Macromolecules Notes
... Organic - compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms Inorganic - compounds that DO NOT contain both carbon and hydrogen There are four classes of organic compounds that are central to life on earth. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids ...
... Organic - compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms Inorganic - compounds that DO NOT contain both carbon and hydrogen There are four classes of organic compounds that are central to life on earth. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids ...
Compounds of Life Chart
... Polyunsaturated – many double or triple bonds between carbon atoms Trans fats – unsaturated fatty acids that have been changed to saturated fatty acids Phospholipids – have hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail, help to make up the cell membrane (lipid bilayer) Steroids – contain four attach ...
... Polyunsaturated – many double or triple bonds between carbon atoms Trans fats – unsaturated fatty acids that have been changed to saturated fatty acids Phospholipids – have hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail, help to make up the cell membrane (lipid bilayer) Steroids – contain four attach ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... Organic - compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms Inorganic - compounds that DO NOT contain both carbon and hydrogen There are four classes of organic compounds that are central to life on earth. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids ...
... Organic - compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms Inorganic - compounds that DO NOT contain both carbon and hydrogen There are four classes of organic compounds that are central to life on earth. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids ...
Midterm Review Key 2014
... etc. (If the resulting product is completely different than the reactants, than its most likely a chemical reaction.) 3. There are many, example includes water, salt, glucose, etc. 4. Neutrons and protons are in the atoms nucleus. Electrons orbit around in a shell or cloud. 5. Macromolecules include ...
... etc. (If the resulting product is completely different than the reactants, than its most likely a chemical reaction.) 3. There are many, example includes water, salt, glucose, etc. 4. Neutrons and protons are in the atoms nucleus. Electrons orbit around in a shell or cloud. 5. Macromolecules include ...
Document
... • Nutrients are chemical substances in food that provide energy, build cells & tissues ...
... • Nutrients are chemical substances in food that provide energy, build cells & tissues ...
Midterm Review Key 2014
... etc. (If the resulting product is completely different than the reactants, than its most likely a chemical reaction.) 3. There are many, example includes water, salt, glucose, etc. 4. Neutrons and protons are in the atoms nucleus. Electrons orbit around in a shell or cloud. 5. Macromolecules include ...
... etc. (If the resulting product is completely different than the reactants, than its most likely a chemical reaction.) 3. There are many, example includes water, salt, glucose, etc. 4. Neutrons and protons are in the atoms nucleus. Electrons orbit around in a shell or cloud. 5. Macromolecules include ...
File
... Nucleotides – These are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are complex molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a 5-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. ...
... Nucleotides – These are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are complex molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a 5-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. ...
Unit Topic: Chemistry of Life
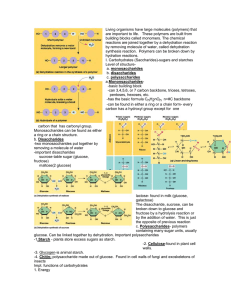
... Explain the role of carbohydrates for living things List the monomers of complex carbohydrates Describe a disaccharide, specifically sucrose Identify the structure of the simple sugar glucose and use this structure to build any of the three major complex carbohydrates: glycogen, starch, cellulose 5. ...
... Explain the role of carbohydrates for living things List the monomers of complex carbohydrates Describe a disaccharide, specifically sucrose Identify the structure of the simple sugar glucose and use this structure to build any of the three major complex carbohydrates: glycogen, starch, cellulose 5. ...
Document
... Monomer: nucleotide (made of 3 parts) a. 5 carbon sugar b. Phosphate group c. Nitrogen base ...
... Monomer: nucleotide (made of 3 parts) a. 5 carbon sugar b. Phosphate group c. Nitrogen base ...
Macromolecules - Van Buren Public Schools
... • Large! • Accomplish all life functions • Types: Carbohydrates, lipids*, proteins, nucleic acids ...
... • Large! • Accomplish all life functions • Types: Carbohydrates, lipids*, proteins, nucleic acids ...
Biology
... Store large amounts of energy (One gram of fat stores twice as much energy as a gram of polysaccharide) ...
... Store large amounts of energy (One gram of fat stores twice as much energy as a gram of polysaccharide) ...
Living organisms have large molecules (polymers) that are
... carbon has a hydroxyl group except for one ...
... carbon has a hydroxyl group except for one ...
Key Terms:
... H+ gradient drives ATP synthesis Glycolysis is universal, anaerobic and cytosolic 2 ATP in; 4 ATP out & 2 reduced coenzymes glucose (six carbons, C6) 2 moleucles of pyruvate (three carbons, C3) Citric Acid Cycle, in the mitochondria Pyruvate crosses into mitochondrial matrix and is converted to ac ...
... H+ gradient drives ATP synthesis Glycolysis is universal, anaerobic and cytosolic 2 ATP in; 4 ATP out & 2 reduced coenzymes glucose (six carbons, C6) 2 moleucles of pyruvate (three carbons, C3) Citric Acid Cycle, in the mitochondria Pyruvate crosses into mitochondrial matrix and is converted to ac ...
2.3: Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Blood contains enzyme carbonic anhydrase – Catalyzes reaction in your blood where carbon dioxide combines with water to form carbonic acid – Makes reaction one million times faster so that carbon dioxide does not build up in your blood, ...
... • Blood contains enzyme carbonic anhydrase – Catalyzes reaction in your blood where carbon dioxide combines with water to form carbonic acid – Makes reaction one million times faster so that carbon dioxide does not build up in your blood, ...
CSM 101 Fall 2010 Timeline
... Tight junctions: Specialized proteins in the plasma membrane line up and bind to one another. This is matched in the nearby cell. The proteins bind to each other and create a water tight seal between the two cells. This won’t allow solutions or any harmful object to pass through. ...
... Tight junctions: Specialized proteins in the plasma membrane line up and bind to one another. This is matched in the nearby cell. The proteins bind to each other and create a water tight seal between the two cells. This won’t allow solutions or any harmful object to pass through. ...
Exam 1 Review KEY
... c. Responsiveness – ability to sense changes in the environment and respond to them d. Digestion – breakdown of ingested food e. Metabolism – all chemical reactions occurring in body f. Excretion – removal of wastes from the body g. Reproduction – cellular and organism levels h. Growth – increase in ...
... c. Responsiveness – ability to sense changes in the environment and respond to them d. Digestion – breakdown of ingested food e. Metabolism – all chemical reactions occurring in body f. Excretion – removal of wastes from the body g. Reproduction – cellular and organism levels h. Growth – increase in ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... 1. Label the pH scale below with the following terms: acid, base, and neutral. ...
... 1. Label the pH scale below with the following terms: acid, base, and neutral. ...
Answers - Shelton State
... carries oxygen. 10. Which of the following are macromolecules? proteins and carbohydrates but not lipids 11. What is the net charge on cysteine, pI=5.1, when the pH=6.3? negative Which way will it move during electrophoresis? Toward the positive electrode. 12. The names of enzymes often identify the ...
... carries oxygen. 10. Which of the following are macromolecules? proteins and carbohydrates but not lipids 11. What is the net charge on cysteine, pI=5.1, when the pH=6.3? negative Which way will it move during electrophoresis? Toward the positive electrode. 12. The names of enzymes often identify the ...
STAAR Review 1
... with one phosphate group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the process. ...
... with one phosphate group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the process. ...
CHAPTER-III CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
... The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is first consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and prod ...
... The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is first consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and prod ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.