BioSc 231 Exam 3 2005
... _____ The presence of a ___ with a free 3'-OH group is essential for DNA polymerase to synthesize DNA since no known DNA polymerase is able to initiate chains. A. B. C. D. E. ...
... _____ The presence of a ___ with a free 3'-OH group is essential for DNA polymerase to synthesize DNA since no known DNA polymerase is able to initiate chains. A. B. C. D. E. ...
Fall 2005 Due: 9/9 GENETICS Homework 1 1. (1 point) The
... What codons could this anticodon interact with? What amino acid is carried by this tRNA? What would be the effect if the G in the anticodon were mutated to a U? ...
... What codons could this anticodon interact with? What amino acid is carried by this tRNA? What would be the effect if the G in the anticodon were mutated to a U? ...
Slide 1
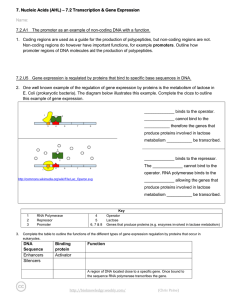
... •DNA makes up GENES, which are found on CHROMOSOMES. •Gene— a segment of DNA that provides information for making a specific protein. ...
... •DNA makes up GENES, which are found on CHROMOSOMES. •Gene— a segment of DNA that provides information for making a specific protein. ...
Transcription
... It is like DNA replication in that a DNA strand is used to synthesize a strand of mRNA. Only one strand of DNA is copied. A single gene may be transcribed thousands of times. After transcription, the DNA strands rejoin. Steps involved in transcription RNA polymerase recognizes a specific base sequen ...
... It is like DNA replication in that a DNA strand is used to synthesize a strand of mRNA. Only one strand of DNA is copied. A single gene may be transcribed thousands of times. After transcription, the DNA strands rejoin. Steps involved in transcription RNA polymerase recognizes a specific base sequen ...
Lecture#7 - Eukaryote gene structure and regulation.
... The biochemistry of intron splicing is well understood and involves the lariat model. For some genes (most) the processed mature mRNA is the same product each time. ...
... The biochemistry of intron splicing is well understood and involves the lariat model. For some genes (most) the processed mature mRNA is the same product each time. ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... cells because of a silencer that binds a cellular factor which repress transcription. However, in cells that are required to produce the hormone the effect of the silencer is itself neutralised by an enhancer located 1.2 kb upstream of the promoter of the gene and is only “activated” in the cells [t ...
... cells because of a silencer that binds a cellular factor which repress transcription. However, in cells that are required to produce the hormone the effect of the silencer is itself neutralised by an enhancer located 1.2 kb upstream of the promoter of the gene and is only “activated” in the cells [t ...
Genetics exam 4
... A. Nucleotides are added to the 5' end of the newly synthesized strand B. A sugar-phosphate bond is formed between the 3' hydroxyl and the 5' phosphate C. Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence D. Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming E. Both RNA and DN ...
... A. Nucleotides are added to the 5' end of the newly synthesized strand B. A sugar-phosphate bond is formed between the 3' hydroxyl and the 5' phosphate C. Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence D. Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming E. Both RNA and DN ...
Webquest
... 1. First go to the page: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/tour/ . Use the tabs at the top of the page and answer the following questions: a. What is DNA? b. What does “DNA” stand for? ...
... 1. First go to the page: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/tour/ . Use the tabs at the top of the page and answer the following questions: a. What is DNA? b. What does “DNA” stand for? ...
Protein Synthesis Notes Review
... 24. How many different amino acids can a tRNA carry? 25. What are the three unpaired bases at the bottom of a tRNA called? 26. What type of bond forms between amino acids? 27. What do the codons on mRNA specify? 28. What are the three main steps of protein synthesis? 29. Put the following terms in o ...
... 24. How many different amino acids can a tRNA carry? 25. What are the three unpaired bases at the bottom of a tRNA called? 26. What type of bond forms between amino acids? 27. What do the codons on mRNA specify? 28. What are the three main steps of protein synthesis? 29. Put the following terms in o ...
Earth`s Early History 10-2
... Identify some of the hypotheses about early Earth and the origin of life. Discuss the hypothesis that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells. ...
... Identify some of the hypotheses about early Earth and the origin of life. Discuss the hypothesis that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells. ...
doc Practice Midterm 2006
... concepts covered in class. As for the questions above, it is important that your answers are concise and unambiguous, and that they directly address the questions posed. 1. Which of the common Watson-Crick base pairs is more stable? Why? How does this property affect the melting temperature of DNA? ...
... concepts covered in class. As for the questions above, it is important that your answers are concise and unambiguous, and that they directly address the questions posed. 1. Which of the common Watson-Crick base pairs is more stable? Why? How does this property affect the melting temperature of DNA? ...
Transcription & Translation
... carry a specific amino acid at one end and an anticodon region that recognizes and binds mRNA at the other end. The tRNA that binds to that mRNA codon determines what amino acid is added to a protein chain. The Three RNAs (mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA) all work together to turn the information in DNA into a ...
... carry a specific amino acid at one end and an anticodon region that recognizes and binds mRNA at the other end. The tRNA that binds to that mRNA codon determines what amino acid is added to a protein chain. The Three RNAs (mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA) all work together to turn the information in DNA into a ...
Plant Molecular Biology
... Luciferase - enzyme that emits light when it oxidizes the substrate, bioluminescent or vital reporter of gene expression in living cells, found in bacteria and invertebrates CAT – chloramphenicol acetyltransferase, used as an early reporter in plants, assay with radioactive substrate, bacterial gene ...
... Luciferase - enzyme that emits light when it oxidizes the substrate, bioluminescent or vital reporter of gene expression in living cells, found in bacteria and invertebrates CAT – chloramphenicol acetyltransferase, used as an early reporter in plants, assay with radioactive substrate, bacterial gene ...
From Gene to Protein—Transcription and Translation
... Complete the following sentence to describe how differences in a gene can result in normal hemoglobin vs. sickle cell. Differences in the sequence of _____________________ in the gene result in differences in the sequence of ______________________ in mRNA which result in differences in the sequence ...
... Complete the following sentence to describe how differences in a gene can result in normal hemoglobin vs. sickle cell. Differences in the sequence of _____________________ in the gene result in differences in the sequence of ______________________ in mRNA which result in differences in the sequence ...
Review Topics for Final Part 1
... General transcription factors are required for translation of all transcripts. Ones to note are TFIIH and TBP. What do they do? Be aware of the different inhibitors mentioned in class. RNA Processing (Eukaryotic) Addition of 5’ cap: where/when does this happen? What does it do? How is the cap ...
... General transcription factors are required for translation of all transcripts. Ones to note are TFIIH and TBP. What do they do? Be aware of the different inhibitors mentioned in class. RNA Processing (Eukaryotic) Addition of 5’ cap: where/when does this happen? What does it do? How is the cap ...
Unit 9 Completed Vocabulary - WAHS
... transfer RNA (tRNA) – type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. transcription – process in which part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence in RNA. RNA polymerase – enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA an ...
... transfer RNA (tRNA) – type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. transcription – process in which part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence in RNA. RNA polymerase – enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA an ...
DNA Quiz #1 - Houston ISD
... 17. Genes are made up of ___________ that determine our traits like hair and eye color. 18. A set of three (3) nitrogen bases makes a ____________. 19. Each tRNA molecule carries an _________ ________ that will become part of a protein. 20. _______________ discovered the base-pair rule A=T and C=G. ...
... 17. Genes are made up of ___________ that determine our traits like hair and eye color. 18. A set of three (3) nitrogen bases makes a ____________. 19. Each tRNA molecule carries an _________ ________ that will become part of a protein. 20. _______________ discovered the base-pair rule A=T and C=G. ...
File
... 3. “snurps’ cluster and for a which removes the introns a) a loop (lariat) is formed and b) exon shuffling – intron – exon arrangements represent the shuffling of the C. Alternative splicing – a single primary is spliced into different mRNAs by the Inclusion of different sets of a) explains how 30,0 ...
... 3. “snurps’ cluster and for a which removes the introns a) a loop (lariat) is formed and b) exon shuffling – intron – exon arrangements represent the shuffling of the C. Alternative splicing – a single primary is spliced into different mRNAs by the Inclusion of different sets of a) explains how 30,0 ...
Genes Expression or Genes and How They Work: Transcription
... RNA polymerase, is a faithful copy of ________________, including _______________________. Before the primary transcript is ________________, the introns are removed by a process called __________________________________. Particles composed of proteins and a special types of RNA called small nuclear ...
... RNA polymerase, is a faithful copy of ________________, including _______________________. Before the primary transcript is ________________, the introns are removed by a process called __________________________________. Particles composed of proteins and a special types of RNA called small nuclear ...
Quiz10ch10.doc
... e. the part of the tRNA that binds to an amino acid 10. DNA a. takes part directly in protein synthesis by leaving the nucleus and being translated on ...
... e. the part of the tRNA that binds to an amino acid 10. DNA a. takes part directly in protein synthesis by leaving the nucleus and being translated on ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.