Name: Chapter 4 and 5 Study Guide Who was the Greek
... 16. What is going on inside the atoms when a neon light glows? 17. In a periodic table, a set of properties repeats from… a. Element to element b. Group to group c. Column to column d. Row to row 18. The usefulness of Mendeleev’s periodic table was confirmed by… a. The discovery of subatomic particl ...
... 16. What is going on inside the atoms when a neon light glows? 17. In a periodic table, a set of properties repeats from… a. Element to element b. Group to group c. Column to column d. Row to row 18. The usefulness of Mendeleev’s periodic table was confirmed by… a. The discovery of subatomic particl ...
3-ELEMENTS AND THE ATOMIC MODEL. C4.8A Identify the
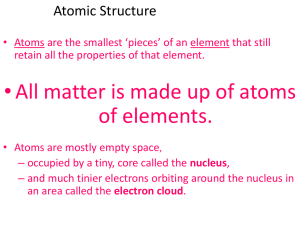
... Describe the atom as mostly empty space with an extremely small, dense nucleus consisting of the protons and neutrons and an electron cloud surrounding the nucleus. Recognize that an element always contains the same number of protons. Describe the location, mass, and charge of protons, electro ...
... Describe the atom as mostly empty space with an extremely small, dense nucleus consisting of the protons and neutrons and an electron cloud surrounding the nucleus. Recognize that an element always contains the same number of protons. Describe the location, mass, and charge of protons, electro ...
Elements Unit Test
... 9. A Dutch scientist by the name of Neils Bohr was the first scientist to figure out that electrons that orbit the nucleus of an atom (sometimes called shells) can only hold a certain number of electrons. Which of the following sets of numbers describe the number of electrons in the first three shel ...
... 9. A Dutch scientist by the name of Neils Bohr was the first scientist to figure out that electrons that orbit the nucleus of an atom (sometimes called shells) can only hold a certain number of electrons. Which of the following sets of numbers describe the number of electrons in the first three shel ...
Atomic Structure
... Different atoms have different ____________ and ____________ The differing properties of matter are due to the size, shape, and movement of ____________ Changes in matter result from changes in the ____________ of atoms and not the atoms themselves ...
... Different atoms have different ____________ and ____________ The differing properties of matter are due to the size, shape, and movement of ____________ Changes in matter result from changes in the ____________ of atoms and not the atoms themselves ...
Nuclear Physics Rutherford`s model of the atom
... Atomic Number: Equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. All atoms have unique atomic numbers; we use these numbers/values to determine the specific element the atom is. The atomic number is found above the elemental symbol. E.g. Helium’s atomic number is 2. Helium is found on righ ...
... Atomic Number: Equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. All atoms have unique atomic numbers; we use these numbers/values to determine the specific element the atom is. The atomic number is found above the elemental symbol. E.g. Helium’s atomic number is 2. Helium is found on righ ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY
... As beta decay was studied over the years following 1899, it was found that the same exact beta decay produced an electron with variable energies. For example, let us study Li-8 becoming Be-8. Each atom of Li-8 produces an electron and the theory says all the electrons should have the same energy. Th ...
... As beta decay was studied over the years following 1899, it was found that the same exact beta decay produced an electron with variable energies. For example, let us study Li-8 becoming Be-8. Each atom of Li-8 produces an electron and the theory says all the electrons should have the same energy. Th ...
The Periodic Table
... Mass number is the count of nucleons in an isotope and atomic mass is the measure of the average mass of an atom including the relative abundance of its element’s isotopes. ...
... Mass number is the count of nucleons in an isotope and atomic mass is the measure of the average mass of an atom including the relative abundance of its element’s isotopes. ...
Atomic Timeline
... Isotopes – atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This change in neutrons is reflected in the Mass Number ...
... Isotopes – atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This change in neutrons is reflected in the Mass Number ...
Isotopes
... time during which 50 % of some bunch of radioactive atoms has split asunder. The atomic number z thus defines completely the type of atom and thus also its general behavior. Since the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is variable to some extent, all atoms come in variants that we call iso ...
... time during which 50 % of some bunch of radioactive atoms has split asunder. The atomic number z thus defines completely the type of atom and thus also its general behavior. Since the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is variable to some extent, all atoms come in variants that we call iso ...
Topic 2.1- The Nuclear Atom
... • the atomic mass on periodic table is the WEIGHTED AVERAGE MASS of “all” the isotopes of that element – this is based on an isotope’s natural abundance • the percentage of each isotope of an element that occurs in nature ...
... • the atomic mass on periodic table is the WEIGHTED AVERAGE MASS of “all” the isotopes of that element – this is based on an isotope’s natural abundance • the percentage of each isotope of an element that occurs in nature ...
Half-Life - Chemistry 1 at NSBHS
... pressure temperature concentration number of neutrons in nucleus ANS: D ...
... pressure temperature concentration number of neutrons in nucleus ANS: D ...
Lecture 2: Atoms - U of L Class Index
... number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more than one naturally occurring isotope: ...
... number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more than one naturally occurring isotope: ...
Early Atomic Theorists
... All nuclear reactions are: transmutation reactions o Some transmutation reactions are induced o All transuranium elements (atomic #93 and greater) have been produced through induced transmutation. ...
... All nuclear reactions are: transmutation reactions o Some transmutation reactions are induced o All transuranium elements (atomic #93 and greater) have been produced through induced transmutation. ...
10B Atoms and Isotopes
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ...
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ...
Periodic Table Vocab page 7
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This number identifies the atom. Mass number: the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number = protons + neutrons Valence #: The number of outermost electrons in an atom. Periodic Table: An arrangement of elem ...
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This number identifies the atom. Mass number: the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number = protons + neutrons Valence #: The number of outermost electrons in an atom. Periodic Table: An arrangement of elem ...
The Atom - VCE Chemistry
... • Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of the atomic nuclei of some elements, such as uranium and radium, into other elements accompanied by the emission of radiation. • After Henri Becquerel's discovery of radioactivity in 1896 and subsequent investigations by the Curies and Rutherford, ...
... • Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of the atomic nuclei of some elements, such as uranium and radium, into other elements accompanied by the emission of radiation. • After Henri Becquerel's discovery of radioactivity in 1896 and subsequent investigations by the Curies and Rutherford, ...
Topic 2.1 The Nuclear Atom
... • this is NOT IB material until indicated • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
... • this is NOT IB material until indicated • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
element - Mrs. Phillips` Physical Science Webpage
... • The periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number. – During Mendeleev’s time, this arrangement left several blanks, however, the table exhibited a regularly repeating pattern, which could be used to predict the properties of elements that had not been discovered yet. – He was proven right ...
... • The periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number. – During Mendeleev’s time, this arrangement left several blanks, however, the table exhibited a regularly repeating pattern, which could be used to predict the properties of elements that had not been discovered yet. – He was proven right ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Quick Notes
... (making it Neutrally Charged) Two types of Atoms: Ions- these are atoms that have LOST or GAINED an ELECTRON during a chemical reaction If an atom loses an electron, it becomes a Positive Ion If an atom gains an electron, it becomes a Negative Ion Ex: when Na reacts with Cl to form NaCl, the Na ...
... (making it Neutrally Charged) Two types of Atoms: Ions- these are atoms that have LOST or GAINED an ELECTRON during a chemical reaction If an atom loses an electron, it becomes a Positive Ion If an atom gains an electron, it becomes a Negative Ion Ex: when Na reacts with Cl to form NaCl, the Na ...
ISOTOPES 3 SUBATOMIC PARTICLES Proton Located inside the
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
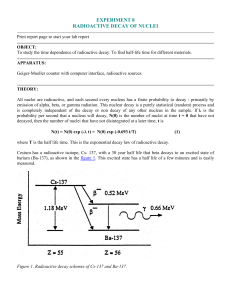
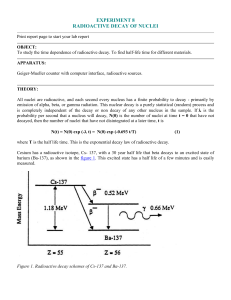
experiment 8 radioactive decay of nuclei
... Indium metal (49In, atomic number of 49) as found on the surface of the earth is 95.72 % mass 115 and 4.28% mass 113. (Using the nuclear masses of 114.9041 and 112.9043 instead of the number of nucleons, 115 and 113, the chemical weight of 114.82 can be calculated.) If the indium is placed where th ...
... Indium metal (49In, atomic number of 49) as found on the surface of the earth is 95.72 % mass 115 and 4.28% mass 113. (Using the nuclear masses of 114.9041 and 112.9043 instead of the number of nucleons, 115 and 113, the chemical weight of 114.82 can be calculated.) If the indium is placed where th ...
Phys 282 EXP 8
... Indium metal (49In, atomic number of 49) as found on the surface of the earth is 95.72 % mass 115 and 4.28% mass 113. (Using the nuclear masses of 114.9041 and 112.9043 instead of the number of nucleons, 115 and 113, the chemical weight of 114.82 can be calculated.) If the indium is placed where th ...
... Indium metal (49In, atomic number of 49) as found on the surface of the earth is 95.72 % mass 115 and 4.28% mass 113. (Using the nuclear masses of 114.9041 and 112.9043 instead of the number of nucleons, 115 and 113, the chemical weight of 114.82 can be calculated.) If the indium is placed where th ...
Test 2 Review Test 2 Review (15-16)_2
... (17) ____________ Which column from above contains VERY non-reactive elements? (18) ____________ How many of these elements are gases at 0 degrees Celsius? (19) ____________ How many of these elements are metalloids? (20) ____________ How many of these elements are NON-metals and solids? (21) ______ ...
... (17) ____________ Which column from above contains VERY non-reactive elements? (18) ____________ How many of these elements are gases at 0 degrees Celsius? (19) ____________ How many of these elements are metalloids? (20) ____________ How many of these elements are NON-metals and solids? (21) ______ ...
Metals
... “elements”: air, fire, water, and earth. People believed this for many centuries! • In the late 1600s, early chemists began to discover that this was not the case, that there are more than 4 elements and they are not what the Greeks thought they were. • Now we know that all matter in the universe is ...
... “elements”: air, fire, water, and earth. People believed this for many centuries! • In the late 1600s, early chemists began to discover that this was not the case, that there are more than 4 elements and they are not what the Greeks thought they were. • Now we know that all matter in the universe is ...