Cell Analogies Worksheet
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
Study Guide
... Study Guide Chapter 2, Section 1 – Cell Structure & Function Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organiza ...
... Study Guide Chapter 2, Section 1 – Cell Structure & Function Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organiza ...
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... study the parts. You must be able to identify the following organelles by shape so you can label each part. You must also know the function of each cell part. Cell wall Mitochondria Chloroplast Nucleus ...
... study the parts. You must be able to identify the following organelles by shape so you can label each part. You must also know the function of each cell part. Cell wall Mitochondria Chloroplast Nucleus ...
Product Information
... The required dose of G 418-BC for the selection of resistant cells varies in dependence of the cell type and the current phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active ce ...
... The required dose of G 418-BC for the selection of resistant cells varies in dependence of the cell type and the current phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active ce ...
Learning Checkpoint ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS p. 16
... 3. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) carries materials throughout the cell. The rough ER is associated with making proteins. The Golgi apparatus receives proteins from the ER and modifies, sorts, and packages these proteins for delivery throughout the cell or out of the cell. 4. The thylakoids act as s ...
... 3. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) carries materials throughout the cell. The rough ER is associated with making proteins. The Golgi apparatus receives proteins from the ER and modifies, sorts, and packages these proteins for delivery throughout the cell or out of the cell. 4. The thylakoids act as s ...
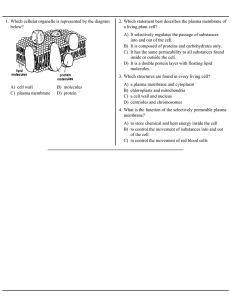
A) cell wall B) molecules C) plasma membrane D) protein 1. Which
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
Cell Transport PP
... 1. How do transport proteins that are pumps differ from those that are channels? ...
... 1. How do transport proteins that are pumps differ from those that are channels? ...
Question Before the video After the video How many cells are there
... stuff to pass in and out? How does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do genes have to do with cells? How many chromosomes do you have and how do you get them? How many cells are there in an egg? Why do they call red blood cells “red”. Explain What do white blood cells do? Wha ...
... stuff to pass in and out? How does it work? What is your fastest growing organ and why? What do genes have to do with cells? How many chromosomes do you have and how do you get them? How many cells are there in an egg? Why do they call red blood cells “red”. Explain What do white blood cells do? Wha ...
Pedigree Analysis of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
... hand. Although various tracking algorithms exist, none of them can adequately track human stem cells and demarcate the time at which cell division events occur. To solve this problem, our approach will be to identify image objects in the full 3-dimensional image data (2D Space x Time), rather than i ...
... hand. Although various tracking algorithms exist, none of them can adequately track human stem cells and demarcate the time at which cell division events occur. To solve this problem, our approach will be to identify image objects in the full 3-dimensional image data (2D Space x Time), rather than i ...
Eukaryotic cells Section review model answers Ribosomes are
... 4. Plant cells have cell walls, but animal cells do not. Plant cells have chloroplasts, which animal cells do not have. Plant cells do not seem to have small lysosomes (they have large vacuoles instead), which animal cells do have. 5. Ribosomes are the organelles where proteins are made. All cells n ...
... 4. Plant cells have cell walls, but animal cells do not. Plant cells have chloroplasts, which animal cells do not have. Plant cells do not seem to have small lysosomes (they have large vacuoles instead), which animal cells do have. 5. Ribosomes are the organelles where proteins are made. All cells n ...
8 CELL THEORY Handouts - Hewlett
... Exceptions to Cell Theory • _________________. They cannot reproduce without a host cell. • Two organelles, ____________and _______________have their own DNA and can ________themselves. • The first cell did not arise from a ________________________. ...
... Exceptions to Cell Theory • _________________. They cannot reproduce without a host cell. • Two organelles, ____________and _______________have their own DNA and can ________themselves. • The first cell did not arise from a ________________________. ...
Studying the Structure of Cells
... • Most of today’s advances in the treatment of diseases would not be possible without an understanding of what happens inside cells • Robert Hooke: 1655 – first person to study cells (piece of cork) ...
... • Most of today’s advances in the treatment of diseases would not be possible without an understanding of what happens inside cells • Robert Hooke: 1655 – first person to study cells (piece of cork) ...
STAAR Review, Friday, Jan 20
... c. New cells are produced only from existing cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells A. Both have a. Cell membranes b. Cytoplasm c. Contain ribosomes d. DNA B. Major differences a. Eukaryotes are more complex and larger in size b. Eukaryotes have organelles, specifically the nucleus c. Prokaryotes d ...
... c. New cells are produced only from existing cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells A. Both have a. Cell membranes b. Cytoplasm c. Contain ribosomes d. DNA B. Major differences a. Eukaryotes are more complex and larger in size b. Eukaryotes have organelles, specifically the nucleus c. Prokaryotes d ...
vocab flip chart - Effingham County Schools
... found in all the cells of all living things, the blueprint for life, is the instructions for proteins ...
... found in all the cells of all living things, the blueprint for life, is the instructions for proteins ...
Matthew Keirle Office: 25-115 Phone: 752
... Cell Function Limits Cell Size • most cells are small, ranging from 1 to 100 micrometers in diameter ...
... Cell Function Limits Cell Size • most cells are small, ranging from 1 to 100 micrometers in diameter ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... These break down large food particles into small ones (scissors of the cell) ...
... These break down large food particles into small ones (scissors of the cell) ...
Biology Study guide
... Stem Cells ( 3 types and examples) Labs: Animal vs. Plant cells Microscope lab – introduction Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
... Stem Cells ( 3 types and examples) Labs: Animal vs. Plant cells Microscope lab – introduction Microscope use and calculations Diagram with parts and function Total magnification Field of view ...
cell specialization
... Name: _____________ Period: ___ Date:________ The human body is made up of billions of cells. The structure of every cell in the body is adapted to the cell’s function. ...
... Name: _____________ Period: ___ Date:________ The human body is made up of billions of cells. The structure of every cell in the body is adapted to the cell’s function. ...
Cell Growth and Division
... keep growing? • Large cells do not have enough DNA to function. • Large cells could not diffuse oxygen and nutrients efficiently. *Agar block lab* ...
... keep growing? • Large cells do not have enough DNA to function. • Large cells could not diffuse oxygen and nutrients efficiently. *Agar block lab* ...
Cell Theory- The basics of Animal and Plant Cells Name: 1. Cell
... 2. Cell Theory Part A: Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. a. Cells are made up of smaller parts called _________________________. b. Organelles act the like the ______________________ of large organisms. c. Organelles common to all cells: i. Cell Membrane: _____ ...
... 2. Cell Theory Part A: Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. a. Cells are made up of smaller parts called _________________________. b. Organelles act the like the ______________________ of large organisms. c. Organelles common to all cells: i. Cell Membrane: _____ ...
CELL CYCLE TEST REVIEW PAP Biology 1. List the three parts of a
... What are the base pairing rules for the nitrogen bases? What type of bond holds the N-bases together? What is helicase? What is DNA polymerase? When and why does DNA replication occur in the cell cycle? Which two scientists are credited with the discovery of the structure of DNA? List the phases in ...
... What are the base pairing rules for the nitrogen bases? What type of bond holds the N-bases together? What is helicase? What is DNA polymerase? When and why does DNA replication occur in the cell cycle? Which two scientists are credited with the discovery of the structure of DNA? List the phases in ...