Isotopes
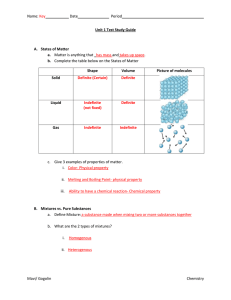
... • Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. • They can be a radioactive form of an element. – Atoms of the same element all have the same number of protons. – Isotopes of the element have different numbers of neutrons. ...
... • Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. • They can be a radioactive form of an element. – Atoms of the same element all have the same number of protons. – Isotopes of the element have different numbers of neutrons. ...
03.03a Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Isotopes
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
PS 2.2 - S2TEM Centers SC
... atoms” (7-5.1). Students have no prior knowledge about the structure of the atom. In Physical Science, students identify and compare the subatomic particles that compose atoms and develop a fundamental concept of the role that these three particles have in determining the properties of the atoms tha ...
... atoms” (7-5.1). Students have no prior knowledge about the structure of the atom. In Physical Science, students identify and compare the subatomic particles that compose atoms and develop a fundamental concept of the role that these three particles have in determining the properties of the atoms tha ...
PowerPoint Presentation - The Atom: Chp 12 sect 2
... the same, • although the physical properties of some isotopes may be different. • Some isotopes are radioactivemeaning they "radiate" energy as they decay to a more stable form, • perhaps another element half-life: time required for half of the atoms of an element to decay into stable form. ...
... the same, • although the physical properties of some isotopes may be different. • Some isotopes are radioactivemeaning they "radiate" energy as they decay to a more stable form, • perhaps another element half-life: time required for half of the atoms of an element to decay into stable form. ...
Study Guide Answer Key
... by which J.J. Thomson demonstrated that cathode rays could be deflected by a magnetic field, and that their negative charge was not a separate phenomenon. i. ...
... by which J.J. Thomson demonstrated that cathode rays could be deflected by a magnetic field, and that their negative charge was not a separate phenomenon. i. ...
3-10 What are isotopes?
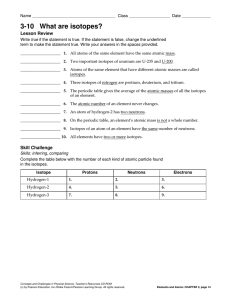
... 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true about the atomic numbers for all the isotopes of carbon? For all the isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen? _____________________________________________________________________ 7. One of thes ...
... 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true about the atomic numbers for all the isotopes of carbon? For all the isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen? _____________________________________________________________________ 7. One of thes ...
Getting to Know: Periodic Table
... element do not have the same number of neutrons. For example, most atoms of the element carbon, C, have 6 neutrons in their nucleus. There are some atoms of carbon that have 7 or even 8 neutrons in their nucleus. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
... element do not have the same number of neutrons. For example, most atoms of the element carbon, C, have 6 neutrons in their nucleus. There are some atoms of carbon that have 7 or even 8 neutrons in their nucleus. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... (amu) is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom. ...
... (amu) is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom. ...
atomic numbers
... - too few or too many neutrons can result in nuclear instability and then radioactivity ...
... - too few or too many neutrons can result in nuclear instability and then radioactivity ...
Name: Period:______ Date: CHEMISTRY Chapter 3 AND Nuclear
... 1. Made a mental model of the atom by thinking about repeatedly cutting a piece of gold in half until he reached a basic particle that could no longer be cut in half and still be gold; he called the smallest particle atomos; Greek philosopher. 2. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom. 3. T ...
... 1. Made a mental model of the atom by thinking about repeatedly cutting a piece of gold in half until he reached a basic particle that could no longer be cut in half and still be gold; he called the smallest particle atomos; Greek philosopher. 2. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom. 3. T ...
Chapter 4 Review
... mass number of an element is equal to _____. The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom equals the __. What is the purpose of comparing the number of atoms of copper in a coin the size of a penny with the number of people on the earth? ...
... mass number of an element is equal to _____. The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom equals the __. What is the purpose of comparing the number of atoms of copper in a coin the size of a penny with the number of people on the earth? ...
File
... of radioactive decay. - Radioactive decay: the atomic nuclei of radioactive isotopes release fast-moving particles and energy. - Example of a nuclear reaction: process that involves the particles of an atom’s nucleus. - Radioactivity: The spontaneous emission of radiation by an unstable atomic nucle ...
... of radioactive decay. - Radioactive decay: the atomic nuclei of radioactive isotopes release fast-moving particles and energy. - Example of a nuclear reaction: process that involves the particles of an atom’s nucleus. - Radioactivity: The spontaneous emission of radiation by an unstable atomic nucle ...
Sub-Atomic Particles and the Nuclear Atom - Chemistry-at-PA
... 5b. Atomos are hard dense spheres true, they are according to Democritus 5c. Atomos have varying density – they are heterogeneous.false- they are homogeneous 5d. Changes in matter are due to the changes in atomos. False –atomos do not change 6a. All matter is made of small particles called atoms. tr ...
... 5b. Atomos are hard dense spheres true, they are according to Democritus 5c. Atomos have varying density – they are heterogeneous.false- they are homogeneous 5d. Changes in matter are due to the changes in atomos. False –atomos do not change 6a. All matter is made of small particles called atoms. tr ...
- Los Banos Unified School District
... 1911 Ernest Rutherford Using alpha particles as atomic bullets, probed the atoms in a piece of thin (0.00006 cm) gold foil. He established that the nucleus was: very dense, very small and positively charged. 1938 Enrico Fermi Conducted the first controlled chain reaction releasing energy from the at ...
... 1911 Ernest Rutherford Using alpha particles as atomic bullets, probed the atoms in a piece of thin (0.00006 cm) gold foil. He established that the nucleus was: very dense, very small and positively charged. 1938 Enrico Fermi Conducted the first controlled chain reaction releasing energy from the at ...
Periodic Scavenger Hunt - bates
... 8. The atomic mass of an element is a combination of the number of protons and neutrons. Because the same element does not always have the same number of neutrons, the atomic mass is an average mass of the element as it occurs in nature. What is the atomic mass of fluorine? ...
... 8. The atomic mass of an element is a combination of the number of protons and neutrons. Because the same element does not always have the same number of neutrons, the atomic mass is an average mass of the element as it occurs in nature. What is the atomic mass of fluorine? ...
Chapter 4 Review “Atomic Structure
... mass number of an element is equal to _____. The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom equals the __. What is the purpose of comparing the number of atoms of copper in a coin the size of a penny with the number of people on the earth? ...
... mass number of an element is equal to _____. The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom equals the __. What is the purpose of comparing the number of atoms of copper in a coin the size of a penny with the number of people on the earth? ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE
... understand how it works, you'll be able to use it to figure out how and why elements interact to make the world you see around you! Let's start with The Basics. Today we know quite a bit about atoms. But how did we ever know about atoms in the first place? The earliest known concept of the atom came ...
... understand how it works, you'll be able to use it to figure out how and why elements interact to make the world you see around you! Let's start with The Basics. Today we know quite a bit about atoms. But how did we ever know about atoms in the first place? The earliest known concept of the atom came ...
Periodic Table
... –Included elements Valence # (bonding power) •How many e- the atom can lose or gain when bonding •Pattern appeared - 1234321 ...
... –Included elements Valence # (bonding power) •How many e- the atom can lose or gain when bonding •Pattern appeared - 1234321 ...
2010 Physical Science Comprehensive Test REVIEW Ch 0.3 Sig
... 38. Be able to identify the atomic number, mass number, and stable isotopes. Your periodic table will not have a key on it. Such as: What is the atomic number of phosphorus? Such as: What is the mass number of K-41? Such as: K-41 is stable, but K-40 is not 42. Many models have been developed to expl ...
... 38. Be able to identify the atomic number, mass number, and stable isotopes. Your periodic table will not have a key on it. Such as: What is the atomic number of phosphorus? Such as: What is the mass number of K-41? Such as: K-41 is stable, but K-40 is not 42. Many models have been developed to expl ...
Chapter 4: Atomic Structure
... the region the nucleus. (a tiny central core of an atom and is composed of protons and neutrons) Rutherford’s atomic model is known as the nuclear atom. In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all of ...
... the region the nucleus. (a tiny central core of an atom and is composed of protons and neutrons) Rutherford’s atomic model is known as the nuclear atom. In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all of ...
Chemistry 1 – Tollett Chapter 5 – Atomic Structure & The Periodic
... Atomic Mass Unit (amu) – is defined as one-twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. ...
... Atomic Mass Unit (amu) – is defined as one-twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. ...
Atom, Ion, Isotope Notes from 10/5 and 10/6
... a good estimation for finding the most common stable isotope of an atom. HOWEVER, it is not a perfect method. Look at Ag for example. It’s atomic mass is 107.87 amu, which would round to 108 amu. This is actually NOT a stable isotope of Ag (only 107 amu and 109 amu are). If you really wanted to know ...
... a good estimation for finding the most common stable isotope of an atom. HOWEVER, it is not a perfect method. Look at Ag for example. It’s atomic mass is 107.87 amu, which would round to 108 amu. This is actually NOT a stable isotope of Ag (only 107 amu and 109 amu are). If you really wanted to know ...
Name
... What effect did Democritus have on the theory of the atom? Was his theory consistent with modern atomic theories? How did it differ? ...
... What effect did Democritus have on the theory of the atom? Was his theory consistent with modern atomic theories? How did it differ? ...