Mixtures, Pure Substance and Isotopes
... from atomic number of N = 7 7 protons isotope number – atomic number (= 16-7) 9 neutrons number of protons = no. of electrons 7 electrons ...
... from atomic number of N = 7 7 protons isotope number – atomic number (= 16-7) 9 neutrons number of protons = no. of electrons 7 electrons ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... 1. Democritus a. 400 BC, first suggested the existence of indivisible atoms b. No research, no experimental support 2. John Dalton a. late 1700’s conducted research and experiments b. result was Dalton’s atomic theory: 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms (we know ...
... 1. Democritus a. 400 BC, first suggested the existence of indivisible atoms b. No research, no experimental support 2. John Dalton a. late 1700’s conducted research and experiments b. result was Dalton’s atomic theory: 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms (we know ...
CS 211 – Spring 2017 Lab 4: Molar Mass
... Also note on rows 6-10, the Element is BLANK, and so the Atomic Weight and Subtotals are EMPTY. When the user selects another atom in A6-10, Columns C and D should be populated. The second example is for Ethanol (C2H6O). ...
... Also note on rows 6-10, the Element is BLANK, and so the Atomic Weight and Subtotals are EMPTY. When the user selects another atom in A6-10, Columns C and D should be populated. The second example is for Ethanol (C2H6O). ...
Academic Chemistry Chapter 3 Review Activity
... What is an Anion? An anion is a negatively charged ion. It results from an atom gaining electrons. ...
... What is an Anion? An anion is a negatively charged ion. It results from an atom gaining electrons. ...
Chapter 3, Part 2 Review Packet
... What is an Anion? An anion is a negatively charged ion. It results from an atom gaining electrons. ...
... What is an Anion? An anion is a negatively charged ion. It results from an atom gaining electrons. ...
Goal 4.01
... Given the notation of an element you should be able to determine the number of p, n, and e. The first step is to find the element on the periodic table and determine its atomic number which gives you the number of p. The number of p’s will never change. From there you must determine the number of n ...
... Given the notation of an element you should be able to determine the number of p, n, and e. The first step is to find the element on the periodic table and determine its atomic number which gives you the number of p. The number of p’s will never change. From there you must determine the number of n ...
File - Biochemistry
... Gamma Ray Emission: following Beta particle decay the nucleus still has ___________ so the nucleus releases it as ______________ - both the atomic mass and number remain the ______ ...
... Gamma Ray Emission: following Beta particle decay the nucleus still has ___________ so the nucleus releases it as ______________ - both the atomic mass and number remain the ______ ...
Isotopes-Chemistry
... Same Element Different AtomIsotopes All atoms of a particular element are not exactly alike. Some elements have atoms with different masses (isotopes) ...
... Same Element Different AtomIsotopes All atoms of a particular element are not exactly alike. Some elements have atoms with different masses (isotopes) ...
Reading Assignment Worksheet on Atoms - District 196 e
... 2. In this table, where are the metals located? 3. Where are the nonmetals located? 4. What are the elements in Groups 3 through 12 called? 5. What are the elements called that are next to the stairstep-shaped line on the right side of the table? 6. What do we call the letter or letters that represe ...
... 2. In this table, where are the metals located? 3. Where are the nonmetals located? 4. What are the elements in Groups 3 through 12 called? 5. What are the elements called that are next to the stairstep-shaped line on the right side of the table? 6. What do we call the letter or letters that represe ...
Isotopes Article
... time taken for the compound present to become its half amount by the decay process is called the half-life period. All the isotopes are not radioactive. Only some isotopic forms are unstable and undergo decay. In nature, many forms of isotopes for every element exist. How they exist is not explained ...
... time taken for the compound present to become its half amount by the decay process is called the half-life period. All the isotopes are not radioactive. Only some isotopic forms are unstable and undergo decay. In nature, many forms of isotopes for every element exist. How they exist is not explained ...
No Slide Title
... • This term describes a metal that can be pounded or rolled into shape. • What is malleable. ...
... • This term describes a metal that can be pounded or rolled into shape. • What is malleable. ...
periodic table elements
... the center of each atom lies the atomic __________________, which consists of _____________and__________. The atomic number refers to the number of ______________ in the nucleus of the atom. Atoms typically have the same number of electrons as the number of protons. All atoms of the same element hav ...
... the center of each atom lies the atomic __________________, which consists of _____________and__________. The atomic number refers to the number of ______________ in the nucleus of the atom. Atoms typically have the same number of electrons as the number of protons. All atoms of the same element hav ...
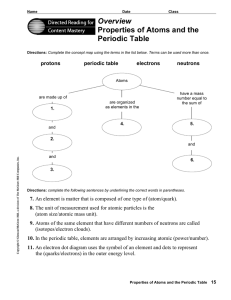
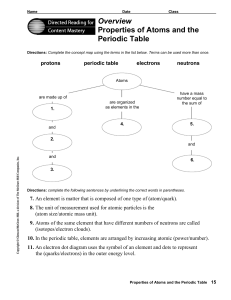
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. ...
The History of the Atom - Brookville Local Schools
... o For a very long time, nobody did any scientific experimentation, so the idea of the atom was left in the realm of pure thought. However, Enlightenment philosophy taught that reason was the only true basis for knowing, so experimentation restarted. o Law of Conservation of Mass (Lavoisier): The wei ...
... o For a very long time, nobody did any scientific experimentation, so the idea of the atom was left in the realm of pure thought. However, Enlightenment philosophy taught that reason was the only true basis for knowing, so experimentation restarted. o Law of Conservation of Mass (Lavoisier): The wei ...
Name ____ Date
... number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atoms of different elements. 8. What is the mole and how is the concept used in measuring quantities of an element? 9. How is the periodic table used to determine protons, neutrons, and electrons (especially valence electrons)? 10. What is a group or ...
... number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atoms of different elements. 8. What is the mole and how is the concept used in measuring quantities of an element? 9. How is the periodic table used to determine protons, neutrons, and electrons (especially valence electrons)? 10. What is a group or ...
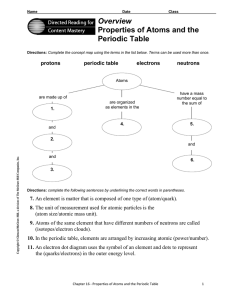
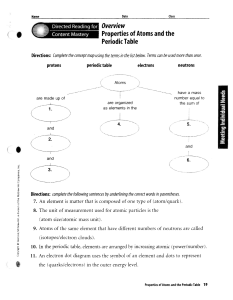
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. ...
chapter 2-1 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Radioactivity—process of spontaneous atomic decay What can we use this for? ...
... Radioactivity—process of spontaneous atomic decay What can we use this for? ...
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. electron cloud six number electrons isotopes six protons neutron(s) proton(s) mass quarks The electron has vcry little mass compared to the 1. ...
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. electron cloud six number electrons isotopes six protons neutron(s) proton(s) mass quarks The electron has vcry little mass compared to the 1. ...
Two valence electrons.
... elements by increasing atomic mass, leaving blank spaces where he was sure elements Dmitri yet to be discovered Mendeleev would fit. ...
... elements by increasing atomic mass, leaving blank spaces where he was sure elements Dmitri yet to be discovered Mendeleev would fit. ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different. What makes atoms of different elements different? The fundamental characteristic that all atoms of the same element share is the number of protons . All atoms of hydrogen have on ...
... The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different. What makes atoms of different elements different? The fundamental characteristic that all atoms of the same element share is the number of protons . All atoms of hydrogen have on ...
isotopes
... superscript to the left of the symbol 3.) the atomic number is written as a subscript to the left. Study the illustration below ...
... superscript to the left of the symbol 3.) the atomic number is written as a subscript to the left. Study the illustration below ...
Elements, Isotopes and Ions
... 1. Any atom of Calcium can have 20, 22, or 24 neutrons. These different versions of Calcium are called ...
... 1. Any atom of Calcium can have 20, 22, or 24 neutrons. These different versions of Calcium are called ...
ISOTOPES
... of atomic structure we have been developing, this would mean that each atom of an element would have the same number of protons, electrons, and neutrons as every other atom of the element. Thus the atomic mass of every atom of an element would be the same. In the early twentieth century, scientists ...
... of atomic structure we have been developing, this would mean that each atom of an element would have the same number of protons, electrons, and neutrons as every other atom of the element. Thus the atomic mass of every atom of an element would be the same. In the early twentieth century, scientists ...