This is Most of an Old Exam
... Cellular oxidation of food fuels is the immediate source of electrons for oxidative phosphorylation. B. In oxidative phosphorylation, both the electron transport proteins and the ATP synthase molecules are in the same membrane. C. NAD+ and FAD+ are hydrogen carrier molecules. NAD+ can carry one hydr ...
... Cellular oxidation of food fuels is the immediate source of electrons for oxidative phosphorylation. B. In oxidative phosphorylation, both the electron transport proteins and the ATP synthase molecules are in the same membrane. C. NAD+ and FAD+ are hydrogen carrier molecules. NAD+ can carry one hydr ...
Organic Molecule
... Organic Molecules • Organic Molecule= A molecule that contains carbon and hydrogen; it may also have O, N. • Formed by biotic factors ...
... Organic Molecules • Organic Molecule= A molecule that contains carbon and hydrogen; it may also have O, N. • Formed by biotic factors ...
Biology-Chapter2 (Biology
... A. Carbohydrates B. Lipids C. Proteins D. Nucleic acids Permission has been granted for reproduction by the Virginia Department of Education © Virginia Department of Education ...
... A. Carbohydrates B. Lipids C. Proteins D. Nucleic acids Permission has been granted for reproduction by the Virginia Department of Education © Virginia Department of Education ...
Ex. glucose, fructose and galactose: these are isomers
... Why are carbohydrates important? Because they contain LARGE amounts of ENERGY! This energy can be released by a process called __________________________________________ ...
... Why are carbohydrates important? Because they contain LARGE amounts of ENERGY! This energy can be released by a process called __________________________________________ ...
C383 Study Guide for the Final Exam Spring 2017 Basic Information
... A. A titration curve for lysine, with a side chain pKa of 10.5. B. A DNA melting curve for a poly(AT) sequence and a poly(GC) sequence (indicate which is poly(AT) and which is poly(GC)) C. A plot of initial velocity versus substrate concentration for a Michaelis-Menton enzyme. D. The same plot as (B ...
... A. A titration curve for lysine, with a side chain pKa of 10.5. B. A DNA melting curve for a poly(AT) sequence and a poly(GC) sequence (indicate which is poly(AT) and which is poly(GC)) C. A plot of initial velocity versus substrate concentration for a Michaelis-Menton enzyme. D. The same plot as (B ...
Carbon Compounds Enzymes Worksheet
... b. Living things use them as their main source of energy. c. The monomers in sugar polymers are starch molecules. d. Plants and some animals use them for skength and rigidity. ...
... b. Living things use them as their main source of energy. c. The monomers in sugar polymers are starch molecules. d. Plants and some animals use them for skength and rigidity. ...
Molecules of Life Review Topics
... Peptide bond- covalent, between amino acids Dipeptide, polypeptide – how is a protein different? – 3-D shape Levels of structure o Primary structure – sequence of amino acids o Secondary and tertiary – coiling and folding into 3-D shape, one chain o Quaternary – two or more polypeptides togeth ...
... Peptide bond- covalent, between amino acids Dipeptide, polypeptide – how is a protein different? – 3-D shape Levels of structure o Primary structure – sequence of amino acids o Secondary and tertiary – coiling and folding into 3-D shape, one chain o Quaternary – two or more polypeptides togeth ...
Carbon Compounds
... • Plants and Animals also use certain carbohydrates as structural building materials ...
... • Plants and Animals also use certain carbohydrates as structural building materials ...
Biosynthesis of Essential Amino Acids
... CHEM–643 Intermediary Metabolism Written by Harold B. White 1. It has been shown in many instances that enzymes catalyzing chemically similar reactions (e.g. malate and lactate dehydrogenases) have amazingly similar tertiary structures which suggests they evolved from a common ancestral protein. Lik ...
... CHEM–643 Intermediary Metabolism Written by Harold B. White 1. It has been shown in many instances that enzymes catalyzing chemically similar reactions (e.g. malate and lactate dehydrogenases) have amazingly similar tertiary structures which suggests they evolved from a common ancestral protein. Lik ...
Document
... •Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. (simple sugars – monosaccharides) -Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. •Lipids have several different functions. (glycerol + fatty acids) -Fats and oils have different types of fatty acids. -Phospholipids make up all ...
... •Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. (simple sugars – monosaccharides) -Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. •Lipids have several different functions. (glycerol + fatty acids) -Fats and oils have different types of fatty acids. -Phospholipids make up all ...
Chapter 1.3 cell processes_1
... • Elements: any substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance (smallest part is an atom) • Compounds: two or more elements chemically joined together • smallest part of a compound is molecule • 1 C and 2 O CO2 ...
... • Elements: any substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance (smallest part is an atom) • Compounds: two or more elements chemically joined together • smallest part of a compound is molecule • 1 C and 2 O CO2 ...
study guide section 3-1 carbon compounds
... 2. ______The different shapes and functions of different proteins are determined by a. the R groups of the amino acids they contain. b. the amino groups of the amino acids they contain. c. the carboxyl groups of the amino acids they contain. d. whether or not they contain any amino acids. 3. ______ ...
... 2. ______The different shapes and functions of different proteins are determined by a. the R groups of the amino acids they contain. b. the amino groups of the amino acids they contain. c. the carboxyl groups of the amino acids they contain. d. whether or not they contain any amino acids. 3. ______ ...
Macromolecules
... energy Why do you strike a match? • Some reactions will occur completely spontaneously (can supply their own activation energy) Vinegar and Baking Soda ...
... energy Why do you strike a match? • Some reactions will occur completely spontaneously (can supply their own activation energy) Vinegar and Baking Soda ...
element Any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler
... Any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances (O, N, Na, S, C) ...
... Any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances (O, N, Na, S, C) ...
File - Mrs. Badger`s Honors Biology Class
... _____ 1. Choose the nucleotide sequence of the RNA strand that would be complementary to the following DNA strand: GTAGTCA a. UATUAGA. b. ACGACTG. c. CAUCAGU. d. CATCAGT. _____ 2. The main function of tRNA is to a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes ...
... _____ 1. Choose the nucleotide sequence of the RNA strand that would be complementary to the following DNA strand: GTAGTCA a. UATUAGA. b. ACGACTG. c. CAUCAGU. d. CATCAGT. _____ 2. The main function of tRNA is to a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes ...
BIOCHEMISTRY 2.1
... and nucleic acids) and their functions in biological systems—CHO focus on glucose polymers including chitin, starch, cellulose, glycogen; Proteins intro enzymes and give common examples including hemoglobin, antibodies, collagen, muscle fibers, hair, nails, and cell fibers actin and myosin; Nucleic ...
... and nucleic acids) and their functions in biological systems—CHO focus on glucose polymers including chitin, starch, cellulose, glycogen; Proteins intro enzymes and give common examples including hemoglobin, antibodies, collagen, muscle fibers, hair, nails, and cell fibers actin and myosin; Nucleic ...
biochemistry - Kuliah FTSL
... energy for the synthesis of sugars. Contains DNA, and like mitochondria is believed to have originated as a captured ...
... energy for the synthesis of sugars. Contains DNA, and like mitochondria is believed to have originated as a captured ...
Macromolecules
... main source of energy for organisms can also be used for structural purposes made of C, H, and O; usually in a 1:2:1 ratio The monomers of carbohydrates are called monosaccharides, like glucose, fructose (in fruits) and galactose (in milk). The breakdown of monosaccharides supplies immediate energy. ...
... main source of energy for organisms can also be used for structural purposes made of C, H, and O; usually in a 1:2:1 ratio The monomers of carbohydrates are called monosaccharides, like glucose, fructose (in fruits) and galactose (in milk). The breakdown of monosaccharides supplies immediate energy. ...
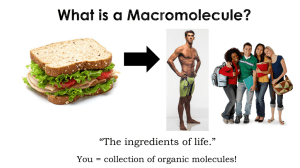
The ingredients of life. - Waterford Public Schools
... Carbon atoms love to form strong bonds to other carbon atoms, creating chains and rings. ...
... Carbon atoms love to form strong bonds to other carbon atoms, creating chains and rings. ...
Macromolecule notes
... Carbon can bond with numerous other elements 1. Carbon has 4 free e- in it’s outer energy level 2. It has the ability to form up to 4 covalent bonds ...
... Carbon can bond with numerous other elements 1. Carbon has 4 free e- in it’s outer energy level 2. It has the ability to form up to 4 covalent bonds ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Principles
... compound are ___________. • Chemical reactions - the making or breaking of _______ between atoms. • A change in chemical energy occurs during a chemical reaction. • _____gonic reactions: _____ energy. • Exergonic reactions: ________ energy. ...
... compound are ___________. • Chemical reactions - the making or breaking of _______ between atoms. • A change in chemical energy occurs during a chemical reaction. • _____gonic reactions: _____ energy. • Exergonic reactions: ________ energy. ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.