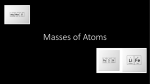* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Quick Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Quick Notes Atom: the smallest unit of an element that contains the properties of that element Ex: if you have 1 gold atom, you can’t break that apart anymore and still have gold Nucleus: the center of an atom. Contains both Protons and Neutrons Protons are POSITIVE Neutrons are NEUTRAL Electrons are NEGATIVE- found in the electron cloud. Atomic Structure and Symbols: *Atomic Number: shows how many Protons are in the atom *Atomic Mass: shows how many Protons + Neutrons are in the atom *To find the number of Neutrons, simply subtract the Atomic Number from the Atomic Mass *Generally speaking, an atom will have the same number of Protons and Electrons, (making it Neutrally Charged) Two types of Atoms: Ions- these are atoms that have LOST or GAINED an ELECTRON during a chemical reaction If an atom loses an electron, it becomes a Positive Ion If an atom gains an electron, it becomes a Negative Ion Ex: when Na reacts with Cl to form NaCl, the Na atom loses an electron, making it a Positive Ion: Na+ The Cl, which gains the electron, now has more negative particles than positive, becoming a Negative Ion: ClIons form when metals react with non-metals to form compounds. These types of chemical bonds are known as Ionic Bonds. See other side for Isotopes and more information Isotopes: these are elements that have abnormal numbers of Neutrons. They tend to be radioactive, and will undergo a radioactive decay (remember: Alpha, Beta, Gamma) - “normal” Carbon has an Atomic Mass of 12; this means it has a total of 12 Protons + Carbon Isotope Normal Carbon Neutrons A common isotope of Carbon, called Carbon 14 has an Atomic Mass of 14. It has 14 Protons + Neutrons, or 2 more Neutrons than “normal”; it is an ISOTOPE of Carbon. Isotopes can have greater or fewer numbers of neutrons. 6 6 NOTE: some texts and charts have the Atomic Number at the top of the symbol; others have the Atomic Mass there! Do not rely solely on where the number is! 14-6 = 8 12-6 = 6 Understand what it is telling you- the Atomic Number is smaller than the Atomic Mass, except for Hydrogen, which is the same. Hydrogen only has a proton and an electron. Periodic Table and its Arrangement Periods are rows across; each element in the period gets more complex as you go right. Groups/Families are in vertical columns. They are chemically similar. Metals make up ¾ of the Periodic Table and are on the left t side of the chart Non-metals are on the right. Metalloids are in between the metals and non-metals. The numbers on the tops of the Families can help determine how many Valence Electrons in the atom