and View
... atom. * Number never changes* b. Isotopes—atoms of same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ex: carbon-12, carbon-13, carbon-14 c. Mass number—number of neutrons plus protons in an atom. i. Neutron number is found by--Mass number - Atomic number _______________ Number of neutrons ...
... atom. * Number never changes* b. Isotopes—atoms of same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ex: carbon-12, carbon-13, carbon-14 c. Mass number—number of neutrons plus protons in an atom. i. Neutron number is found by--Mass number - Atomic number _______________ Number of neutrons ...
Chapter 10 Test A
... c. there are no elements associated with these light sources. d. all elements have the same spectral pattern. ____ 18. Heisenburg’s uncertainty principle tells us that: a. the act of observing in the quantum world changes the very system you are trying to measure. b. we are always uncertain about th ...
... c. there are no elements associated with these light sources. d. all elements have the same spectral pattern. ____ 18. Heisenburg’s uncertainty principle tells us that: a. the act of observing in the quantum world changes the very system you are trying to measure. b. we are always uncertain about th ...
Isotope PPT - MrsPage.com
... • You will be able to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in different isotopes of the same element. • You will understand that atomic mass • You will understand what radioactivity is the average of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. • You will be able to give examp ...
... • You will be able to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in different isotopes of the same element. • You will understand that atomic mass • You will understand what radioactivity is the average of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. • You will be able to give examp ...
Isotope Practice Worksheet
... Atoms of a given element which have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes have the same position in the periodic table, the same chemical properties and the same atomic charge. ...
... Atoms of a given element which have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes have the same position in the periodic table, the same chemical properties and the same atomic charge. ...
Chapter 5 “Atomic Structure and the Periodic table”
... 2)Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3)Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 4)In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed ...
... 2)Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3)Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 4)In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed ...
The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 2 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... 1. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, the properties of the elements recur periodically, i.e. the properties displayed by the element are repeated at regular intervals in oth ...
... 1. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, the properties of the elements recur periodically, i.e. the properties displayed by the element are repeated at regular intervals in oth ...
Another look at chemical reactions HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WATER
... - The AVERAGE MASS of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. Example: Hydrogen has an atomic weight of 1.008 "atomic mass units" (Naturally-occurring hydrogen is almost all Hydrogen-1!) ...
... - The AVERAGE MASS of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. Example: Hydrogen has an atomic weight of 1.008 "atomic mass units" (Naturally-occurring hydrogen is almost all Hydrogen-1!) ...
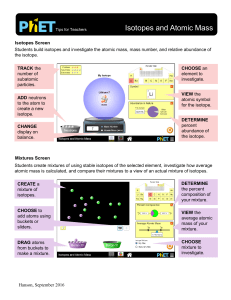
Isotopes and Atomic Mass
... • Calculate the mass number and write the name and atomic symbol for these isotopes of hydrogen: protium (0 neutrons), deuterium (1 neutron), and tritium (2 neutrons). • Your friend claims, “The chance of finding a specific isotope of an element is the same for all isotopes of that element”. Explain ...
... • Calculate the mass number and write the name and atomic symbol for these isotopes of hydrogen: protium (0 neutrons), deuterium (1 neutron), and tritium (2 neutrons). • Your friend claims, “The chance of finding a specific isotope of an element is the same for all isotopes of that element”. Explain ...
Chapter 4.3: How Atoms Differ
... When writing radioactive decomposition reactions, the mass numbers (top) and the atomic numbers (bottom) must be equal on both sides. Radioactivity Problems – write the equations for the following radioactive decomposition reactions ...
... When writing radioactive decomposition reactions, the mass numbers (top) and the atomic numbers (bottom) must be equal on both sides. Radioactivity Problems – write the equations for the following radioactive decomposition reactions ...
Some isotopes - Red Hook Central School District
... Which atoms are unstable? • All atoms with more than 83 protons • Some isotopes of atoms with less than 83 protons do not have the right proton to neutron ratio to be stable ...
... Which atoms are unstable? • All atoms with more than 83 protons • Some isotopes of atoms with less than 83 protons do not have the right proton to neutron ratio to be stable ...
are made up of
... that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron arrangement from your textbook.In Table I, write.the maximum number of electrons that can f ...
... that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron arrangement from your textbook.In Table I, write.the maximum number of electrons that can f ...
Atomic Timeline - Ms Brown`s Chemistry Page
... elements can be combined; that atoms cannot be divided or separated; and that elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. • Used actual experimental work from Antoine Lavoisier (Law of conservation of Mass) and Joseph Proust (Law of Definite Proportions) to support his theory. ...
... elements can be combined; that atoms cannot be divided or separated; and that elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. • Used actual experimental work from Antoine Lavoisier (Law of conservation of Mass) and Joseph Proust (Law of Definite Proportions) to support his theory. ...
Structure-Prop of Matter session
... Carbon-14 and Carbon-13 atoms’ are not as stable as carbon-12 and easily break down. If an isotope has too many or too few neutrons compared to the number of protons, it is unstable and will undergo radioactive decay. These radioactive isotopes become different elements in an effort to become more s ...
... Carbon-14 and Carbon-13 atoms’ are not as stable as carbon-12 and easily break down. If an isotope has too many or too few neutrons compared to the number of protons, it is unstable and will undergo radioactive decay. These radioactive isotopes become different elements in an effort to become more s ...
SS18A - Atoms, Isotopes and Ions
... have different numbers of neutrons. These different forms of the same element are called isotopes. Sometimes the mass number for an element is included in its symbol. When the symbol is written in this way, we call it isotope notation. The isotope notation for carbon-12 is shown to the right. You ca ...
... have different numbers of neutrons. These different forms of the same element are called isotopes. Sometimes the mass number for an element is included in its symbol. When the symbol is written in this way, we call it isotope notation. The isotope notation for carbon-12 is shown to the right. You ca ...
Alpha Decay Alpha decay can most simply be described like this: 1
... Gamma radiation ( ) is the emission of high energy photons in the range of 10-10 m, with no matter associated with it. Gamma rays are normally the by-products of other alpha or beta emissions. Gamma rays have no effect on either mass or charge, gamma rays only stabilize the nucleus by releasing some ...
... Gamma radiation ( ) is the emission of high energy photons in the range of 10-10 m, with no matter associated with it. Gamma rays are normally the by-products of other alpha or beta emissions. Gamma rays have no effect on either mass or charge, gamma rays only stabilize the nucleus by releasing some ...
Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Isotopes
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
Atomic Structure
... (Figure 18.1) this nuclide is neutron-poor, so it must do something to decrease the number of protons or increase the number of neutrons. ...
... (Figure 18.1) this nuclide is neutron-poor, so it must do something to decrease the number of protons or increase the number of neutrons. ...
14_1_atoms and isotopes FPS3
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ...
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ...
12.1 Atoms and Isotopes
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
Lesson Outline - WordPress.com
... 1. Boron has two isotopes. The first, has a mass of 10.01 u and makes up 19.78%. The second, has a mass of 11.01 u and makes up 80.22%. What is the average atomic mass of Boron? 2. Silver has two isotopes, the first has a mass of 106.9 u and an abundance of 51.8%, the second has a mass of 108.9 u an ...
... 1. Boron has two isotopes. The first, has a mass of 10.01 u and makes up 19.78%. The second, has a mass of 11.01 u and makes up 80.22%. What is the average atomic mass of Boron? 2. Silver has two isotopes, the first has a mass of 106.9 u and an abundance of 51.8%, the second has a mass of 108.9 u an ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... – Other isotopes are radioactive, having unstable atoms that spontaneously break apart (decay) to form other atoms – When radioactive atoms decay, energy is released ...
... – Other isotopes are radioactive, having unstable atoms that spontaneously break apart (decay) to form other atoms – When radioactive atoms decay, energy is released ...