RNA? a. uracil c. cytosine b. guanine d. adenine 3. What is produced during transcription? a. RNA molecules c. RNA polymerase b. DNA molecules d. proteins 4. During eukaryotic transcription, the molecule that is formed is a. comp ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 3. Dropsphila melanogaster is known as the common _____________ _____________. 4. Human females have 2 _____ chromosomes, while human males have 1 _____ and 1 _____ chromosome. 5. Morgan was awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine in the year _________. #3- Genes Control Biochemical Events ...
... 3. Dropsphila melanogaster is known as the common _____________ _____________. 4. Human females have 2 _____ chromosomes, while human males have 1 _____ and 1 _____ chromosome. 5. Morgan was awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine in the year _________. #3- Genes Control Biochemical Events ...
Chapter 11 Transcription and RNA Processing
... Conserved sequences for removal of the introns of nuclear mRNA genes are minimal. – Dinucleotide sequences at the 5’ and 3’ ends of introns. – An A residue about 30 nucleotides upstream from the 3’ splice site is needed for lariat formation. ...
... Conserved sequences for removal of the introns of nuclear mRNA genes are minimal. – Dinucleotide sequences at the 5’ and 3’ ends of introns. – An A residue about 30 nucleotides upstream from the 3’ splice site is needed for lariat formation. ...
From Gene to Protein Part 2
... FROM GENE TO PROTEIN PART 2 Goal 1- Understand the process of transcription • How is RNA made? •How ...
... FROM GENE TO PROTEIN PART 2 Goal 1- Understand the process of transcription • How is RNA made? •How ...
Chapter 36: RNA Synthesis and Regulation in Bacteria.
... 8. What is a consensus sequence? 9. What is the function of the σ unit of RNA polymerase? 10. RNA polymerase does not have a proofreading activity to correct errors resulting in a higher error frequency in the transcript than for DNA polymerase. Why is the higher frequency of RNA polymerase acceptab ...
... 8. What is a consensus sequence? 9. What is the function of the σ unit of RNA polymerase? 10. RNA polymerase does not have a proofreading activity to correct errors resulting in a higher error frequency in the transcript than for DNA polymerase. Why is the higher frequency of RNA polymerase acceptab ...
Lec:1 Dr.Mohammed Alhamdany Molecular and genetic factors in
... polymerase II proceeds along one strand of DNA, producing an RNA molecule which is complementary to the DNA template. A DNA sequence close to the end of the gene, called the polyadenylation signal, acts as a signal for termination of the RNA transcript. The activity of RNA polymerase II is regulated ...
... polymerase II proceeds along one strand of DNA, producing an RNA molecule which is complementary to the DNA template. A DNA sequence close to the end of the gene, called the polyadenylation signal, acts as a signal for termination of the RNA transcript. The activity of RNA polymerase II is regulated ...
The Central Dogma of Genetics
... chain using anticoding DNA as template. –New RNA nucleotides are added to 3’ end (like DNA) ...
... chain using anticoding DNA as template. –New RNA nucleotides are added to 3’ end (like DNA) ...
RNA
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – formed during transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – formed during transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
lesson viii - MisterSyracuse.com
... specific sequence of bases. It signals the start of a gene. 12. RNA polymerase attaches here, and starts adding bases, using the DNA as a template strand. It is much slower than DNA polymerase, at only 40 bases per second. 13. It moves along until it hits the terminator. “You have been targeted for ...
... specific sequence of bases. It signals the start of a gene. 12. RNA polymerase attaches here, and starts adding bases, using the DNA as a template strand. It is much slower than DNA polymerase, at only 40 bases per second. 13. It moves along until it hits the terminator. “You have been targeted for ...
Practice Multiple Choice- Set 1 - mvhs
... c) The amount of energy indicates what is passed out as feces d) It indicates the diversity of an environment f) Animals can only be at the top level ...
... c) The amount of energy indicates what is passed out as feces d) It indicates the diversity of an environment f) Animals can only be at the top level ...
Chapter 12 SWBAT`s and Standards
... flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
... flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.