Isotope Worksheet
... ATOMIC! MASS. In other words, isotopes have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Since any atom having 9 protons (Z = 9) must be an atom of fluorine, we can omit the Z-value and just use the symbol F for many purposes, i.e., we can write 19F instead of 19F. ...
... ATOMIC! MASS. In other words, isotopes have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Since any atom having 9 protons (Z = 9) must be an atom of fluorine, we can omit the Z-value and just use the symbol F for many purposes, i.e., we can write 19F instead of 19F. ...
chapter_3_study_guide
... __________________ alpha particles. He found that most alpha particles passed through the gold foil but some were mysteriously deflected by something in the gold. Rutherford concluded there must be a ___________________ ____________________ in the center of the gold atoms that deflected the alpha pa ...
... __________________ alpha particles. He found that most alpha particles passed through the gold foil but some were mysteriously deflected by something in the gold. Rutherford concluded there must be a ___________________ ____________________ in the center of the gold atoms that deflected the alpha pa ...
Radioactivity2015
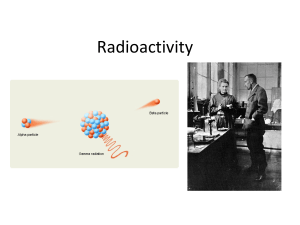
... • The helium nucleus is known as an alpha particle. This process is known as emission. In this case, an atom of uranium changes into an atom of thorium. • The general process of atoms changing into different elements is known as transmutation. • These alpha particles are less dangerous than other ...
... • The helium nucleus is known as an alpha particle. This process is known as emission. In this case, an atom of uranium changes into an atom of thorium. • The general process of atoms changing into different elements is known as transmutation. • These alpha particles are less dangerous than other ...
Isotopes
... Know how to calculate the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons. I’m going to ask you to complete a table like on our ...
... Know how to calculate the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons. I’m going to ask you to complete a table like on our ...
Atomic Structure ppt
... • Protons and neutrons have essentially the same mass. • The mass of an electron is so small we ignore it. ...
... • Protons and neutrons have essentially the same mass. • The mass of an electron is so small we ignore it. ...
Chapter 5 - Effingham County Schools
... Atoms are extremely small. Over a million can fit in the period at the end of this sentence. The identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus, called the ________ ________. For example, a hydrogen atom has 1 proton so its atomic number is 1. The total number of _______ a ...
... Atoms are extremely small. Over a million can fit in the period at the end of this sentence. The identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus, called the ________ ________. For example, a hydrogen atom has 1 proton so its atomic number is 1. The total number of _______ a ...
Radioactive Decay Mechanisms
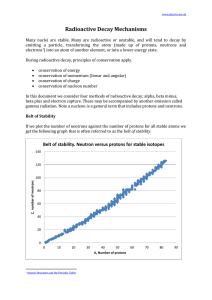
... Note that 1. there are no stable nuclei with an atomic number of 84 or greater. 2. for smaller atoms the ratio neutrons:protons is 1:1 3. for larger atoms the ratio of neutrons:protons approaches about 1.5:1 Since the strong nuclear force weakens significantly with distance, as the atom gets bigger. ...
... Note that 1. there are no stable nuclei with an atomic number of 84 or greater. 2. for smaller atoms the ratio neutrons:protons is 1:1 3. for larger atoms the ratio of neutrons:protons approaches about 1.5:1 Since the strong nuclear force weakens significantly with distance, as the atom gets bigger. ...
Lecture4
... light and have negative. Isotopes of elements contain nuclei with same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Atom where the number of protons does not equal to the number of neutrons is unstable. ...
... light and have negative. Isotopes of elements contain nuclei with same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Atom where the number of protons does not equal to the number of neutrons is unstable. ...
Radioactivity
... light and have negative. Isotopes of elements contain nuclei with same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Atom where the number of protons does not equal to the number of neutrons is unstable. ...
... light and have negative. Isotopes of elements contain nuclei with same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Atom where the number of protons does not equal to the number of neutrons is unstable. ...
Atoms and Atomic Theory
... mean? A good starting point is to analyze what it does not mean. For example, the atomic mass of Cl is often quoted on a periodic table as 35.5 and can be represented by the following symbol; ...
... mean? A good starting point is to analyze what it does not mean. For example, the atomic mass of Cl is often quoted on a periodic table as 35.5 and can be represented by the following symbol; ...
Unit 2 - Chapter 3 Elements, Atoms, Ions The elements Can we
... always has the same composition regardless of where it comes from or how it is made ...
... always has the same composition regardless of where it comes from or how it is made ...
Electron Configuration, Noble Gas Configuration
... Compare and contrast isotopes of Uranium – 234, Uranium – 235 & Uranium – 238? C4.10c Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I can calculate the average atomic mass of an element given the percent abundance and mass of the individual isotopes. Calculate the atomic mass of rubidium. ...
... Compare and contrast isotopes of Uranium – 234, Uranium – 235 & Uranium – 238? C4.10c Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I can calculate the average atomic mass of an element given the percent abundance and mass of the individual isotopes. Calculate the atomic mass of rubidium. ...
Chapter 3 notes
... • Orbital- or energy shell/level is a region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons. • Valence electron- an electron in the outermost energy level of an atom. So in Al valence 3. ...
... • Orbital- or energy shell/level is a region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons. • Valence electron- an electron in the outermost energy level of an atom. So in Al valence 3. ...
Classifying Matter and the Periodic Table
... was scattered by atomic nuclei in a piece of gold foil. A lead shield protected researchers from the radiation. ...
... was scattered by atomic nuclei in a piece of gold foil. A lead shield protected researchers from the radiation. ...
Unit 3 - Princeton High School
... radioactive material present. A sample decays at the rate of 544 counts/min (cpm) in 1995. In what year will the decay rate be 27 cpm? – Answ: 130 yrs, 2125 ...
... radioactive material present. A sample decays at the rate of 544 counts/min (cpm) in 1995. In what year will the decay rate be 27 cpm? – Answ: 130 yrs, 2125 ...
Chapter Review - BAschools.org
... 13. The modern periodic table is organized by a. size of atom b. atomic mass c. number of neutrons d. atomic number 14. Elements in a group have a. a wide range of chemical properties b. the same atomic radius c. similar chemical properties d. the same number of protons 15. Elements in a period have ...
... 13. The modern periodic table is organized by a. size of atom b. atomic mass c. number of neutrons d. atomic number 14. Elements in a group have a. a wide range of chemical properties b. the same atomic radius c. similar chemical properties d. the same number of protons 15. Elements in a period have ...
Average Atomic Mass
... hydronitric acid zinc nitrate cobalt (III) hydroxide pentanitrogen octoxide ...
... hydronitric acid zinc nitrate cobalt (III) hydroxide pentanitrogen octoxide ...
The Basics of Atomic Structure
... number of neutrons; therefore, the mass number will be different for the same element. All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, some are more common than others. • An Ion is an element with a number of electrons that differ from its number of protons. An ion is a charged atom. – Cation is ...
... number of neutrons; therefore, the mass number will be different for the same element. All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, some are more common than others. • An Ion is an element with a number of electrons that differ from its number of protons. An ion is a charged atom. – Cation is ...
Ch 3 studentElements Ions Isotopes
... – If it’s an atom, the protons and electrons must be the SAME so that it is has a net charge of zero (equal numbers of + and -) – If it does NOT have an equal number of electrons, it is not an atom, it is an ION. For each negative charge, add an extra electron. For each positive charge, subtract an ...
... – If it’s an atom, the protons and electrons must be the SAME so that it is has a net charge of zero (equal numbers of + and -) – If it does NOT have an equal number of electrons, it is not an atom, it is an ION. For each negative charge, add an extra electron. For each positive charge, subtract an ...
ps-5-1-and-5-2-ws
... 16.The average mass of all the isotopes of an element is called the ___________________________ 17.The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing _______________________________ 18. Information found on the periodic table for each element includes its atomic number, , name, and atomic ...
... 16.The average mass of all the isotopes of an element is called the ___________________________ 17.The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing _______________________________ 18. Information found on the periodic table for each element includes its atomic number, , name, and atomic ...
Periodic Table Review Key
... H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductors? G 7. Which elements are considered poor conductors? F, B, A,H 8. Which element is considered met ...
... H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductors? G 7. Which elements are considered poor conductors? F, B, A,H 8. Which element is considered met ...
Chemistry Notes (pg. # 1)
... 2.)Also, the positive charge is very c________ in a small _________. 3.) This experiment disproved the _____ _____ ______. ...
... 2.)Also, the positive charge is very c________ in a small _________. 3.) This experiment disproved the _____ _____ ______. ...