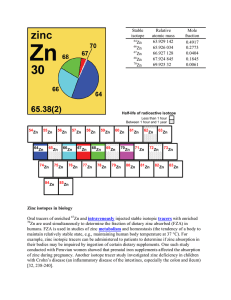
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... by a radioactive isotope used as a tracer, which emits positrons and which is introduced into the body on a biologically-active molecule. Three-dimensional images of the concentration of the radioactive isotope within the body are then constructed by computer analysis. The imaging often is performed ...
... by a radioactive isotope used as a tracer, which emits positrons and which is introduced into the body on a biologically-active molecule. Three-dimensional images of the concentration of the radioactive isotope within the body are then constructed by computer analysis. The imaging often is performed ...
1. Of the three major categories of elements (metals, non
... They are called groups or families. 12. What are the horizontal rows on the periodic table called? They are called periods. 13. Explain the relationship between elements in the same group. They have similar chemical and physical properties because each one has the same number of valence electrons. ...
... They are called groups or families. 12. What are the horizontal rows on the periodic table called? They are called periods. 13. Explain the relationship between elements in the same group. They have similar chemical and physical properties because each one has the same number of valence electrons. ...
Atoms - ChemistryatBiotech
... lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus Proton and neutrons stay the same number. ...
... lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus Proton and neutrons stay the same number. ...
and the atomic
... • this is NOT IB material until Rutherford • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
... • this is NOT IB material until Rutherford • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
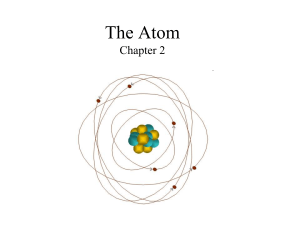
The Atom Chapter 2
... • The existence of multiple pure forms of an element, in the same phase (solid, liquid, or gas), that differ in structure • Different forms are called allotropes • Can exhibit varied physical properties and chemical behaviors ...
... • The existence of multiple pure forms of an element, in the same phase (solid, liquid, or gas), that differ in structure • Different forms are called allotropes • Can exhibit varied physical properties and chemical behaviors ...
Problem Set 4 - Morrisville.org
... positive end of a magnet is brought near the ray. 10) What key conclusions did Thomson draw from his observations? 11) Rutherford used radioactive material to fire positively charged particles at thin sheets of metal. a. What is the name of those particles? b. What is the composition of those partic ...
... positive end of a magnet is brought near the ray. 10) What key conclusions did Thomson draw from his observations? 11) Rutherford used radioactive material to fire positively charged particles at thin sheets of metal. a. What is the name of those particles? b. What is the composition of those partic ...
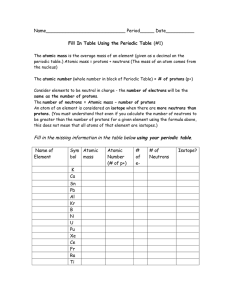
Periodic Table Fill in Table 1
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
CHEMISTRY The Molecular Science
... • An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements have different properties. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relative number of atoms of ea ...
... • An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements have different properties. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relative number of atoms of ea ...
Chemistry lecture notes
... The heavier ones have higher proportion of neutrons as pb 208. As Z increases the electro static repulsion comes to be dominate. There is a limit to the number of stable nuclei. All elements beyond Bi (z=83)being radioactive. ...
... The heavier ones have higher proportion of neutrons as pb 208. As Z increases the electro static repulsion comes to be dominate. There is a limit to the number of stable nuclei. All elements beyond Bi (z=83)being radioactive. ...
Physical Science Notes–Ch. 17-Glencoe
... So far, scientists have confirmed the existence of __________uniquely different ...
... So far, scientists have confirmed the existence of __________uniquely different ...
Periodic Table
... • Many are gases at room temperature; those that are solids lack the luster of metals. ...
... • Many are gases at room temperature; those that are solids lack the luster of metals. ...
Atoms - Science with Mrs. Schulte
... Also arranged in rows and columns, where elements share properties with the other elements in their groups ...
... Also arranged in rows and columns, where elements share properties with the other elements in their groups ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom Early Ideas about Matter Name
... Oil drop experiment (gravity, e– charge, and charged plates) α – particle / gold foil ...
... Oil drop experiment (gravity, e– charge, and charged plates) α – particle / gold foil ...
Present - Images
... Nuclear reactions change the composition of an atom’s nucleus –the element will change!! Examples of naturally occurring nuclear reactions include alpha and beta decay, and fission and fusion. Some nuclei can become unstable by artificial transmutation, where a nucleus is bombarded (or shot) wit ...
... Nuclear reactions change the composition of an atom’s nucleus –the element will change!! Examples of naturally occurring nuclear reactions include alpha and beta decay, and fission and fusion. Some nuclei can become unstable by artificial transmutation, where a nucleus is bombarded (or shot) wit ...
Atomic Structure Power Point
... is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each isotope may have different characteristics. ...
... is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each isotope may have different characteristics. ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... down into another substance by chemical or physical means. ...
... down into another substance by chemical or physical means. ...
Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
levels of organization and the atom
... The subatomic particles that make up the atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Strong forces bind protons and neutrons together to form the nucleus, which is at the center of the atom. Here is the atom’s mass. Protons and neutrons have the same mass, 1 atomic mass unit (amu). However, protons ...
... The subatomic particles that make up the atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Strong forces bind protons and neutrons together to form the nucleus, which is at the center of the atom. Here is the atom’s mass. Protons and neutrons have the same mass, 1 atomic mass unit (amu). However, protons ...
Abstract
... lighter ones. Such isotope changes are called mass-dependent fractionation. The large isotope fractionation takes place between two isotopes with a large mass difference. In the case of oxygen, the fractionation in (18O/16O) is two times larger than that in (17O/16O). It comes to be known that some ...
... lighter ones. Such isotope changes are called mass-dependent fractionation. The large isotope fractionation takes place between two isotopes with a large mass difference. In the case of oxygen, the fractionation in (18O/16O) is two times larger than that in (17O/16O). It comes to be known that some ...
Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... Mass number (A) = # protons + # neutrons Atomic number (Z) = # protons ...
... Mass number (A) = # protons + # neutrons Atomic number (Z) = # protons ...
Lecture 2
... number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more than one naturally occurring isotope: ...
... number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more than one naturally occurring isotope: ...
atom - Images
... Nuclear reactions change the composition of an atom’s nucleus –the element will change!! Examples of naturally occurring nuclear reactions include alpha and beta decay, and fission and fusion. Some nuclei can become unstable by artificial transmutation, where a nucleus is bombarded (or shot) wit ...
... Nuclear reactions change the composition of an atom’s nucleus –the element will change!! Examples of naturally occurring nuclear reactions include alpha and beta decay, and fission and fusion. Some nuclei can become unstable by artificial transmutation, where a nucleus is bombarded (or shot) wit ...
Chapter 14: Inside the Atom
... • Beta particle = high energy electron that comes from the nucleus, not from the electron cloud. • Neutron becomes unstable and splits into a proton (+) and an electron (-) • Electron (-) is given off • Nucleus now has 1 more proton (+), and is a new element. ...
... • Beta particle = high energy electron that comes from the nucleus, not from the electron cloud. • Neutron becomes unstable and splits into a proton (+) and an electron (-) • Electron (-) is given off • Nucleus now has 1 more proton (+), and is a new element. ...